MySQL CHAR() function
CHAR() function
MySQL CHAR() returns the character value of the given integer value according to the ASCII table. It ignores the NULL value.
This function is useful in -
- It allows you to generate a character based on its ASCII value. For example, CHAR(67) will return the uppercase letter 'C', as 67 is the ASCII value for 'C'.
- CHAR() can be used to transform numeric or ASCII-based data into character representations.
- The CHAR() function can be used in conditional expressions or in CASE statements to conditionally return different characters based on certain conditions or criteria.
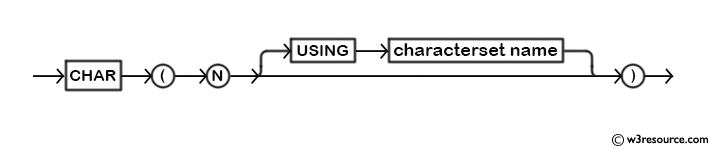
Syntax:
CHAR (N…[USING characterset name])
Argument:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| N | Integers whose character values (according to the ASCII table) are to be retrieved. |
Syntax Diagram:
MySQL Version: 8.0
Example: MySQL CHAR() function
The following MySQL statement returns character values (according to the ASCII table) of the integers 67, 72, 65 and 82.
Code:
SELECT CHAR(67,72,65,82);
Output:
mysql> SELECT CHAR(67,72,65,82); +-------------------+ | CHAR(67,72,65,82) | +-------------------+ | CHAR | +-------------------+ 1 row in set (0.02 sec)
Video Presentation:
All String Functions (Slides presentation)
PREV : BIT_LENGTH
NEXT : CHARACTER_LENGT