MySQL GET_FORMAT() function
GET_FORMAT() function
MySQL GET_FORMAT() converts a date or time or datetime in a formatted manner as specified in the argument. This function is useful in combination with DATE_FORMAT(). The various formats have been described bellow. It helps determine the appropriate format for date and time representations based on different locale settings.
This function is useful in -
- The function helps ensure that date and time values are presented to users in a format they are familiar with and can easily understand.
- The function is valuable for international applications that need to display date and time values in various formats based on regional conventions.
- In systems where users can set their preferred date and time formats, GET_FORMAT() helps retrieve and apply those preferences.
- GET_FORMAT() ensures consistent formatting of date and time values throughout an application, regardless of the user's locale.
- GET_FORMAT() enables customization of date and time formatting based on different locales, allowing for consistent user experiences.
- GET_FORMAT() allows dynamic adjustment of date and time formatting without hardcoding specific formats.
- When generating reports or outputs that involve date and time values, GET_FORMAT() ensures that the format aligns with the user's locale.
Syntax:
GET_ FORMAT([date | time | datetime ],[‘EUR’ |‘USA’ |’JIS’|’ISO’|‘INTERNAL’])
Arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| date | time | datetime | A date or time or datetime. |
| EUR’ | ‘USA’ | ’JIS’ |’ISO’ | ‘INTERNAL | Different formats. |
Pictorial Presentation:
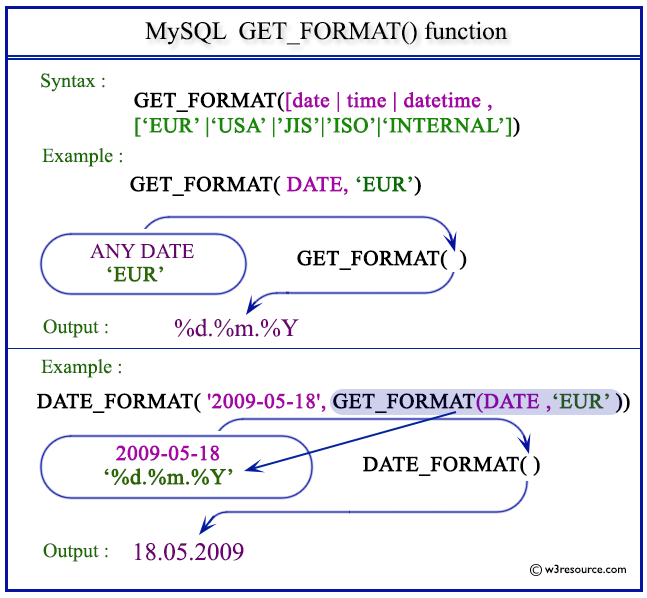
Different function calls
| Function Call | Result |
|---|---|
| GET_FORMAT(DATE,'USA') | '%m.%d.%Y' |
| GET_FORMAT(DATE,'JIS') | '%Y-%m-%d' |
| GET_FORMAT(DATE,'ISO') | '%Y-%m-%d' |
| GET_FORMAT(DATE,'EUR') | '%d.%m.%Y' |
| GET_FORMAT(DATE,'INTERNAL') | '%Y%m%d' |
| GET_FORMAT(DATETIME,'USA') | '%Y-%m-%d %H.%i.%s' |
| GET_FORMAT(DATETIME,'JIS') | '%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s' |
| GET_FORMAT(DATETIME,'ISO') | '%Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s' |
| GET_FORMAT(DATETIME,'EUR') | '%Y-%m-%d %H.%i.%s' |
| GET_FORMAT(DATETIME,'INTERNAL') | '%Y%m%d%H%i%s' |
| GET_FORMAT(TIME,'USA') | '%h:%i:%s %p' |
| GET_FORMAT(TIME,'JIS') | '%H:%i:%s' |
| GET_FORMAT(TIME,'ISO') | '%H:%i:%s' |
| GET_FORMAT(TIME,'EUR') | '%H.%i.%s' |
| HOUR_MINUTE | 'HOURS:MINUTES' |
| DAY_MICROSECOND | 'DAYS HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS.MICROSECONDS' |
| DAY_SECOND | 'DAYS HOURS:MINUTES:SECONDS' |
| DAY_MINUTE | 'DAYS HOURS:MINUTES' |
| DAY_HOUR | 'DAYS HOURS' |
| YEAR_MONTH | 'YEARS-MONTHS' |
MySQL Version: 8.0
Example: MySQL GET_FORMAT() function
The following statement will arrange the date format in EUR.
Code:
SELECT GET_FORMAT(DATE,'EUR');
Output:
mysql> SELECT GET_FORMAT(DATE,'EUR'); +------------------------+ | GET_FORMAT(DATE,'EUR') | +------------------------+ | %d.%m.%Y | +------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.02 sec)
Example: GET_FORMAT() function with DATE_FORMAT()
The following statement will format and return the specified date 2009-05-18 in the format obtained from GET_FORMAT(DATE,'EUR').
Code:
SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2009-05-18',GET_FORMAT(DATE,'EUR'));
Output:
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2009-05-18',GET_FORMAT(DATE,'EUR'));
+--------------------------------------------------+
| DATE_FORMAT('2009-05-18',GET_FORMAT(DATE,'EUR')) |
+--------------------------------------------------+
| 18.05.2009 |
+--------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: GET_FORMAT() function using 'USA' format
The following statement will arrange the time format in USA format.
Code:
SELECT GET_FORMAT(TIME,'USA');
Output:
mysql> SELECT GET_FORMAT(TIME,'USA'); +------------------------+ | GET_FORMAT(TIME,'USA') | +------------------------+ | %h:%i:%s %p | +------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: GET_FORMAT() function with STR_TO_DATE()
The following statement will format and return the specified time 11:15:46 PM in a specific format as obtained from STR_TO_DATE(TIME,'USA').
Code:
SELECT STR_TO_DATE('11:15:46 PM',GET_FORMAT(TIME,'USA'));
Output:
mysql> SELECT STR_TO_DATE('11:15:46 PM',GET_FORMAT(TIME,'USA'));
+---------------------------------------------------+
| STR_TO_DATE('11:15:46 PM',GET_FORMAT(TIME,'USA')) |
+---------------------------------------------------+
| 23:15:46 |
+---------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example : GET_FORMAT() function in 'JIS' format
The following statement will arrange the datetime format in JIS format.
Code:
SELECT GET_FORMAT(DATETIME,'JIS');
Output:
mysql> SELECT GET_FORMAT(DATETIME,'JIS'); +----------------------------+ | GET_FORMAT(DATETIME,'JIS') | +----------------------------+ | %Y-%m-%d %H:%i:%s | +----------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example : GET_FORMAT() function with DATE_FORMAT() and 'JIS' format
The following statement will arrange the datetime 2009-05-18 11:15:46 in a format obtained from GET_FORMAT(DATETIME,'JIS').
Code:
SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2009-05-18 11:15:46',GET_FORMAT(DATETIME,'JIS'));
Output:
mysql> SELECT DATE_FORMAT('2009-05-18 11:15:46',GET_FORMAT(DATETIME,'JIS'));
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| DATE_FORMAT('2009-05-18 11:15:46',GET_FORMAT(DATETIME,'JIS')) |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
| 2009-05-18 11:15:46 |
+---------------------------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Video Presentation:
All Date and Time Functions:
Click here to see the MySQL Date and time functions.
Previous: FROM_UNIXTIME()
Next: HOUR()
