NumPy: numpy.atleast_1d() function
numpy.atleast_1d() function
The numpy.atleast_1d() function is used to convert inputs to arrays with at least one dimension. Scalar inputs are converted to 1-dimensional arrays, whilst higher-dimensional inputs are preserved.
This function is useful when you want to ensure that the input to a function is at least one-dimensional, regardless of whether it is a scalar or an array. For example, some functions in NumPy only accept arrays as inputs, and will raise an error if given a scalar.
Syntax:
numpy.atleast_1d(*arys)
Parameter:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| arys1, arys2, . . | One or more input arrays. | Required |
Return value:
An array, or list of arrays, each with a.ndim >= 1. Copies are made only if necessary.
Example: Convert scalar to 1D array using numpy.atleast_1d()
>>> import numpy as np
>>> np.atleast_1d(2.0)
array([ 2.])
In the above code, the scalar value 2.0 is passed to the numpy.atleast_1d() function. The function returns a 1D array containing the input value, i.e., [2.].
Example: Using numpy.atleast_1d() to ensure 1-dimensional array
>>> import numpy as np
>>> a = np.arange(12.0).reshape(3,4)
>>> np.atleast_1d(a)
array([[ 0., 1., 2., 3.],
[ 4., 5., 6., 7.],
[ 8., 9., 10., 11.]])
The above code uses the numpy.arange() function to create a 1-dimensional array of 12 elements.
The numpy.reshape() function is then used to reshape the 1D array into a 3x4 2-dimensional array named 'a'. The np.atleast_1d() function is then used to ensure that the input array 'a' is at least a 1-dimensional array. Since 'a' is already a 2-dimensional array, np.atleast_1d() returns the same array 'a' as a 2-dimensional array.
The resulting array is a 2D array with 3 rows and 4 columns.
Example: Using numpy.atleast_1d() function to create 1-dimensional arrays
>>> import numpy as np
>>> a = np.arange(12.0).reshape(3,4)
>>> np.atleast_1d(a) is a
True
>>> np.atleast_1d(2,[4, 5])
[array([2]), array([4, 5])]
In the above code - the first example, an existing 2-dimensional array a is passed to the function. The function returns a new array with at least one dimension, in this case a 2-dimensional array. However, since the original array a already had at least one dimension, the returned array is the same as the original a. The expression np.atleast_1d(a) is a evaluates to True since the two arrays are the same object in memory.
In the second example, the function is called with two arguments, a scalar value 2 and a list [4, 5]. The function returns a list of arrays, each with at least one dimension. The scalar value 2 is converted to a 1-dimensional array [2], while the list [4, 5] is already a 1-dimensional array, so it is returned unchanged.
The returned list of arrays is [array([2]), array([4, 5])].
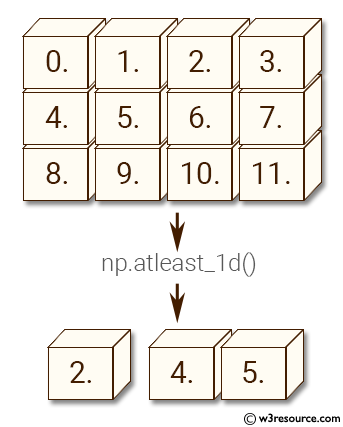
Pictorial Presentation:
Python - NumPy Code Editor:
Previous: transpose()
Next: arleast_2d()
