Java Numbers Programming: Exercises, Practice, Solution
This resource offers a total of 145 Java Number problems for practice. It includes 29 main exercises, each accompanied by solutions, detailed explanations, and four related problems.
[An Editor is available at the bottom of the page to write and execute the scripts.]
1. Check Ugly Number
Write a Java program to check whether a given number is ugly.
In number system, ugly numbers are positive numbers whose only prime factors are 2, 3 or 5. First 10 ugly numbers are 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12. By convention, 1 is included.
Test Date:Input an integer number: 235
Expected Output :
It is not an ugly number.
2. Categorize Numbers: Abundant, Deficient, Perfect
Write a Java program that categorizes integers between 1 and 10,000 as Abundant, Deficient, and Perfect.
In number theory, an abundant number is a number for which the sum of its proper divisors is greater than the number itself.
Example :
The first few abundant numbers are:
12, 18, 20, 24, 30, 36, 40, 42, 48, 54, 56, 60, 66, 70, 72, 78, 80, 84, 88, 90, 96, 100, 102,…
The integer 12 is the first abundant number. Its proper divisors are 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6 for a total of 16.
Deficient number: In number theory, a deficient number is a number n for which the sum of divisors σ(n)<2n, or, equivalently, the sum of proper divisors (or aliquot sum) s(n)<n. The value 2n − σ(n) (or n − s(n)) is called the number's deficiency.
As an example, divisors of 21 are 1, 3 and 7, and their sum is 11. Because 11 is less than 21, the number 21 is deficient. Its deficiency is 2 × 21 − 32 = 10.
The first few deficient numbers are:
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17, 19, 21, 22, 23, 25, 26, 27, 29, 31, 32, 33, …….
Perfect number: In number system, a perfect number is a positive integer that is equal to the sum of its proper positive divisors, that is, the sum of its positive divisors excluding the number itself.
Equivalently, a perfect number is a number that is half the sum of all of its positive divisors (including itself) i.e. σ1(n) = 2n.
The first perfect number is 6. Its proper divisors are 1, 2, and 3, and 1 + 2 + 3 = 6. Equivalently, the number 6 is equal to half the sum of all its positive divisors: ( 1 + 2 + 3 + 6 ) / 2 = 6. The next perfect number is 28 = 1 + 2 + 4 + 7 + 14. This is followed by the perfect numbers 496 and 8128.
Expected Output :
Number Counting [(integers) between 1 to 10,000]:
Deficient number: 7508
Perfect number: 4
Abundant number: 2488
3. Generate Random Integers in Range
Write a Java program to generate random integers in a specific range.
Click me to see the solution
4. Kaprekar Numbers < 1000
Write a Java program to generate and show all Kaprekar numbers less than 1000.
Expected Output :
1 1 0 + 1 9 81 8 + 1 45 2025 20 + 25 55 3025 30 + 25 99 9801 98 + 01 297 88209 88 + 209 703 494209 494 + 209 999 998001 998 + 001 8 Kaprekar numbers.
5. Seed Lychrel Numbers
Write a Java program to find the number of seed Lychrel number candidates and related numbers for n in the range 1..10000 inclusive. (With a 500-iteration limit).
A Lychrel number is a natural number that cannot form a palindrome through the iterative process of repeatedly reversing its digits and adding the resulting numbers. This process is sometimes called the 196-algorithm, after the most famous number associated with the process.
The first few Lychrel numbers are 196, 295, 394, 493, 592, 689, 691, 788, 790, 879, 887, ... .
Expected Output :
5 Lychrel seeds: [196, 879, 1997, 7059, 9999]
244 Lychrel related
5 Lychrel palindromes: [196, 879, 1997, 7059, 9999]
6. First 15 Narcissistic Numbers
Write a Java program to generate and show the first 15 narcissistic decimal numbers.
Expected Output :
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 153 370 371 407 1634
7. First 10 Lucas Numbers
Write a Java program to display the first 10 lucus numbers.
