Oracle ADD_MONTHS function
Add a month or months to a given date in Oracle
ADD_MONTHS() function returns a date with a given number of months added (date plus integer months). A month is defined by the session parameter NLS_CALENDAR.
Uses of Oracle ADD_MONTHS() Function
- Date Adjustment: Adjust dates by adding a specific number of months.
- Expiration Date Calculation: Calculate expiration dates by adding months to a start date.
- Recurring Event Scheduling: Determine future dates for recurring events.
- Project Timeline Management: Adjust project timelines or deadlines by months.
- Milestone and Anniversary Calculation: Calculate anniversaries or milestones by adding months to the original date.
- Date-based Report Generation: Generate reports based on date calculations for past or future dates.
- Billing Cycle Adjustment: Shift billing cycles or payment schedules by a set number of months.
- Trend Analysis with Date Intervals: Analyze trends by comparing dates separated by specific month intervals.
- Financial Forecasting: Perform date arithmetic to forecast future dates in financial models.
- Month-end Period Calculation: Compute the date of a month-end period by adding months to a base date.
Syntax:
ADD_MONTHS(date, integer)
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| date | A datetime value or any value that can be implicitly converted to DATE. |
| integer | An integer or any value that can be implicitly converted to an integer. |
Return value type :
The return type is always DATE, regardless of the datatype of date.
Note: If the date is the last day of the month or if the resulting month has fewer days than the day component of date, then the result is the last day of the resulting month. Otherwise, the result has the same day component as a date.
Applies to :
Oracle 12c, Oracle 11g, Oracle 10g, Oracle 9i
Pictorial Presentation
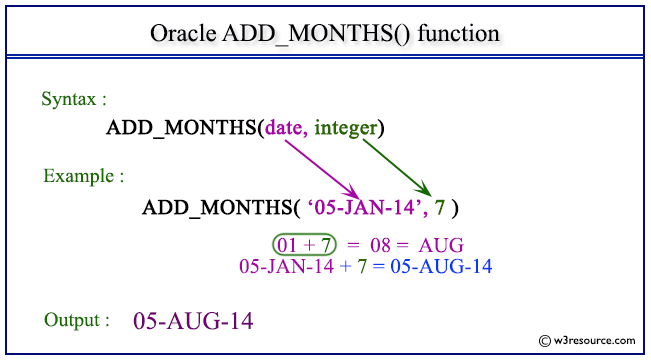
Example: Oracle ADD_MONTHS() function
The following statement returns the hire date, month before and after the hire_date in the sample table employees :
Sample table: employees
SQL> SELECT hire_date, TO_CHAR(ADD_MONTHS(hire_date, -1), 'DD-MON-YYYY') "Previous month",
TO_CHAR(ADD_MONTHS(hire_date, 1), 'DD-MON-YYYY') "Next month"
FROM employees
WHERE first_name = 'Lex';
Sample Output:
HIRE_DATE Previous month Next month --------- -------------------- -------------------- 13-JAN-01 13-DEC-2000 13-FEB-2001
Example-2:
Sample table: employees
This following query demonstrates adding three months to the hire date for employees.
SELECT employee_id, hire_date,
ADD_MONTHS(hire_date, 3) AS "After 3 Months"
FROM hr.employees;
Sample Output:
EMPLOYEE_ID HIRE_DATE After 3 Months ----------------------------------------- 100 17-JUN-03 17-SEP-03 101 21-SEP-05 21-DEC-05 102 13-JAN-01 13-APR-01 .......
Example-3:
Sample table: employees
This following example calculates the experiences of employees by subtracting their hire date from the current date.
SELECT employee_id, last_name, hire_date,
FLOOR(MONTHS_BETWEEN(SYSDATE, hire_date) / 12) AS "Age"
FROM hr.employees;
Sample Output:
EMPLOYEE_ID LAST_NAME HIRE_DATE Age ---------------------------------------------- 100 King 17-JUN-03 20 101 Kochhar 21-SEP-05 18 102 De Haan 13-JAN-01 22 .......
Example-4:
Sample table: employees
This following example calculates the difference in months between two dates.
SELECT hire_date,
ADD_MONTHS(hire_date, -6) AS "Six months ago",
MONTHS_BETWEEN(SYSDATE, ADD_MONTHS(hire_date, -6)) AS "Months passed"
FROM employees;
Sample Output:
HIRE_DATE Six months ago Months passed -------------------------------------------------------------------- 17-JUN-87 17-DEC-86 443.337354764038231780167264038231780167 18-JUN-87 18-DEC-86 443.305096699522102747909199522102747909 19-JUN-87 19-DEC-86 443.272838635005973715651135005973715651 .......
Previous:
Oracle Datetime Functions Introduction
Next:
CURRENT_DATE
