MySQL MICROSECOND() function
MICROSECOND() function
MySQL MICROSECOND() returns MICROSECONDs from the time or datetime expression. The return value is within the range of 0 to 999999. It provides a way to isolate the microsecond part of a time for precise time-based calculations and analysis.
This function is useful in -
- The function is used to capture and analyze extremely fine-grained timing information, useful in scenarios requiring high accuracy.
- The function is used in benchmarking scenarios where the goal is to measure the performance of operations with microsecond-level accuracy.
- MICROSECOND() can be used to calculate time intervals or durations with microsecond-level accuracy.
- MICROSECOND() aids in handling high-frequency data streams that require time-based analysis at the microsecond level.
- MICROSECOND() aids in performance analysis of code or processes that require microsecond-level timing measurements.
- The function is valuable for monitoring network latencies and response times at a very granular level.
- MICROSECOND() is valuable when working with high-precision time calculations, as it allows you to access the microsecond-level details.
Syntax:
MICROSECOND(expr)
Where expr is a time or datetime.
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
Pictorial Presentation:
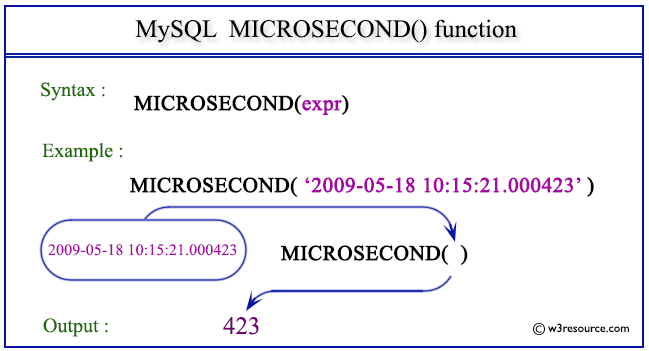
Example: MySQL MICROSECOND() function
The following statement will return MICROSECONDs from the datetime 2009-05-18 10:15:21.000423.
Code:
SELECT MICROSECOND('2009-05-18 10:15:21.000423');
Output:
mysql> SELECT MICROSECOND('2009-05-18 10:15:21.000423');
+-------------------------------------------+
| MICROSECOND('2009-05-18 10:15:21.000423') |
+-------------------------------------------+
| 423 |
+-------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: MICROSECOND() function with DATE_FORMAT()
The following statement will return MICROSECONDs from a datetime which will come from the CURRENT_TIMESTAMP() and will format it as a datetime expression by DATE_FORMAT() as given in the argument (%Y-%c-%d %H:%i:%s %f) .
Code:
SELECT MICROSECOND(DATE_FORMAT( CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(),'%Y-%c-%d %H:%i:%s %f'));
Output:
mysql> SELECT MICROSECOND(DATE_FORMAT( CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(),'%Y-%c-%d %H:%i:%s %f')); +-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ | MICROSECOND(DATE_FORMAT( CURRENT_TIMESTAMP(),'%Y-%c-%d %H:%i:%s %f')) | +-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ | 0 | +-----------------------------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set, 1 warning (0.01 sec)
Video Presentation:
All Date and Time Functions :
Click here to see the MySQL Date and time functions.
Previous: MAKETIME()
Next: MINUTE()
