Oracle FLOOR() function
Description
The FLOOR() function returns the largest integer value not greater than a number specified as an argument.
The function accepts any numeric or nonnumeric data type (can be implicitly converted to a numeric data type) as an argument.
Uses of Oracle FLOOR() Function
- Rounding Down: Round down a floating-point number to the nearest integer.
- Mathematical Calculations: Perform floor operations in mathematical expressions.
- Data Analysis: Use in data processing to ensure integer values.
- Financial Analysis: Apply in financial calculations where rounding down is required.
- Engineering Applications: Utilize in engineering computations requiring floor values.
- Algorithm Development: Implement in algorithms needing integer floor values.
Syntax :
FLOOR(N)
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| N | A number. |
The function returns the same data type as the numeric data type of the argument.
Pictorial Presentation of FLOOR() function
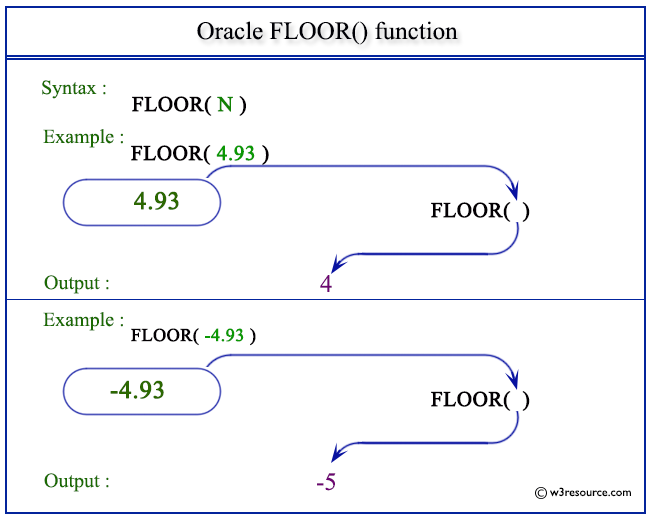
Example
The statement below returns 4 which is the largest integer value of given number (4.93) as specified in the argument.
SELECT FLOOR(4.93) FROM dual;
Here is the result.
FLOOR(4.93)
-----------
4
Example: FLOOR() with negative value
The above MySQL statement return -5 which is not the largest integer value of given number (-4.93) as specified in the argument.
SELECT FLOOR(-4.93) FROM dual;
Here is the result.
FLOOR(-4.93)
------------
-5
