MySQL ROUND() function
ROUND() function
MySQL ROUND() rounds a number specified as an argument up to a number specified as another argument.
This function is useful in -
- ROUND() allows you to control the precision of numeric values, ensuring that they have a specific number of decimal places.
- In data analysis and reporting, ROUND() is useful for aggregating and summarizing data.
- ROUND() is commonly used in financial applications for handling currency values.
- In cases where the result of a calculation might exceed the maximum precision of the data type, ROUND() can be used to prevent overflow errors and maintain data integrity.
- ROUND() can be used to facilitate numeric comparisons.
- When performing statistical calculations, such as calculating means or variances, ROUND() can be applied to the results to maintain consistent precision throughout the analysis.
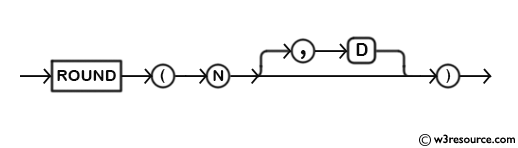
Syntax:
ROUND(N,[D]);
Argument:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| N | A number which will be rounded upto D decimal places. |
| D | A number indicating up to how many decimal places N will be rounded. |
Note: The arguments can be zero(0) or negative. The default value of ‘D’ is 0 if not specified. if ‘D’ is 0, the round will happen from the left of the ‘D’ decimal point of the value ‘N’.
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
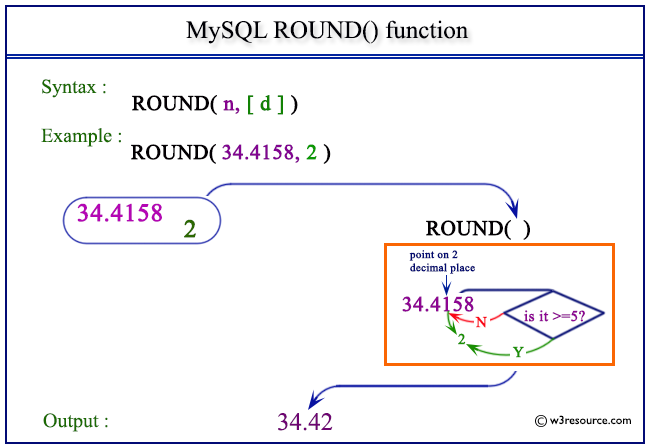
Pictorial presentation of MySQL ROUND() function
Example of MySQL ROUND() function
Code:
SELECT ROUND(4.43);
Explanation:
The above MySQL statement will round the given number 4.43. No decimal places have been defined, so the default decimal value is 0.
Output:
mysql> SELECT ROUND(4.43); +-------------+ | ROUND(4.43) | +-------------+ | 4 | +-------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: ROUND() function with negative value
Code:
SELECT ROUND(-4.53);
Explanation:
The above MySQL statement will round the given number -4.53. No decimal places have been defined, so the default decimal value is 0.
Output:
mysql> SELECT ROUND(-4.53); +--------------+ | ROUND(-4.53) | +--------------+ | -5 | +--------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: ROUND() function using decimal places
Code:
SELECT ROUND(-4.535,2);
Explanation:
The above MySQL statement will round the given number -4.535 up to 2 decimal places.
Output:
mysql> SELECT ROUND(-4.535,2); +-----------------+ | ROUND(-4.535,2) | +-----------------+ | -4.54 | +-----------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example: ROUND() function using negative decimal places
Code:
SELECT ROUND(34.4158,-1);
Explanation:
The above MySQL statement will round the given number 34.4158 from the left of decimal place up to 1 place.
Output:
mysql> SELECT ROUND(34.4158,-1); +-------------------+ | ROUND(34.4158,-1) | +-------------------+ | 30 | +-------------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)