MySQL NOW() function
NOW() function
MySQL NOW() returns the value of current date and time in ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS’ format or YYYYMMDDHHMMSS.uuuuuu format depending on the context (numeric or string) of the function.
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(), LOCALTIME, LOCALTIME(), LOCALTIMESTAMP, LOCALTIMESTAMP() are synonyms of NOW(). The NOW() returns the constant time when the statement began to work.
Note: If an example code uses NOW(), your output may vary from the output shown.
This function is useful in -
- NOW() is valuable for capturing and logging real-time timestamps when recording events, transactions, or activities.
- In applications, NOW() is used to provide users with real-time information, such as when an action was performed.
- NOW() can be used to generate formatted date and time strings for various display purposes.
- The function supports scheduling tasks or events based on the current date and time.
- The function is used in date and time calculations, such as finding time intervals or determining relative time differences.
- When working with batch data processing, NOW() helps capture the time when batches are executed.
- NOW() is used to create timestamps in logs to track the timing of system events or errors.
Syntax:
NOW();
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
Pictorial Presentation:
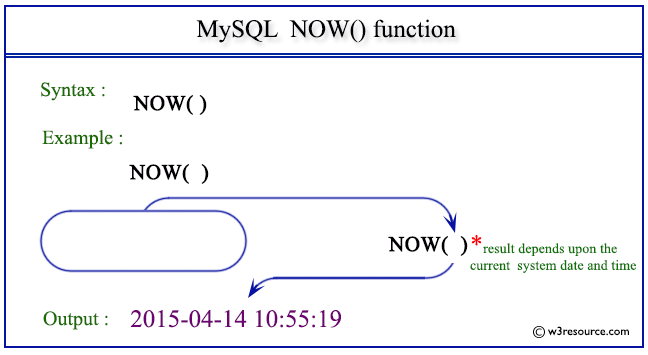
Example : MySQL NOW() function
The following statement will return the current date and time in ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:SS:MM’ format.
Code:
SELECT NOW();
Output:
mysql> SELECT NOW(); +---------------------+ | NOW() | +---------------------+ | 2015-04-14 10:55:19 | +---------------------+ 1 row in set (0.02 sec)
Example: NOW() function in numeric format
The following statement will return the current date and time in YYYYMMDDHHSSMM.uuuuuu format.
Code:
SELECT NOW(),NOW()+1;
Output:
mysql> SELECT NOW(),NOW()+1; +---------------------+-----------------------+ | NOW() | NOW()+1 | +---------------------+-----------------------+ | 2015-04-14 11:15:32 | 20150414111533.000000 | +---------------------+-----------------------+ 1 row in set (0.03 sec)
Example: NOW() function using INTERVAL
The following statement will return the date and current time in ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:SS:MM’ format for the previous day. The keyword ‘INTERVAL’ have been introduced to get the result.
Code:
SELECT NOW(),NOW()-INTERVAL 1 DAY;
Output:
mysql> SELECT NOW(),NOW()-INTERVAL 1 DAY; +---------------------+----------------------+ | NOW() | NOW()-INTERVAL 1 DAY | +---------------------+----------------------+ | 2015-04-14 11:17:25 | 2015-04-13 11:17:25 | +---------------------+----------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: NOW() function using negative INTERVAL
The following statement will return the date and time in ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:SS:MM’ format before 1 hour of current datetime. The keyword ‘INTERVAL’ have been introduced to get the result.
Code:
SELECT NOW(),NOW()-INTERVAL 1 HOUR;
Output:
mysql> SELECT NOW(),NOW()-INTERVAL 1 HOUR; +---------------------+-----------------------+ | NOW() | NOW()-INTERVAL 1 HOUR | +---------------------+-----------------------+ | 2015-04-14 11:19:01 | 2015-04-14 10:19:01 | +---------------------+-----------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: NOW() function using INTERVAL for a day
The following statement will return the date and time in ‘YYYY-MM-DD HH:SS:MM’ format after 1 day of the current datetime . The keyword ‘INTERVAL’ have been introduced to get the result.
Code:
SELECT NOW(),NOW()+INTERVAL 1 DAY;
Output:
mysql> SELECT NOW(),NOW()+INTERVAL 1 DAY; +---------------------+----------------------+ | NOW() | NOW()+INTERVAL 1 DAY | +---------------------+----------------------+ | 2015-04-14 11:20:42 | 2015-04-15 11:20:42 | +---------------------+----------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Video Presentation:
All Date and Time Functions :
Click here to see the MySQL Date and time functions.
Previous: MONTHNAME()
Next: PERIOD_ADD()
