PostgreSQL LOWER() function
LOWER() function
The PostgreSQL lower function is a built-in function used to convert all uppercase characters in a given string to lowercase. This function is particularly useful for case-insensitive comparisons, data normalization, and ensuring consistency in string data across your database.
Uses of LOWER() Function
- Data Normalization: Ensures consistency in string data by converting all characters to lowercase.
- Case-Insensitive Comparisons: Facilitates comparisons and searches that ignore case differences.
- Data Cleaning: Helps in cleaning and standardizing data by converting mixed-case strings to lowercase.
- User Input Processing: Standardizes user input to lowercase for consistent storage and processing.
- Text Analysis: Prepares text data for analysis by normalizing case differences.
- Display Formatting: Converts text to a uniform case for display purposes.
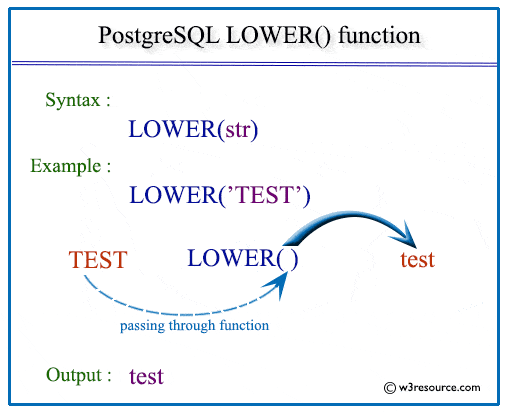
Syntax:
lower(string)
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| string | A string whose characters are going to be converted to lowercase. |
PostgreSQL Version: 9.3
- Compatible with PostgreSQL version 9.3 and later.
Visual Presentation
Example: PostgreSQL LOWER() function
The following PostgreSQL statement returns the given string after converting all of its characters in lowercase.
SQL Code:
SELECT lower('W3RESOURCE') AS "Upper to Lower";
Output:
Upper to Lower ---------------- w3resource (1 row)
Example: LOWER() on column of a table
Sample Table: employees.
If we want to display the first name, last name, email and the lower of email of those employees who belong to the dept 20 from the employee table, the following SQL can be executed:
SQL Code:
SELECT first_name,last_name,
email,LOWER(email)
FROM employees
WHERE department_id=20;
Output:
first_name | last_name | email | lower ------------+-----------+----------+---------- Michael | Hartstein | MHARTSTE | mhartste Pat | Fay | PFAY | pfay (2 rows)
Example LOWER(): Using with TEXT Type
SQL Code:
SELECT lower(CAST('HELLO' AS TEXT)) AS "Lowercase Text";
Output:
Lowercase Text| --------------+ hello |
Example LOWER(): Using with CHAR Type
SQL Code:
SELECT lower(CAST('HELLO' AS CHAR(10))) AS "Lowercase Char";
Output:
Lowercase Char| --------------+ hello |
Example LOWER(): Using with VARCHAR Type
SQL Code:
SELECT lower(CAST('HELLO' AS VARCHAR(10))) AS "Lowercase Varchar";
Output:
Lowercase Varchar| -----------------+ hello |
Example LOWER(): Using with CONCAT() Function
SQL Code:
SELECT lower(CONCAT('Hello', 'World')) AS "Lowercase String";
Output:
Lowercase String| ----------------+ helloworld |
Example LOWER(): Using with SUBSTRING() Function
SQL Code:
SELECT lower(SUBSTRING('HELLO WORLD' FROM 1 FOR 5)) AS "Lowercase Substring";
Output:
Lowercase Substring| -------------------+ hello |
Example LOWER(): Using with TRIM() Function
SQL Code:
SELECT lower(TRIM(' HELLO ')) AS "Lowercase Trimmed";
Output:
Lowercase Trimmed| -----------------+ hello |
Previous: CHAR_LENGTH function
Next: OCTET_LENGTH function