The Lucas numbers or series are an integer sequence named after the mathematician François Édouard Anatole Lucas, who studied both that sequence and the closely related Fibonacci numbers. Lucas numbers and Fibonacci numbers form complementary instances of Lucas sequences.
The sequence of Lucas numbers is: 2, 1, 3, 4, 7, 11, 18, 29, ….
Expected Output :
First ten Lucas a numbers: 2 1 3 4 7 11 18 29 47 76
8. First 10 Catalan Numbers
Write a Java program to print out the first 10 Catalan numbers by extracting them from Pascal's triangle.
In combinatorial mathematics, the Catalan numbers form a sequence of natural numbers that occur in various counting problems, often involving recursively-defined objects. They are named after the Belgian mathematician Eugène Charles Catalan.
The first Catalan numbers for n = 0, 1, 2, 3, … are 1, 1, 2, 5, 14, 42, 132, 429, 1430, 4862, 16796, 58786, 208012, 742900, 2674440, 9694845, 35357670, 129644790, 477638700, 1767263190, 6564120420, 24466267020, 91482563640, 343059613650, 1289904147324, 4861946401452,
List 10 Catalan numbers:-
1
2
5
14
42
132
429
1430
4862
16796
9. First 10 Happy Numbers
Write a Java program to find and print the first 10 happy numbers.
Happy number: Starting with any positive integer, replace the number by the sum of the squares of its digits, and repeat the process until the number equals 1, or it loops endlessly in a cycle which does not include 1.
Example: 19 is a happy number
12 + 92=82
82 + 22=68
62 + 82=100
12 + 02 + 02=1
Expected Output
First 10 Happy numbers: 1 7 10 13 19 23 28 31
10. Check Happy or Unhappy Number
Write a Java program to check whether a given number is a happy number or unhappy number.
Happy number: Starting with any positive integer, replace the number by the sum of the squares of its digits, and repeat the process until the number equals 1, or it loops endlessly in a cycle which does not include 1.
An unhappy number is a number that is not happy.
The first few unhappy numbers are 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 11, 12, 14, 15, 16, 17, 18, 20.
Expected Output
Input a number: 5 Unhappy Number
11. Check Disarium or Unhappy Number
Write a Java program to check whether a given number is a Disarium number or an unhappy number.
A Disarium number is a number defined by the following process :
Sum of its digits powered with their respective position is equal to the original number.
For example 175 is a Disarium number :
As 11+32+53 = 135
Some other DISARIUM are 89, 175, 518 etc.
A number will be called Disarium if the sum of its digits powered with their respective position is equal with the number itself. Sample Input: 135.
Expected Output
Input a number : 25 Not a Disarium Number.
12. Check Harshad Number
Write a Java program to check whether a number is a Harshad Number or not.
In recreational mathematics, a harshad number in a given number base, is an integer that is divisible by the sum of its digits when written in that base.
Example: Number 200 is a Harshad Number because the sum of digits 2 and 0 and 0 is 2(2+0+0) and 200 is divisible by 2. Number 171 is a Harshad Number because the sum of digits 1 and 7 and 1 is 9(1+7+1) and 171 is divisible by 9.
Expected Output
Input a number : 353
353 is not a Harshad Number.
13. Check Pronic Number
Write a Java program to check whether a number is a Pronic or Heteromecic Number or not.
A pronic number is a number which is the product of two consecutive integers, that is, a number of the form n(n + 1).
The first few pronic numbers are:
0, 2, 6, 12, 20, 30, 42, 56, 72, 90, 110, 132, 156, 182, 210, 240, 272, 306, 342, 380, 420, 462 … etc.
Expected Output
Input a number : 110
Pronic Number.
14. Check Automorphic Number
Write a Java program to check whether a number is an automorphic number or not.
In mathematics, an automorphic number is a number whose square "ends" in the same digits as the number itself. For example, 52 = 25, 62 = 36, 762 = 5776, and 8906252 = 793212890625, so 5, 6, 76 and 890625 are all automorphic numbers.
