MySQL TAN() function
TAN() function
MySQL TAN() returns the tangent of the argument. The argument is given in radians.
This function is useful in -
- TAN() is a fundamental trigonometric function that is used extensively in mathematics and engineering to solve problems related to angles, distances, and periodic phenomena.
- In geometry and physics, TAN() is crucial for calculating distances, angles, and trajectories.
- In computer graphics and animation, TAN() is used to generate smooth and realistic motion, especially in scenarios involving rotation and oscillation.
- TAN() is used in various simulations to model natural phenomena, such as the motion of pendulums, the behavior of springs, and the propagation of waves.
- TAN() might be used in algorithms that require understanding or manipulation of spatial relationships, which can be relevant in fields like computer vision and robotics.
- Engineers use TAN() for tasks like structural analysis, where understanding the behavior of materials under different loads and angles is essential.
Syntax:
TAN(X);
Where X is a number
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
Pictorial presentation of MySQL TAN() function
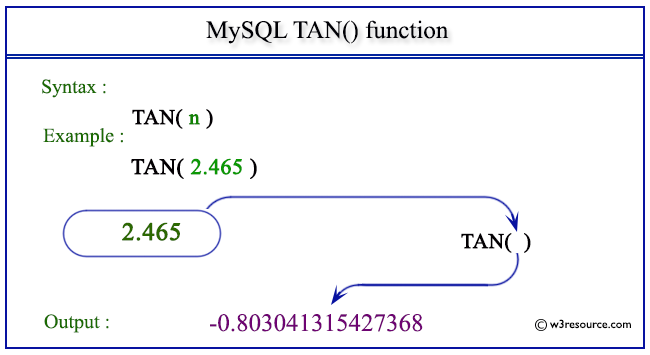
Example of MySQL TAN() function
Code:
SELECT TAN(2.465);
Explanation:
The above statement will return the tangent of the given number 2.465.
Output:
mysql> SELECT TAN(2.465); +--------------------+ | TAN(2.465) | +--------------------+ | -0.803041315427368 | +--------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
PREV : SQRT()
NEXT : TRUNCATE()