Oracle CHR function
Description
The CHR function in Oracle is used to return the character having the binary equivalent to n as a VARCHAR2 value in either the database character set or, from the NCHAR_CS.
For single-byte character sets, when n > 256, then returns the binary equivalent of n mod 256.
This function takes a number as an argument a , or any value that can be implicitly converted to NUMBER, and returns a character.
Uses of Oracle CHR Function
- Generating Characters from Numeric Codes: Converts numeric codes to their corresponding characters, useful in various encoding and decoding scenarios.
- Formatting Output: Helps in creating formatted output by combining characters represented by their ASCII codes.
- Constructing Strings: Facilitates the construction of strings from numeric values, especially when working with dynamic content generation.
- Special Characters: Useful for inserting special characters into strings, such as control characters in text processing.
Syntax:
CHR(n [ USING NCHAR_CS ])
Arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| n | A number. |
| NCHAR_CS | national character set |
Applies to
Oracle 12c, Oracle 11g, Oracle 10g, Oracle 9i, Oracle 8i
Pictorial Presentation
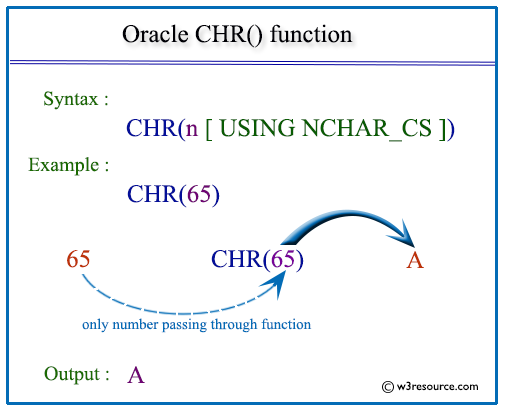
Examples: Oracle CHR function
The following example is run on an ASCII-based machine with the database character set.
SELECT CHR(7)||CHR(65)||CHR(84) "Cap"
FROM DUAL;
Sample Output:
Cap --- HAT
The following example assumes that the national character set is UTF16:
SELECT CHR (210 USING NCHAR_CS)
FROM DUAL;
Sample Output:
C - ╥
Previous:
Oracle-character-functions Introduction
Next:
CONCAT
