MySQL TIME() function
TIME() function
MySQL TIME() extracts the time part of a time or datetime expression as string format. It allows to work specifically with the time component of a datetime, which can be very useful in various scenarios.
This function is useful in -
- TIME() can be used to format and present the time component of a datetime value in a custom way.
- TIME() is valuable for filtering records or data based on time criteria, such as selecting records within a specific time range.
- It's useful for displaying only the time part of a datetime value when presenting data to users or in reports.
- It allows you to perform time-based operations, such as comparing times, calculating durations, or performing time-based arithmetic.
- TIME() is used in time series analysis to work specifically with the time component of datetime values.
- It can be used to extract and display the time when certain events or records were created or updated.
- The function supports various time-related calculations, such as finding the time difference between two events.
Syntax:
TIME(expr);
Where expr is a datetime.
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
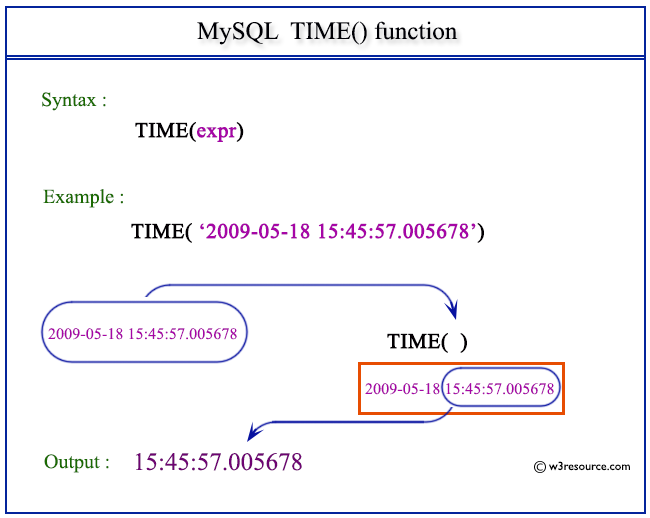
Pictorial Presentation:
Example:
The following statement will return the time portion from the given date-time value 2009-05-18 15:45:57.005678.
Code:
SELECT TIME('2009-05-18 15:45:57.005678');
Output:
mysql> SELECT TIME('2009-05-18 15:45:57.005678');
+------------------------------------+
| TIME('2009-05-18 15:45:57.005678') |
+------------------------------------+
| 15:45:57.005678 |
+------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.01 sec)
Video Presentation:
All Date and Time Functions:
Click here to see the MySQL Date and time functions.
PREV : TIME_TO_SEC()
NEXT : TIMEDIFF()