MySQL DEGREES() function
DEGREES() function
MySQL DEGREES() converts the value in radians which is specified as the argument, to degrees.
This function is useful in -
- The DEGREES() function allows for easy conversion from the more mathematical radian unit to degrees.
- Many mapping and geographical systems use degrees to represent latitude and longitude. It is crucial when working with GIS.
- In fields like civil engineering and architecture, angles are typically expressed in degrees.
- The DEGREES() function facilitates the conversion from the more mathematical radian unit to a format more familiar to professionals in these fields.
- When working with navigation systems (both terrestrial and celestial), degrees are the standard unit of measuring angles.
- In computer graphics and animation, angles for rotations and transformations are typically specified in degrees.
Syntax:
DEGREES(N);
Argument:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| N | A number in radians whose value in degrees is to be retrieved. |
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
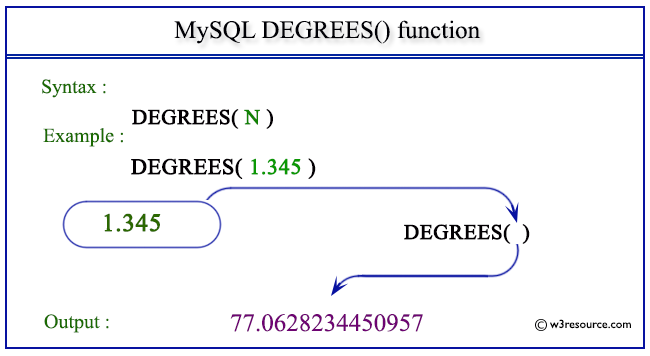
Pictorial presentation of MySQL DEGREES() function
Example of MySQL DEGREES() function
Code:
SELECT DEGREES(1.345);
Explanation:
The above MySQL statement will return the value of 1.345 in degrees.
Output:
mysql> SELECT DEGREES(1.345); +------------------+ | DEGREES(1.345) | +------------------+ | 77.0628234450957 | +------------------+ 1 row in set (0.03 sec)
Example: degrees() with PI()
Code:
SELECT DEGREES(PI());
Explanation:
The above MySQL statement will convert the radians value of PI() in degrees.
Output:
mysql> SELECT DEGREES(PI()); +---------------+ | DEGREES(PI()) | +---------------+ | 180 | +---------------+ 1 row in set (0.00 sec)