NumPy String: numpy.char.split() function
numpy.char.split() function
The numpy.char.split() function is used to split the string element-wise based on a specified delimiter or separator.
This function is useful in -
- Cleaning and preprocessing text data for natural language processing tasks.
- Separating data elements from raw text data files such as CSV files or log files
Syntax:
numpy.char.split(a, sep=None, maxsplit=None)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| a: array_like of str or unicode | Input an array_like of string or unicode. | Required |
| sep | If sep is not specified or None, any whitespace string is a separator. | Optional |
| maxsplit | If maxsplit is given, at most maxsplit splits are done. | Optional |
Return value:
Array of list objects.
Example: Splitting a string into words using numpy.char.split()
>>> import numpy as np
>>> a = np.char.split('the quick brown fox')
>>> a
array(list(['the', 'quick', 'brown', 'fox']), dtype=object)
In the above example the numpy.char.split() function splits a string into individual words and the resulting output is an array of strings, where each string represents a word.
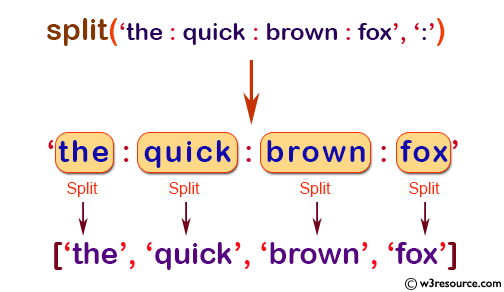
Example: Splitting a string with numpy.char.split()
>>> import numpy as np
>>> a = np.char.split('the:quick:brown:fox', ':')
>>> print(a)
['the', 'quick', 'brown', 'fox']
In the above example, the function numpy.char.split() splits the string 'the:quick:brown:fox' using ':' as a separator and returns a list of the resulting strings. The separator ':' is passed as an argument to the function to specify the splitting point.
Pictorial Presentation:
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
Previous:
rstrip()
Next:
splitlines()
