NumPy: numpy.broadcast_to() function
numpy.broadcast_to() function
The numpy.broadcast_to() function is used to produce an object that mimics broadcasting.
This function is useful when we want to broadcast an array to a larger shape or for arithmetic operations on arrays with different shapes.
Syntax:
numpy.broadcast_to(array, shape, subok=False)
Parameters:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| array | The array to broadcast. | Required |
| shape | The shape of the desired array. | Required |
| subok | If True, then sub-classes will be passed-through, otherwise the returned array will be forced to be a base-class array (default). | Optional |
Return value:
If True, then sub-classes will be passed-through, otherwise the returned array will be forced to be a base-class array (default).
Raises: ValueError - If the array is not compatible with the new shape according to NumPy’s broadcasting rules.
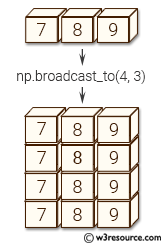
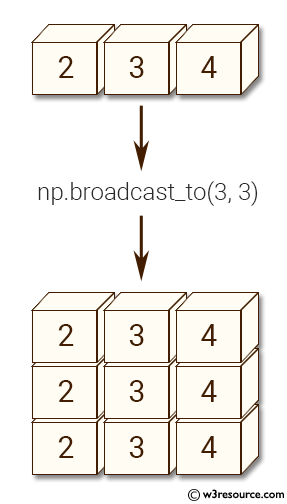
Example: Broadcasting an array to a larger shape using numpy.broadcast_to()
>>> import numpy as np
>>> a = np.array([2,3,4])
>>> np.broadcast_to(a, (3, 3))
array([[2, 3, 4],
[2, 3, 4],
[2, 3, 4]])
In the above code, an array 'a' is created with the values [2, 3, 4]. The numpy.broadcast_to() function is then used to create a new array with shape (3, 3) by repeating the values of 'a'. The resulting array has the values [[2, 3, 4], [2, 3, 4], [2, 3, 4]].
Pictorial Presentation:
Example: Broadcasting and Masked Arrays
>>> import numpy as np
>>> x = np.ma.array([2, 3, 4], mask=[False, True, False])
>>> y = np.broadcast_to(x, (3, 3), subok=True)
>>> y.mask
False
>>> y.mask = np.broadcast_to(x.mask, y.shape)
>>> y
masked_array(data =
[[2 -- 4]
[2 -- 4]
[2 -- 4]],
mask =
[[False True False]
[False True False]
[False True False]],
fill_value = 999999)
In the above code, first a masked array 'x' is created using the numpy.ma.array() function. The mask parameter specifies which elements of the array are masked (in this case, the second element is masked).
Then, numpy.broadcast_to() is used to create a new array y with the same shape as a 3x3 matrix. The subok parameter is set to True to allow the output to be a masked array.
Next, the mask of y is set to a broadcasted version of the mask of x, which ensures that the masked elements are propagated to the new array.
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
Previous: broadcast
Next: broadcast_arrays()
