PostgreSQL BIT_LENGTH() function
BIT_LENGTH() function
The PostgreSQL bit_length function is used to count the number of bits in a specified string. It is a built-in function, is particularly useful when you need to determine the bit length of string data, which can be important for storage, transmission, and encryption purposes.
Uses of BIT_LENGTH() Function
- Storage Analysis: Helps in determining the storage requirements for string data in bits.
- Data Transmission: Useful in scenarios where data needs to be transmitted in bit-form.
- Encryption: Assists in encryption algorithms that operate on bit-level data.
- Data Compression: Useful for analyzing the bit-length to understand potential compression ratios.
- Validation: Ensures the integrity of data by validating the bit length of strings.
Syntax:
bit_length (str1)
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| str1 | A string whose BIT_LENGTH value is to be retrieved. |
PostgreSQL Version: 9.3
- Compatible with PostgreSQL version 9.3 and later.
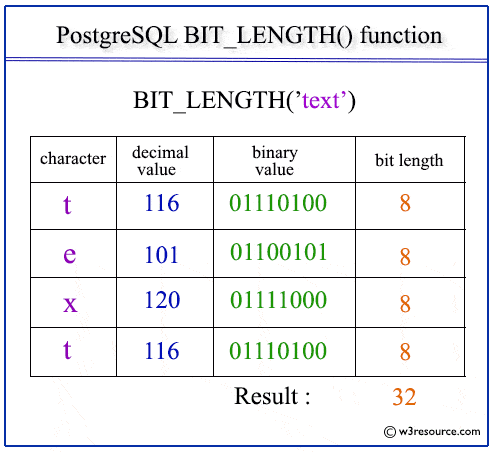
Pictorial Presentation of PostgreSQL BIT_LENGTH() function
Example: PostgreSQL BIT_LENGTH() function
The following PostgreSQL statement will return the length of the given string 'w3resource'' in bits, i.e. 80.
SQL Code:
SELECT bit_length('w3resource') AS "bit_length";
Output:
bit_length
------------
80
(1 row)
Example: Empty String
The following PostgreSQL statement will return the length of the given empty string.
SQL Code:
SELECT bit_length('') AS "bit_length";
Output:
bit_length|
----------+
0|
(1 row)
Example: String with Spaces
SQL Code:
SELECT bit_length('w3 resource') AS "bit_length";
Output:
bit_length|
----------+
88|
Example: Multibyte Character String
SQL Code:
SELECT bit_length('こんにちは') AS "bit_length";
Output:
bit_length|
----------+
120|
Example: Using with TEXT Type Data Type
SQL Code:
SELECT bit_length(CAST('hello' AS TEXT)) AS "bit_length";
Output:
bit_length|
----------+
40|
Example: Using with CHAR Type Data Type
SQL Code:
SELECT bit_length(CAST('hello' AS CHAR(10))) AS "bit_length";
Output:
bit_length|
----------+
40|
Example: Using with VARCHAR Type Data Type
SQL Code:
SELECT bit_length(CAST('hello' AS VARCHAR(10))) AS "bit_length";
Output:
bit_length|
----------+
40|
Example: Using with CONCAT() Function
SQL Code:
SELECT bit_length(CONCAT('hello', 'world')) AS "bit_length";
Output:
bit_length|
----------+
80|
Example: Using with SUBSTRING() Function
SQL Code:
SELECT bit_length(SUBSTRING('hello world' FROM 1 FOR 5)) AS "bit_length";
Output:
bit_length|
----------+
40|
Example: Using with TRIM() Function
SQL Code:
SELECT bit_length(TRIM(' hello ')) AS "bit_length";
Output:
bit_length|
----------+
40|
Previous: PostgreSQL String Functions Introduction
Next: CHAR_LENGTH function