MySQL INSERT() function
INSERT() function
MySQL INSERT() function inserts a string within a string, removing a number of characters from the original string.
The original string, the string which will be inserted, a position of insertion within the original string and number of characters to be removed from the original string - all are specified as arguments of the function.
This function is useful in -
- String modification: A string can be modified by inserting another string at a specific position within the original string.
- Substring insertion: You can use INSERT() to insert a substring into a string, replacing a specific number of characters.
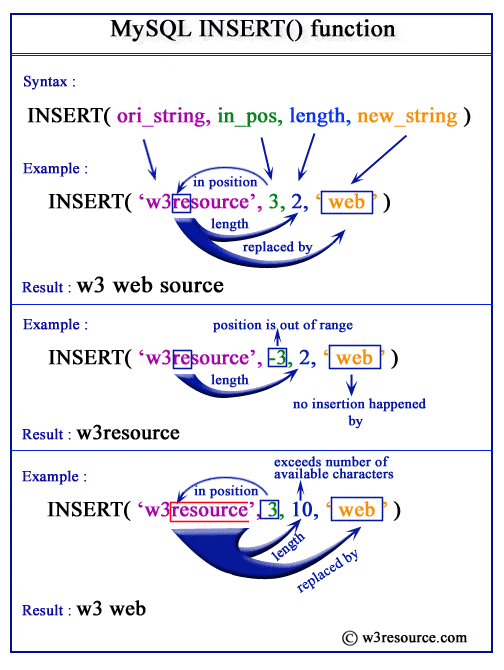
Syntax:
INSERT (ori_string, in_pos, length, new_string)
Arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ori_string | Original string. |
| in_pos | Position of insertion within the original string. |
| length | Number of characters to be removed from the original string. |
| new_string | The string to be inserted. |
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
Pictorial Presentation:
Example of MySQL INSERT() function
In the following MySQL statement, string ' insert ' is inserted into the string 'Originalstring', removing 5 characters from the 4th character of the 'Originalstring'. The output is "Ori insert string".
Code:
SELECT INSERT('Originalstring', 4, 5, ' insert ');
Output:
mysql> SELECT INSERT('Originalstring', 4, 5, ' insert ');
+--------------------------------------------+
| INSERT('Originalstring', 4, 5, ' insert ') |
+--------------------------------------------+
| Ori insert string |
+--------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
MySQL INSERT(): Basic usage
In the following MySQL statement, we insert the substring 'Beautiful ' into the original string 'Hello World' starting from position 7. No characters are removed from the original string before the insertion.
Code:
SELECT INSERT('Hello World', 7, 0, 'Beautiful ');
Output:
INSERT('Hello World', 7, 0, 'Beautiful ')|
-----------------------------------------+
Hello Beautiful World |
Example of MySQL INSERT() function with negative value
The following MySQL statement returns Originalstring, the actual string itself. This happens because the position of insertion, which is specified as -3, is out of range, so no insertion takes place.
Code:
SELECT INSERT('Originalstring', -3, 5, ' insert ');
Output:
mysql> SELECT INSERT('Originalstring', -3, 5, ' insert ');
+---------------------------------------------+
| INSERT('Originalstring', -3, 5, ' insert ') |
+---------------------------------------------+
| Originalstring |
+---------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.02 sec)
Example of MySQL INSERT() function exceeded length
The following MySQL statement returns "Ori insert". This happens because the number of characters to be removed (from the 4th position of the original string) exceeds the number of characters available (after the 4th position) in the original string. So it continues to remove the characters untill the end of the original string.
Code:
SELECT INSERT('Originalstring', 4,15, ' insert ');
Output:
mysql> SELECT INSERT('Originalstring', 4,15, ' insert ');
+--------------------------------------------+
| INSERT('Originalstring', 4,15, ' insert ') |
+--------------------------------------------+
| Ori insert |
+--------------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Example of MySQL INSERT() function using where
The following MySQL statement takes the aut_id from the author table checking if the country of the author is USA, if so, then it returns a string by inserting a new string ‘/’ at the 4th position (of the aut_id), removing 0 number of characters from the 4th position (of the aut_id).
Code:
SELECT INSERT(aut_id,4,0, '/')
FROM author
WHERE country='USA';
Sample table: author
+--------+----------------------+-----------+----------------+ | aut_id | aut_name | country | home_city | +--------+----------------------+-----------+----------------+ | AUT001 | William Norton | UK | Cambridge | | AUT002 | William Maugham | Canada | Toronto | | AUT003 | William Anthony | UK | Leeds | | AUT004 | S.B.Swaminathan | India | Bangalore | | AUT005 | Thomas Morgan | Germany | Arnsberg | | AUT006 | Thomas Merton | USA | New York | | AUT007 | Piers Gibson | UK | London | | AUT008 | Nikolai Dewey | USA | Atlanta | | AUT009 | Marquis de Ellis | Brazil | Rio De Janerio | ........... | AUT015 | Butler Andre | USA | Florida | +--------+----------------------+-----------+----------------+
Output:
mysql> SELECT INSERT(aut_id,4,0, '/')
-> FROM author
-> WHERE country='USA';
+-------------------------+
| INSERT(aut_id,4,0, '/') |
+-------------------------+
| AUT/006 |
| AUT/008 |
| AUT/010 |
| AUT/015 |
+-------------------------+
4 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Video Presentation: