MySQL POW() function
POW() function
MySQL POW() returns the value of a number raised to the power of another number. The synonym of POW() is POWER().
This function is useful in -
- POW() allows for the modeling of phenomena like compound interest, population growth, and radioactive decay.
- In engineering, POW() is used in various fields, including electrical engineering, mechanical engineering, and chemical engineering.
- In finance, POW() is used to calculate compound interest and growth rates.
- POW() is used in signal processing to calculate the power of a signal, which is essential in areas like telecommunications, audio processing, and image processing.
- POW() is an essential component in many scientific formulas, especially those that involve exponential relationships, such as the decay of radioactive isotopes or the charging/discharging of capacitors.
- POW() is used in probability and statistics for various calculations, including likelihood ratios, likelihood functions, and power functions in hypothesis testing.
- The POW() function is valuable in educational settings, helping students and learners understand and perform calculations involving exponential growth, decay, and related concepts.
Syntax:
POW(M,N);
Arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| M | A number which is the base of the exponentiation. |
| N | A number which is the exponent of the exponentiation. |
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
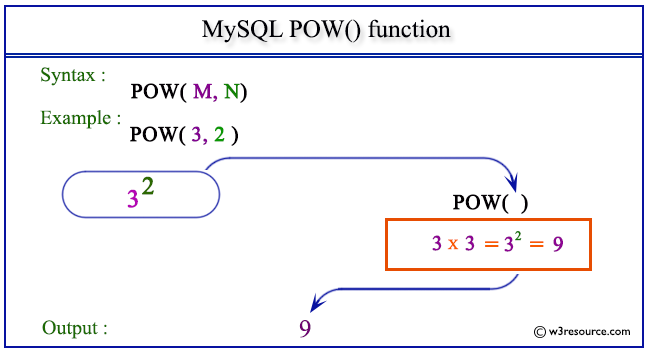
Pictorial presentation of MySQL POW() function
Example of MySQL POW() function
Code:
SELECT POW(3, 2);
Explanation:
The above MySQL statement returns the value of 32, i.e. 9.
Output:
mysql> SELECT POW(3, 2); +-----------+ | POW(3, 2) | +-----------+ | 9 | +-----------+ 1 row in set (0.04 sec)
Example: POW() function with negative value
Code:
SELECT POW(4,-2);
Explanation:
The above MySQL statement returns the value of 4-2, i.e. 0.0625.
Output:
mysql> SELECT POW(4,-2); +-----------+ | POW(4,-2) | +-----------+ | 0.0625 | +-----------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)