Expected Output
Input a number : 76 Automorphic Number.
15. Check Duck Number
Write a Java program to check whether a number is a Duck Number or not.
Note: A Duck number is a number which has zeroes present in it, but there should be no zero present in the beginning of the number. For example 3210, 7056, 8430709 are all duck numbers whereas 08237, 04309 are not.
Expected Output
Input a number : 3210 Duck number
16. Check Amicable Numbers
Write a Java program to check two numbers are Amicable numbers or not.
Amicable numbers are two different numbers so related that the sum of the proper divisors of each is equal to the other number.
The first ten amicable pairs are: (220, 284), (1184, 1210), (2620, 2924), (5020, 5564), (6232, 6368), (10744, 10856), (12285, 14595), (17296, 18416), (63020, 76084), and (66928, 66992).
Expected Output
Input the first number: 220 Input the second number: 284 These numbers are amicable.
17. Check Circular Prime Number
Write a Java program to check if a given number is a circular prime or not.
Circular Prime : A circular prime is a prime number with the property that the number generated at each intermediate step when cyclically permuting its (base 10) digits will be prime.
For example, 1193 is a circular prime, since 1931, 9311 and 3119 all are also prime. A circular prime with at least two digits can only consist of combinations of the digits 1, 3, 7 or 9, because having 0, 2, 4, 6 or 8 as the last digit makes the number divisible by 2, and having 0 or 5 as the last digit makes it divisible by 5.
Input Data:
Input a number: 35
Expected Output
It is not a Circular Prime number.
18. Check Cube Number
Write a Java program to check if a number is a cube or not.
In arithmetic and algebra, the cube of a number n is its third power: the result of the number multiplied by itself twice:
n3 = n × n × n.
Input Data:
Input a number: 8
Expected Output
Number is a cube.
19. Check Cyclic Number
Write a Java program to check if a number is cyclic or not.
A cyclic number is an integer in which cyclic permutations of the digits are successive multiples of the number. The most widely known are 142857:
142857 × 1 = 142857
142857 × 2 = 285714
142857 × 3 = 428571
142857 × 4 = 571428
142857 × 5 = 714285
142857 × 6 = 857142
Input Data:
Input a number: 142857
Expected Output
It is a cyclic number.
20. First 10 Fermat Numbers
Write a Java program to display the first 10 Fermat numbers.
In mathematics, a Fermat number is a positive integer of the form
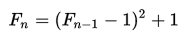
where n is a nonnegative integer.
The first few Fermat numbers are:
3, 5, 17, 257, 65537, 4294967297, 18446744073709551617, …
Expected Output
3.0 5.0 17.0 257.0 65537.0 4.294967297E9 1.8446744073709552E19 3.4028236692093846E38 1.157920892373162E77 1.3407807929942597E154 Infinity
21. Ramanujan Numbers
Write a Java program to find any number between 1 and n that can be expressed as the sum of two cubes in two (or more) different ways.
//http://introcs.cs.princeton.edu/java/13flow/Ramanujan.java.html
Here are some examples of Ramanujan numbers :
1729 = 1^3 + 12^3 = 9^3 + 10^3
* 10000
1729 = 1^3 + 12^3 = 9^3 + 10^3
4104 = 2^3 + 16^3 = 9^3 + 15^3
* 100000
1729 = 1^3 + 12^3 = 9^3 + 10^3
4104 = 2^3 + 16^3 = 9^3 + 15^3
13832 = 2^3 + 24^3 = 18^3 + 20^3
39312 = 2^3 + 34^3 = 15^3 + 33^3
46683 = 3^3 + 36^3 = 27^3 + 30^3
32832 = 4^3 + 32^3 = 18^3 + 30^3
40033 = 9^3 + 34^3 = 16^3 + 33^3
20683 = 10^3 + 27^3 = 19^3 + 24^3
65728 = 12^3 + 40^3 = 31^3 + 33^3
64232 = 17^3 + 39^3 = 26^3 + 36^3
1729 = 1^3 + 12^3 = 9^3 + 10^3 4104 = 2^3 + 16^3 = 9^3 + 15^3 13832 = 2^3 + 24^3 = 18^3 + 20^3 39312 = 2^3 + 34^3 = 15^3 + 33^3 46683 = 3^3 + 36^3 = 27^3 + 30^3 32832 = 4^3 + 32^3 = 18^3 + 30^3 40033 = 9^3 + 34^3 = 16^3 + 33^3 20683 = 10^3 + 27^3 = 19^3 + 24^3 65728 = 12^3 + 40^3 = 31^3 + 33^3 64232 = 17^3 + 39^3 = 26^3 + 36^3
22. Check Mersenne Number
Write a program to check if a number is a Mersenne number or not.
