Oracle LOG() function
Description
The Oracle LOG() function is used to return the logarithm, base B of N. The base can be any positive value other than 0 or 1 and the number can be any positive value.
The function takes any numeric or nonnumeric data type (can be implicitly converted to a numeric data type) as an argument.
If any argument is BINARY_FLOAT or BINARY_DOUBLE, then the function returns BINARY_DOUBLE. Otherwise, the function returns NUMBER.
Uses of Oracle LOG() Function
- Mathematical Calculations: Calculate logarithms with different bases for mathematical equations.
- Data Analysis: Apply logarithmic transformations to datasets for analysis.
- Financial Modeling: Compute logarithmic growth rates with custom bases in financial models.
- Scientific Research: Perform logarithmic computations in various scientific fields.
- Algorithm Development: Use in algorithms that require logarithms with specific bases.
- Statistical Methods: Incorporate in statistical analyses involving logarithmic calculations.
Syntax:
LOG(B, N);
Argument:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| B | Indicates the base of N. |
| N | A number. |
Pictorial Presentation of LOG() function
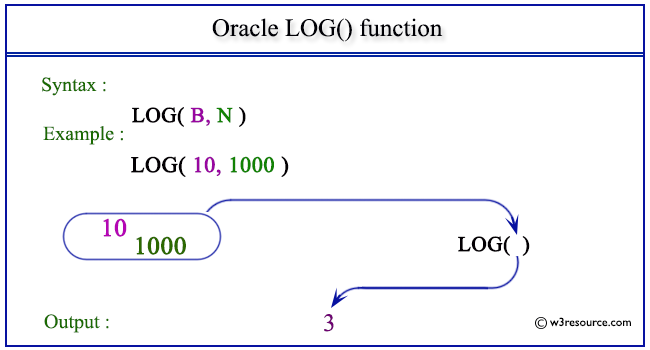
Example: LOG() function using base of a number system
The statement below returns the natural logarithm of 1000 divided by the natural logarithm of 10.
SELECT LOG(10,1000) FROM dual;
Here is the result.
LOG(10,1000)
------------
3
