MySQL RADIANS() function
RADIANS() function
MySQL RADIANS() converts the value of a number from degrees to radians. (pi radians equals to 180 degrees).
This function is useful in -
- In scientific modeling and simulations, angles are commonly represented in radians.
- This is especially true in fields like physics, astronomy, and engineering, where precise angular measurements are required.
- The RADIANS() function ensures that the angles are in the correct unit for accurate results.
- Functions like sine, cosine, and tangent in MySQL's mathematical functions library expect angles to be in radians.
- The RADIANS() function is crucial for ensuring the correct input format for these functions.
- In navigation and GPS systems, angles are typically represented in radians. The RADIANS() function helps in converting angles from degrees to radians.
- In computer graphics and visualization, radians are often used to represent angles.
Syntax:
RADIANS(M);
Argument:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| M | A number in degrees which is to be converted to radians. |
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
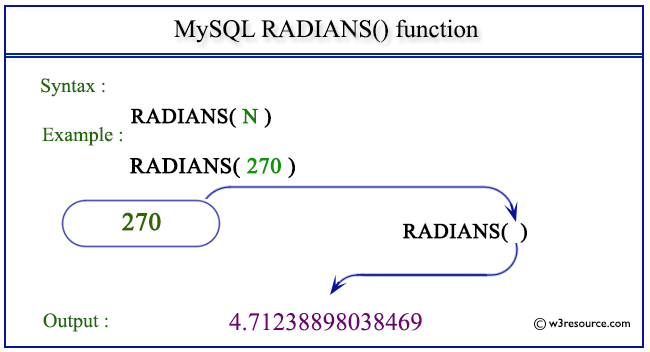
Pictorial presentation of MySQL RADIANS() function
Example of MySQL RADIANS() function
Code:
SELECT RADIANS(270);
Explanation:
The above MySQL statement converts 270 (in degrees) to radians.
Output:
mysql> SELECT RADIANS(270); +------------------+ | RADIANS(270) | +------------------+ | 4.71238898038469 | +------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)