Oracle EXTRACT (datetime) function
Extract date, time from a given datetime in Oracle
The EXTRACT() function is used to extract the value of a specified datetime field from a datetime or interval expression.
Uses of Oracle EXTRACT (datetime) Function:
- Extracting Year, Month, or Day from a Date: Retrieve the year, month, or day from any valid date expression for reporting or filtering.
- Retrieving Time Components from a Timestamp: Isolate time components such as hour, minute, or second from a timestamp.
- Extracting Time Zone Information: Extract time zone details like timezone hour, timezone minute, timezone region, and timezone abbreviation from datetime expressions.
- Filtering Records by Year or Month: Filter records based on a specific year or month in date-based fields.
- Performing Date Arithmetic: Use date components to perform arithmetic operations like finding records from a certain day or range.
- Extracting Data from INTERVAL Data Types: Extract specific parts from INTERVAL data types, such as year or day.
- Timezone Calculations and Reporting: Retrieve time zone details for global applications involving different regions.
- Combining EXTRACT with Other Functions: Combine with other Oracle functions for advanced date and time manipulations.
Syntax:
EXTRACT( { { YEAR
| MONTH
| DAY
| HOUR
| MINUTE
| SECOND
}
| { TIMEZONE_HOUR
| TIMEZONE_MINUTE
}
| { TIMEZONE_REGION
| TIMEZONE_ABBR
}
}
FROM { expr }
)
The expr can be any expression that evaluates to a datetime or interval datatype compatible with the requested field :
- If YEAR or MONTH is requested, then expr must evaluate to an expression of datatype DATE, TIMESTAMP, TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE, or INTERVAL YEAR TO MONTH.
- If DAY is requested, then expr must evaluate to an expression of datatype DATE, TIMESTAMP, TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE, or INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND.
- If HOUR, MINUTE, or SECOND is requested, then expr must evaluate to an expression of datatype TIMESTAMP, TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE, TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE, or INTERVAL DAY TO SECOND. DATE is not valid here because Oracle Database treats it as ANSI DATE datatype, which has no time fields.
- If TIMEZONE_HOUR, TIMEZONE_MINUTE, TIMEZONE_ABBR, TIMEZONE_REGION, or TIMEZONE_OFFSET is requested, then expr must evaluate to an expression of datatype TIMESTAMP WITH TIME ZONE or TIMESTAMP WITH LOCAL TIME ZONE.
Applies to:
Oracle 12c, Oracle 11g, Oracle 10g, Oracle 9i
Pictorial Presentation
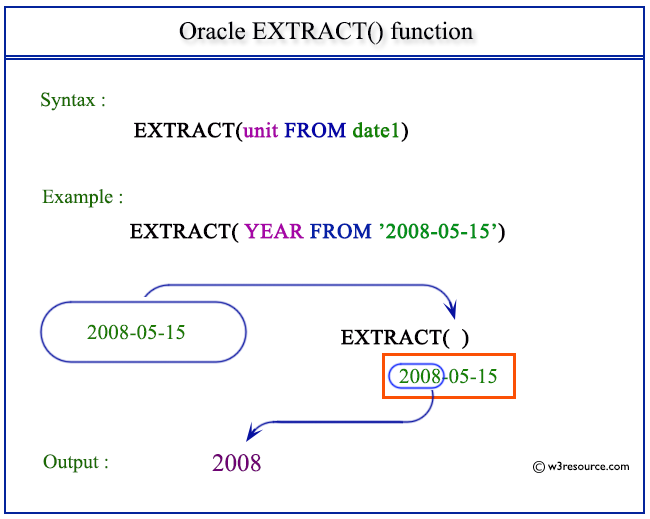
Examples: Oracle EXTRACT (datetime)() function
The following example returns the year 2015.
SQL> SELECT EXTRACT(YEAR FROM DATE '2015-03-03') FROM DUAL;
Sample Output:
EXTRACT(YEARFROMDATE'2015-03-03')
---------------------------------
2015
The following example selects all employees who were hired in and after 2008 :
Sample table: employees
SQL> SELECT first_name,last_name, employee_id, hire_date
2 FROM employees
3 WHERE EXTRACT(YEAR FROM TO_DATE(hire_date, 'DD-MON-RR')) >= 2008
4 ORDER BY hire_date;;
Sample Output:
FIRST_NAME LAST_NAME EMPLOYEE_ID HIRE_DATE -------------------- ------------------------- ----------- --------- Charles Johnson 179 04-JAN-08 Douglas Grant 199 13-JAN-08 Mattea Marvins 164 24-JAN-08 Eleni Zlotkey 149 29-JAN-08 Girard Geoni 183 03-FEB-08 Hazel Philtanker 136 06-FEB-08 David Lee 165 23-FEB-08 Steven Markle 128 08-MAR-08 Sundar Ande 166 24-MAR-08 Amit Banda 167 21-APR-08 Sundita Kumar 173 21-APR-08 11 rows selected.
Previous:
DBTIMEZONE
Next:
FROM_TZ