In mathematics, a Mersenne number is a number that can be written in the form M(n) = 2n − 1 for some integer n.
The first four Mersenne primes are 3, 7, 31, and 127
Expected Output
Input a number: 127 127 is a Mersenne number.
23. Narcissistic Numbers Between 1 and 1000
Write a Java program to find all narcissistic numbers between 1 and 1000.
In number theory, a narcissistic number is a number that is the sum of its own digits each raised to the power of the number of digits.
For example:
153 = 13 + 53 + 33
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 153 370 371 407
24. Check Palindrome Number
Write a Java program to check if a number is a palindrome or not.
In number system a palindromic number is a number that is the same when written forwards or backwards, i.e., of the form .
The first few palindromic numbers are therefore are 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 101, 111, …
Input a number: 5 It is a Palindrome number.
25. First 15 Pell Numbers
Write a Java program to print the first 15 numbers of the Pell series.
In mathematics, the Pell numbers are an infinite sequence of integers. The sequence of Pell numbers starts with 0 and 1, and then each Pell number is the sum of twice the previous Pell number and the Pell number before that.:
thus, 70 is the companion to 29, and 70 = 2 × 29 + 12 = 58 + 12.
The first few terms of the sequence are :
0, 1, 2, 5, 12, 29, 70, 169, 408, 985, 2378, 5741, 13860,…
First 20 Pell numbers: 1 2 5 12 29 70 169 408 985 2378 5741 13860 33461 80782 195025 470832 113 6689 2744210 6625109 15994428
26. Check Keith Number
Write a Java program to check whether a number is a Keith Number or not.
In recreational mathematics, a Keith number or repfigit number (short for repetitive Fibonacci-like digit) is a number in the following integer sequence:
14, 19, 28, 47, 61, 75, 197, 742, 1104, 1537, 2208, 2580, 3684, 4788, 7385, 7647, 7909, 31331, 34285, 34348, 55604, 62662, 86935, 93993, 120284, 129106, 147640, 156146, 174680, 183186, 298320, 355419, 694280, 925993,
Input a number: 75 Keith Number
27. First 20 Hamming Numbers
Write a Java program to create the first twenty Hamming numbers.
In computer science, regular numbers are often called Hamming numbers, Hamming Numbers are numbers whose only prime factors are 2, 3 and 5.
The first few hamming numbers are :
1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 8, 9, 10, 12, 15, 16, 18, 20, 24, 25, 27, 30, 32
First Twenty Hamming numbers: 1 2 3 4 5 6 8 9 10 12 15 16 18 20 24 25 27 30 32 36
28. Check Armstrong Number
Write a Java program to check whether a number is an Armstrong Number or not.
Armstrong (Michael F. Armstrong) number is a number that is equal to the sum of cubes of its digits. For example 0, 1, 153, 370, 371 and 407 are the Armstrong numbers
Expected Output
Input an integer: 153 Is Armstrong number? true
29. Check Lucky Number
Write a Java program to check whether a number is a Luck number or not.
Expected Output
Input an integer: 25 Is Lucky number? true
Java Code Editor
More to Come !
Do not submit any solution of the above exercises at here, if you want to contribute go to the appropriate exercise page.
