Oracle LPAD function
Description
The Oracle LPAD() function is used to pad the left side of a string with a specific set of characters. The function is useful for formatting the output of a query.
Uses of Oracle LPAD Function
- Formatting Data Output: Aligns text data in query results for better readability.
- Creating Fixed-Length Strings: Ensures strings meet a specified length by padding them with characters.
- Data Presentation in Reports: Formats data in reports to maintain a uniform appearance.
- Generating Identifiers: Pads numbers or strings to create standardized identifiers.
- Preparing Data for Export: Ensures data meets format requirements when exporting to external systems.
- Enhancing Data Display in GUIs: Improves the visual presentation of data in graphical user interfaces.
Syntax:
LPAD(expr1, n [, expr2 ])
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Data Types |
|---|---|---|
| expr1 | Original string. | CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB |
| n | A number indicating the total length of the string ( in characters) returned after padding. | NUMBER integer or a value that can be implicitly converted to a NUMBER integer. |
| expr2 | String which is used for left padding. | CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB |
Return Value
CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB
Applies to
Oracle 12c, Oracle 11g, Oracle 10g, Oracle 9i, Oracle 8i
Pictorial Presentation
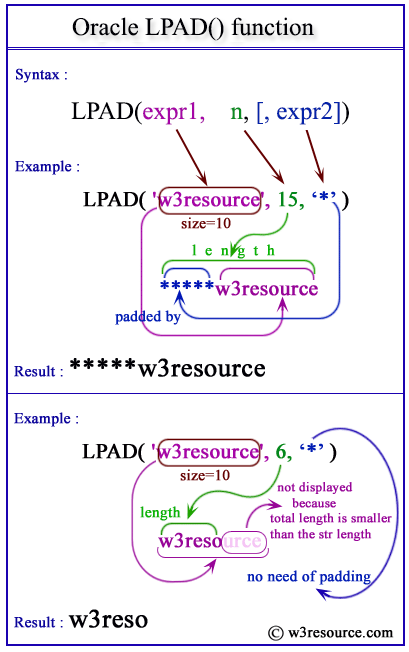
Example: Oracle LPAD() function
In the following Oracle statement, the first argument specifies a string of 6 characters, the second argument specifies that the length of the string returned after padding will be 10 characters and the third argument specifies the string to be used for left padding. So, 4 characters (10-6) being used for left padding and the function thus returns '++++Oracle'.
SQL> SELECT LPAD('Oracle',10,'+') FROM DUAL;
Sample Output:
LPAD('ORAC
----------
++++Oracle
Example: Oracle of LPAD() function with less than the original string
The following Oracle statement returns 'Orac'. This happens because, the first argument has 6 characters, second argument 4 is the total number of characters after left padding and the third argument is the padding string. Since a total number of characters after padding is less than the total number of characters in the first argument, so to meet the condition, two characters are omitted from the actual string (i.e. the first argument).
SQL> SELECT LPAD('Oracle',4,'*') FROM DUAL;
Sample Output:
LPAD
----
Orac
