MySQL FIND_IN_SET() function
FIND_IN_SET() function
The MySQL FIND_IN_SET() function is a powerful tool used to locate the position of a substring within a comma-separated list of substrings. This function is particularly useful for searching and filtering data stored in a comma-delimited format. It returns the position of the substring if found, 0 if not found, and NULL if any argument is NULL.
This function is useful in -
- Determining Position: Identify the exact position of a value within a comma-separated list.
- Filtering data: You can use FIND_IN_SET() in WHERE clauses to filter data based on the presence or absence of a value.
- Dynamic Value Checks: Compare values dynamically fetched from other tables or queries.
- Conditional Updates: Update records conditionally based on the presence of a substring.
- Data Validation: Validate if a particular value exists within a predefined list.
Syntax:
FIND_IN_SET (search string, string list)
Arguments:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| search string | A string which is to be looked for in following a list of arguments. |
| string list | List of strings to be searched if they contain the search string. |
Syntax Diagram:

MySQL Version: 8.0
Pictorial Presentation:
Basic Usage:
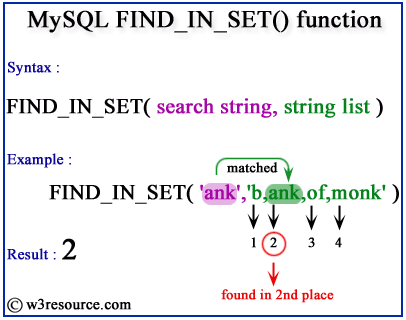
The following MySQL statement finds the search string ‘ank’ at the 2nd place within the string list. So it returns 2.
Code:
-- The following SQL query uses the FIND_IN_SET() function to find the position of the string 'ank' within a comma-separated list of strings.
SELECT FIND_IN_SET('ank', 'b,ank,of,monk');
Explanation:
- This SQL query calls the FIND_IN_SET() function to search for the substring 'ank' within the comma-separated list 'b,ank,of,monk'.
- The function returns the position of 'ank' in the list, which is 2 in this case because 'ank' is the second element in the list.
- If the substring were not found, the function would return 0. If any argument were NULL, the function would return NULL.
Output:
mysql> SELECT FIND_IN_SET('ank','b,ank,of,monk');
+------------------------------------+
| FIND_IN_SET('ank','b,ank,of,monk') |
+------------------------------------+
| 2 |
+------------------------------------+
1 row in set (0.00 sec)
Filtering Data in WHERE Clause:
Sample table: fun_n_veg
Code:
-- The following SQL query selects all columns from the table 'fru_n_veg'
-- where the string 'Cabbage' is found within the comma-separated values of the 'pkt_desc' column.
SELECT * FROM fru_n_veg WHERE FIND_IN_SET('Cabbage', pkt_desc);
Output:
item_id|weight|category |pkt_desc |
-------+------+----------+--------------------------+
5| 1500|Vegetables|Cabbage, Carrot, Broccoli |
8| 2500|Vegetables|Cabbage, Eggplant, Pumpkin|
This will return all rows where the vegetable 'Cabbage' is found in the pkt_desc column.
MySQL FIND_IN_SET with other function:
The following MySQL statement find the search string as defined first 7 characters from aut_name column from the table author within the given string as specified in the argument and retrieves all columns from the concern rows.
Sample table: author
Code:
-- The following SQL query selects all columns from the table 'author'
-- where the first 7 characters of the 'aut_name' column match any of the
-- comma-separated values in the specified string 'William,steven,jung,angalo'.
SELECT *
FROM author
WHERE FIND_IN_SET(left(aut_name,7),'William,steven,jung,angalo') > 0;
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves all rows and columns from the author table where the first 7 characters of the aut_name column match any of the names in the comma-separated list 'William,steven,jung,angalo'.
- The LEFT(aut_name, 7) function extracts the first 7 characters of aut_name, and FIND_IN_SET() checks if this substring is present in the specified list.
Output:
+--------+-----------------+---------+-----------+ | aut_id | aut_name | country | home_city | +--------+-----------------+---------+-----------+ | AUT001 | William Norton | UK | Cambridge | | AUT002 | William Maugham | Canada | Toronto | | AUT003 | William Anthony | UK | Leeds | +--------+-----------------+---------+-----------+ 3 rows in set (0.13 sec)
Using a specific value and condition:
Sample table: fun_n_veg
Code:
-- The following SQL query selects all columns from the table 'fru_n_veg'
-- where the 'category' column has the value 'Fruits' and
-- the string 'Guava' is present in the 'pkt_desc' column.
SELECT *
FROM fru_n_veg
WHERE category = 'Fruits'
AND FIND_IN_SET('Guava', pkt_desc);
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves all rows and columns from the fru_n_veg table where the category column is 'Fruits' and the pkt_desc column contains the value 'Guava' within its comma-separated list of items.
Output:
item_id|weight|category|pkt_desc |
-------+------+--------+-----------------------+
1| 500|Fruits |Guava, Papaya, Pear |
2| 500|Fruits |Guava, Watermelon, Pear|
This will return items from the 'Fruits' category where the item 'Guava' found in their pkt_desc column.
Using Multiple Values:
Sample table: fun_n_veg
Code:
-- The following SQL query selects all columns from the table 'fru_n_veg'
-- where the string 'Guava' is present in the 'pkt_desc' column or
-- the string 'Grapes' is present in the 'pkt_desc' column.
SELECT *
FROM fru_n_veg
WHERE FIND_IN_SET('Guava', pkt_desc)
OR FIND_IN_SET('Grapes', pkt_desc);
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves all rows and columns from the fru_n_veg table where the pkt_desc column contains either 'Guava' or 'Grapes' within its comma-separated list of items.
Output:
item_id|weight|category|pkt_desc |
-------+------+--------+-------------------------+
1| 500|Fruits |Guava, Papaya, Pear |
2| 500|Fruits |Guava, Watermelon, Pear |
4| 1000|Fruits |Grapes, pear, Watermelon |
This will return rows which contains either 'Guava' or 'Grapes' in their pkt_desc column.
Using Dynamic Values:
Sample table: fun_n_veg
Sample table: items
Code:
-- The following SQL query selects all columns from the 'fru_n_veg' table
-- where the 'pkt_desc' column contains an item name fetched from the 'items' table.
-- Specifically, it looks for the item name associated with 'item_code' 2.
SELECT *
FROM fru_n_veg
WHERE FIND_IN_SET((SELECT item_name FROM items WHERE item_code = 2), pkt_desc);
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves all rows and columns from the fru_n_veg table where the pkt_desc column contains the item name corresponding to item_code 2 in the items table.
- The subquery (SELECT item_name FROM items WHERE item_code = 2) fetches the item name which is then used by FIND_IN_SET to check its presence in the pkt_desc column of fru_n_veg.
Output:
item_id|weight|category |pkt_desc |
-------+------+----------+--------------------------+
5| 1500|Vegetables|Cabbage, Carrot, Broccoli |
8| 2500|Vegetables|Cabbage, Eggplant, Pumpkin|
This will return pkt_desc which contain the items specified by item_code 2 in their item_code column, with the item name fetched from the items table.
Updating Records Based on List Membership:
Sample table: fun_n_veg
Code:
-- The following SQL query updates the 'weight' column to 400
-- for rows in the 'fru_n_veg' table where the 'pkt_desc' column
-- contains the substring 'Dates'.
UPDATE fru_n_veg
SET weight = 400
WHERE FIND_IN_SET('Dates', pkt_desc);
Explanation:
- This SQL query updates the weight column to 400 for all rows in the fru_n_veg table where the pkt_desc column contains the item 'Dates'.
- It uses the FIND_IN_SET function to check if 'Dates' is present in the comma-separated list of items in the pkt_desc column.
The table have been updated. The data shows, in the item_id 6 row, the weight column have been updated by 400 for the pkt_desc 'Dates', which was 250.
item_id|weight|category |pkt_desc |
-------+------+----------+--------------------------+
1| 500|Fruits |Guava, Papaya, Pear |
2| 500|Fruits |Guava, Watermelon, Pear |
3| 1000|Vegetables|Potato, Onion, Ginger |
4| 1000|Fruits |Grapes, pear, Water melon |
5| 1500|Vegetables|Cabbage, Carrot, Broccoli |
6| 400|Dry Fruits|Dates, Almond, Dry fig |
7| 400|Dry Fruits|Walnuts, Almond, Cashew |
8| 2500|Vegetables|Cabbage, Eggplant, Pumpkin|
Difference between LOCATE() and FIND_IN_SET() Function
When using LOCATE() function for integers, suppose we need 1 to return from LOCATE() if integer 3 is in the set '1,2,3,4,5,..' the following MySQL commands can be written :
Code:
-- The following SQL query checks if the number 3 is present
-- in the comma-separated string '1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9' using the LOCATE() function.
-- If the number 3 is found, it returns 1. Otherwise, it returns 0.
SELECT IF(LOCATE(3,'1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9') > 0, 1, 0);
Explanation:
- This SQL query uses the LOCATE function to check if the number 3 is present in the string '1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9'.
- If the number 3 is found (i.e., LOCATE returns a position greater than 0), the IF function returns 1.
- Otherwise, it returns 0.
Output:
mysql> SELECT IF(LOCATE(3,'1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9')>0,1,0); +-----------------------------------------+ | IF(LOCATE(3,'1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9')>0,1,0) | +-----------------------------------------+ | 1 | +-----------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.06 sec)
The above command working rightly because the set contains the number 3.
LOCATE() Misinterpreting Integers:
Code:
-- This SQL query checks if the number 3 is present in the comma-separated string '11,12,13,14,15' using the LOCATE() function.
-- LOCATE() returns the position of the first occurrence of the substring '3'.
-- If the substring '3' is found in the string, LOCATE() will return a position greater than 0,
-- and the IF function will return 1. If not found, LOCATE() returns 0, and the IF function will return 0.
SELECT IF(LOCATE(3, '11,12,13,14,15') > 0, 1, 0);
Explanation:
- This SQL query uses the LOCATE function to search for the number 3 in the string '11,12,13,14,15'.
- Even though the number 3 is part of 13 in the string, LOCATE treats the input as a substring and thus returns a position greater than 0.
- The IF function then returns 1, indicating that the substring '3' is found, even though it is part of a larger number.
Output:
mysql> SELECT IF(LOCATE(3,'11,12,13,14,15')>0,1,0); +--------------------------------------+ | IF(LOCATE(3,'11,12,13,14,15')>0,1,0) | +--------------------------------------+ | 1 | +--------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.02 sec)
Here we see from above example that, the 3 not present as a number three(3) in the given set, though the LOCATE() returns 1, because LOCATE() treate the given set as a string but not a comma seperated value, and the 3 present in the number 13.
Using FIND_IN_SET() Correctly:
To avoid this type of situation you can use the FIND_IN_SET() function. Here is the example below -
Code:
-- This SQL query checks if the number 3 is present in the comma-separated string '11,12,13,4,5,6,7,8,9' using the FIND_IN_SET() function.
-- FIND_IN_SET() returns the position of the string '3' within the comma-separated list.
-- If '3' is found, FIND_IN_SET() will return a position greater than 0,
-- and the IF function will return 1. If '3' is not found, FIND_IN_SET() returns 0, and the IF function will return 0.
SELECT IF(FIND_IN_SET(3, '11,12,13,4,5,6,7,8,9') > 0, 1, 0);
Explanation:
- This SQL query uses the FIND_IN_SET function to search for the number 3 in the comma-separated string '11,12,13,4,5,6,7,8,9'.
- FIND_IN_SET looks for exact matches of '3' as a separate item in the list.
- Since '3' is present as a separate item, FIND_IN_SET returns its position (greater than 0), and the IF function returns 1 to indicate that '3' was found.
Output:
mysql> SELECT IF(FIND_IN_SET(3,'11,12,13,4,5,6,7,8,9')>0,1,0); +-------------------------------------------------+ | IF(FIND_IN_SET(3,'11,12,13,4,5,6,7,8,9')>0,1,0) | +-------------------------------------------------+ | 0 | +-------------------------------------------------+ 1 row in set (0.05 sec)
So, LOCATE() function is very much suitable for string but not as much suitable for integer.
Performance Considerations:
- Indexing: FIND_IN_SET() does not utilize indexes, which can lead to slower performance on large datasets. Consider alternative methods or restructuring data for optimization.
- Large Data Sets: For large data sets, using FIND_IN_SET() might cause performance issues. Use it judiciously and consider data restructuring if performance becomes a concern.
Common Pitfalls and Troubleshooting:
- Null Values: If any argument is NULL, the function returns NULL. It should be ensure that our inputs are not NULL.
- Empty Strings: An empty search string or list can lead to unexpected results. We should handle these cases appropriately in our code.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) - MySQL FIND_IN_SET() function
1. What is the MySQL FIND_IN_SET() function?
- The MySQL FIND_IN_SET() function is used to determine the position of a substring within a comma-separated list of substrings. It is useful for searching and filtering data that is stored in a comma-delimited format.
2. What does MySQL FIND_IN_SET() return?
- Position: The function returns the position of the substring within the list, where positions start at 1.
- 0: If the substring is not found in the list.
- NULL: If any argument provided to the function is NULL.
3. What happens if the search string is not found?
- The function returns 0.
4. Can MySQL FIND_IN_SET() handle multiple delimiters?
- No, it only works with comma-separated lists.
5. How does MySQL FIND_IN_SET() compare with LOCATE()?
- FIND_IN_SET() is better for comma-separated lists, while LOCATE() is more suitable for general substring searches.
Video Presentation: