PostgreSQL TRANSLATE() function
TRANSLATE() function
The PostgreSQL translate() function is used to translate any character in the string by a character in replace_string. The characters in replace_string are corresponding to the characters in matching_string. The translate will happen when any character in the string matching with the character in the matching_string.
Uses of TRANSLATE() Function
- Character Replacement: Replace characters in a string based on matching and replacement strings.
- Data Cleaning: Standardize data by replacing unwanted characters.
- String Manipulation: Perform custom character substitutions in text fields.
- Text Formatting: Reformat strings by translating specific characters to desired ones.
- Data Transformation: Modify string data dynamically for various applications.
Syntax:
translate(<string>,<matching_string>, <replace_string>])
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Return Type |
|---|---|---|
| string | Each character of this string will be matched against each character of 'matching_string'. | text |
| matching_string | Each character of 'string' will be matched against each character of this string. | text |
| replace_string | If a character of 'string' finds a match in 'matching_string', and if any character in the corresponding position in 'replace_string' found, that character will replace all the occurrences of the matching character(s) in 'string'. | text |
PostgreSQL Version: 9.3
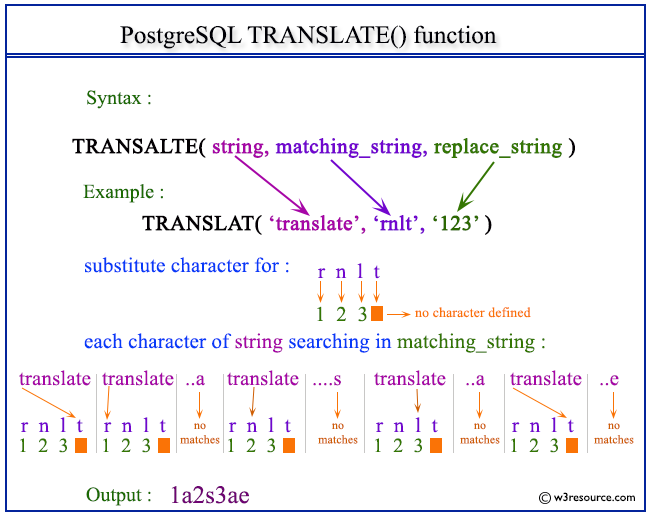
Visual Presentation of TRANSLATE() function
Example 1: PostgreSQL TRANSLATE() function:
SQL Code:
SELECT translate('translate', 'rnlt', '123');
Output:
translate ----------- 1a2s3ae (1 row)
Explanation:
In the above example, the each character in the first parameter is searching in the second parameter and replacing by the substitute character from the third parameter. Here 't' found in the fourth place in the second parameter and no substitute character defined for this place, so no translate will take place. The second character 'r' is matching with the first character of 'rnlt' and translate with '1'. Thus 'a' is not matching and no translate have done, 'n' is matching and translate with '2', 's' is not matching and no translate have done, 'l' is matching and translate with '3', 'a' is not matching and no translate have done, 't' is matching but no substitute character defined, so no translate will take place, 'e' is not matching and no translate have done.
Example 2:
SQL Code:
SELECT translate('translate', 'rnlt', '1234');
Output:
translate ----------- 41a2s3a4e (1 row)
Explanation:
In the above example, the each character in the first parameter is searching in the second parameter and replacing by the substitute character from the third parameter. Here 't' found in the fourth place in the second parameter and matching with the forth character of 'rnlt' and translate with '4'. The second character 'r' is matching with the first character of 'rnlt' and translate with '1'. Thus 'a' is not matching and no translate have done, 'n' is matching and translate with '2', 's' is not matching and no translate have done, 'l' is matching and translate with '3', 'a' is not matching and no translate have done, 't' is matching and translate with '4', 'e' is not matching and no translate have done.
Previous: SUBSTR function
Next: RIGHT function