MySQL FLOOR() function
FLOOR() function
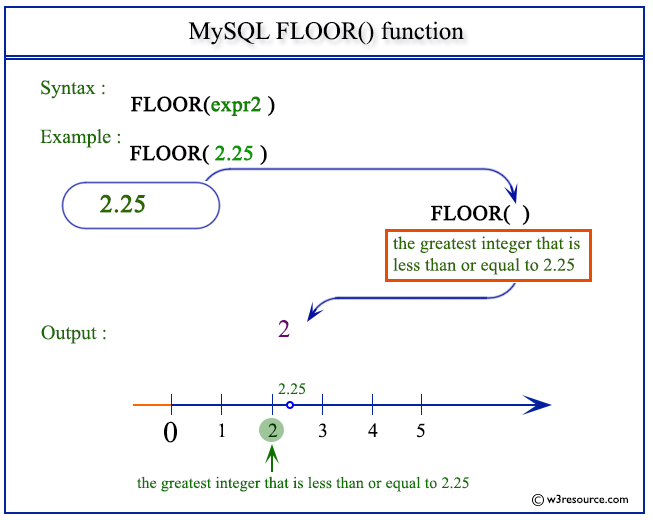
MySQL FLOOR() returns the largest integer value not greater than a number specified as an argument.
This function is useful in -
- FLOOR() works consistently with negative numbers, always rounding towards negative infinity.
- The FLOOR() function mirrors the mathematical floor function, which rounds a real number down to the largest preceding integer.
- In statistics, the FLOOR() function is used in various calculations and modeling where integer values or integer-like results are required.
- In machine learning and data mining, FLOOR() can be used to convert continuous variables into discrete intervals, which can be useful for building models.
- In SQL queries, the FLOOR() function can be employed to round down numerical values, which can be crucial for generating accurate reports or conducting financial analyses.
- In data cleaning processes, FLOOR() can be used to remove decimal points or irrelevant precision from numerical data, making it easier to work with.
Syntax:
FLOOR(N);
Argument:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| N | A number. |
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
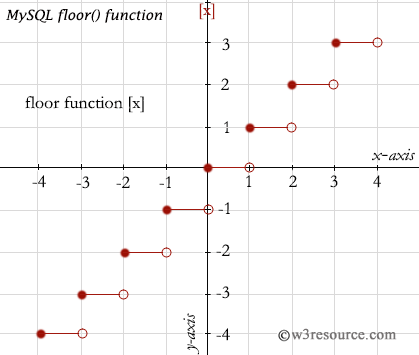
Pictorial presentation of FLOOR() Function
Pictorial presentation of MySQL FLOOR() function
Example of MySQL FLOOR() function
The following MySQL statement returns 1 which is the largest integer value of given number (1.72) as specified in the argument.
Code:
SELECT FLOOR(1.72);
Output:
mysql> SELECT FLOOR(1.72); +-------------+ | FLOOR(1.72) | +-------------+ | 1 | +-------------+ 1 row in set (0.02 sec)
Example: FLOOR() with negative value
The following MySQL statement return -3 which is not the largest integer value of given number (-2.72) as specified in the argument.
Code:
SELECT FLOOR (-2.72);
Output:
mysql> SELECT FLOOR (-2.72); +---------------+ | FLOOR (-2.72) | +---------------+ | -3 | +---------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)