MySQL SYSDATE() function
SYSDATE() function
MySQL SYSDATE() returns the current date and time in YYYY-MM-DD HH:MM:SS or YYYYMMDDHHMMSS.uuuuuu format depending on the context of the function.
Note:For example codes using SYSDATE(), your output may vary from the output shown.
This function is useful in -
- It ensures accuracy by retrieving the current date and time directly from the system clock, making it suitable for real-time applications.
- SYSDATE() is commonly used as a default value for timestamp columns when inserting new records, ensuring that they contain the current date and time.
- SYSDATE() is valuable for scheduling tasks or events that need to occur at specific times based on the current system time.
- The function is used to calculate the age of data by comparing it with the current timestamp.
- SYSDATE() enables real-time reporting and analysis by providing the current timestamp for immediate use.
- SYSDATE() can be used to generate time series data for analysis and reporting.
- It's used for time-stamping records when they are created or updated, helping to track when specific actions occurred.
Syntax:
SYSDATE()
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
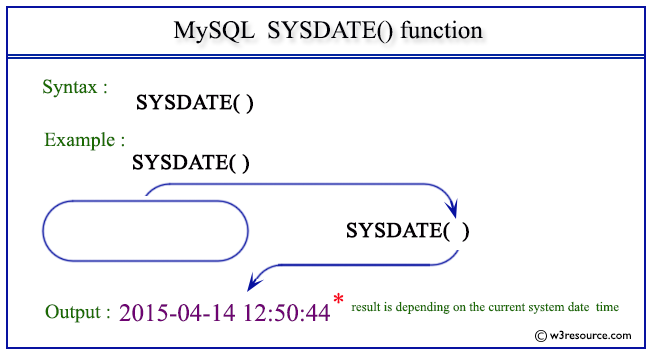
Pictorial Presentation:
Example:
The following statement will return current date and time.
Code:
SELECT SYSDATE();
Output:
mysql> SELECT SYSDATE(); +---------------------+ | SYSDATE() | +---------------------+ | 2015-04-14 12:50:44 | +---------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: SYSDATE() function in numeric format
The following statement will return current date and time in numeric format.
Code:
SELECT SYSDATE()+0;
Output:
mysql> SELECT SYSDATE()+0; +----------------+ | SYSDATE()+0 | +----------------+ | 20150414125237 | +----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Video Presentation:
All Date and Time Functions:
Click here to see the MySQL Date and time functions.
PREV : SUBTIME()
NEXT : TIME_FORMAT()