Oracle LOWER function
Description
The Oracle LOWER() function returns a specified character expression in lowercase letters.
Uses of Oracle LOWER Function
- Converting Text to Uniform Case: Ensures consistent data storage by converting text to lowercase.
- Case-Insensitive Comparison: Prepares data for comparisons that are not case-sensitive.
- Formatting Output for User Interfaces: Ensures a consistent appearance in user interfaces by standardizing the case of text.
- Standardizing Text Data for String Operations: Prepares text for operations like searches or replacements by converting it to lowercase.
- Data Normalization in Databases: Helps normalize text data within databases.
- Processing Text for NLP Tasks: Prepares textual data for natural language processing tasks by converting it to lowercase.
Syntax:
LOWER(cExpression)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Data Types |
|---|---|---|
| cExpression | The given character expression. | CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB |
Return Value Type
CHAR, VARCHAR2, NCHAR, NVARCHAR2, CLOB, or NCLOB
Note: For linguistic-sensitive uppercase and lowercase, refer to NLS_INITCAP.
Applies to
Oracle 12c, Oracle 11g, Oracle 10g, Oracle 9i, Oracle 8i
Pictorial Presentation
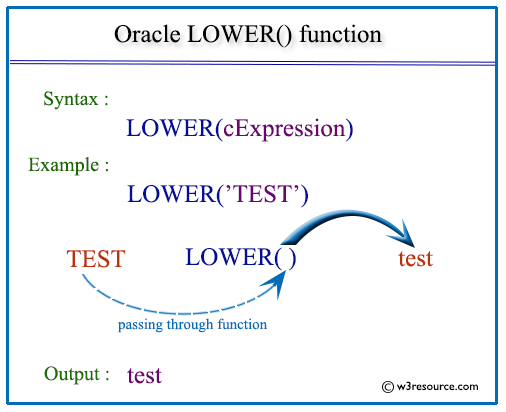
Examples: Oracle LOWER function
The following example returns the first name of the employees in lower case.
Sample table: employees
SQL> SELECT LOWER(first_name) FROM employees;
Output :
LOWER(FIRST_NAME) -------------------- ellen sundar mozhe david hermann shelli amit elizabeth sarah david ......
