Java ArrayList.subList() Method
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
The subList() method is used to get a portion of this list between the specified fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex, exclusive. If fromIndex and toIndex are equal, the returned list is empty.
The returned list is backed by this list, so non-structural changes in the returned list are reflected in this list, and vice-versa. The returned list supports all of the optional list operations.
This method eliminates the need for explicit range operations (of the sort that commonly exist for arrays). Any operation that expects a list can be used as a range operation by passing a subList view instead of a whole list. For example, the following idiom removes a range of elements from a list:
list.subList(from, to).clear();
Package: java.util
Java Platform:Java SE 8
Syntax:
subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Type |
|---|---|---|
| fromIndex | The minimum length for an ArrayList instance. | int |
| toIndex | high endpoint (exclusive) of the subList | int |
Return Value:
a view of the specified ranges within this list
Throws:
- IndexOutOfBoundsException - if an endpoint index value is out of range (fromIndex < 0 || toIndex > size)
- IllegalArgumentException - if the endpoint indices are out of order (fromIndex > toIndex)
Pictorial presentation of ArrayList.subList() Method
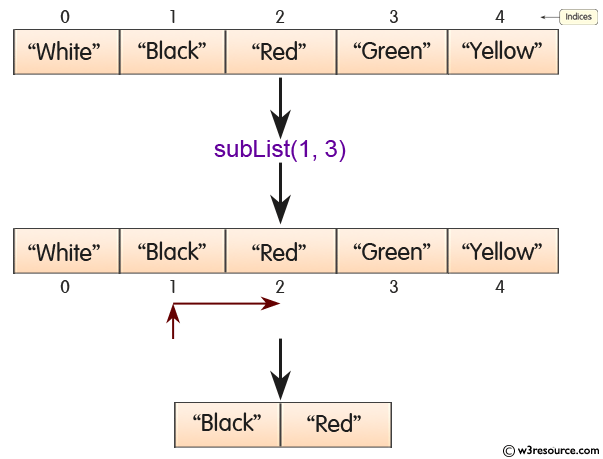
Example: Java ArrayList.subList Method
In the following example the subList() method is used to get a portion of this list between the specified fromIndex, inclusive, and toIndex.
import java.util.*;
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an empty array list
ArrayList<String> color_list = new ArrayList<String>();
// use add() method to add values in the list
color_list.add("White");
color_list.add("Black");
color_list.add("Red");
color_list.add("Green");
color_list.add("Yellow");
System.out.println("List of the colors :" + color_list);
//Return portion of the list : fromindex(inclusive)->1, toindex(exclusive)->3
ArrayList<String> new_color_list1 = new ArrayList<String>(color_list.subList(1, 3));
System.out.println("Portion of the list: "+new_color_list1);
//Return empty list as fromindex and toindex are equal
ArrayList<String> new_color_list2 = new ArrayList<String>(color_list.subList(3, 3));
System.out.println("Portion of the list: "+new_color_list2);
}
}
Output:
F:\java>javac test.java F:\java>java test List of the colors :[White, Black, Red, Green, Yellow] Portion of the list: [Black, Red] Portion of the list: []
Example of Throws: subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) Method
IndexOutOfBoundsException - if an endpoint index value is out of range (fromIndex < 0 || toIndex > size)
IllegalArgumentException - if the endpoint indices are out of order (fromIndex > toIndex)
Let
ArrayListnew_color_list1 = new ArrayList (color_list.subList(1, 8));
in the above example.
Output:
List of the colors :[White, Black, Red, Green, Yellow]
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsEx
ception: toIndex = 8
at java.util.ArrayList.subListRangeCheck(ArrayL
ist.java:962)
at java.util.ArrayList.subList(ArrayList.java:9
54)
at test.main(test.java:18
Java Code Editor:
Previous:iterator Method
Next:foreach Method
