Oracle ATAN() function
Description
The ATAN() function is used to calculate the angle value (in radians) of a specified tangent. The specified number can be in an unbounded range and returns a value in the range of -pi/2 to pi/2, expressed in radians.
The function takes any numeric or nonnumeric data type (can be implicitly converted to a numeric data type) as an argument.
If the argument is BINARY_FLOAT, then the function returns BINARY_DOUBLE. Otherwise, the function returns the same numeric data type as the argument.
Uses of Oracle ATAN() Function
- Trigonometric Calculations: Determine the angle corresponding to a given tangent value.
- Mathematical Modeling: Useful in mathematical models and simulations requiring inverse trigonometric functions.
- Engineering Applications: Applied in various engineering fields for angle calculations in radian measure.
- Data Analysis: Assist in data analysis involving trigonometric transformations and calculations.
- Scientific Research: Employed in scientific research for computations involving trigonometric functions and angles.
Syntax:
ATAN(N)
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| N | A number whose arc tangent value is to be retrieved. |
Pictorial Presentation of ATAN() function
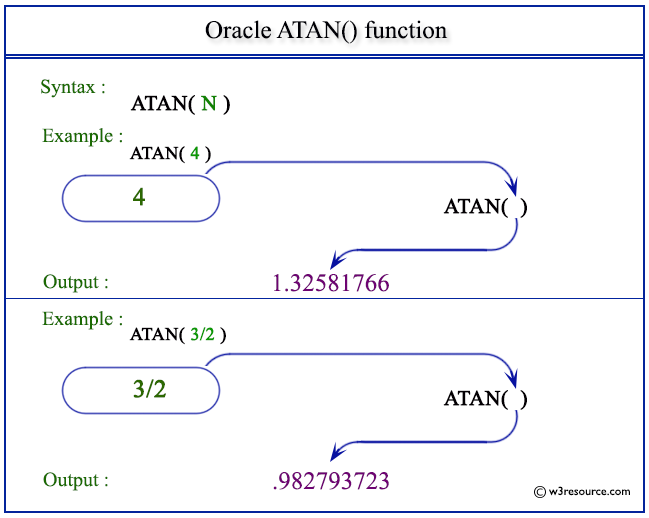
Example:
The statement below will return the arc tangent value of the number specified as an argument.
SELECT ATAN(4) FROM dual;
Here is the result.
ATAN(4) ---------- 1.32581766
Example: ATAN() function using negative value
This statement below will return the arc tangent value of the number defined as an argument.
SELECT ATAN(-4) FROM dual;
Here is the result.
ATAN(-4) ---------- -1.3258177
Example: ATAN() function using a division
This statement below will return the arc tangent value of the number (3 divided by 2) defined as arguments.
SELECT ATAN(3/2) FROM dual;
Here is the result.
ATAN(3/2) ---------- .982793723
