MongoDB connections
Description
In this tutorial, we will discuss how to connect to a MongoDB Server using different options.
Start MongoDB Server
In a previous tutorial, we have already discussed how to start a MongoDB Server, you have to execute 'mongod' from bin folder of your MongoDB installation folder.
After you execute this, it stops printing any output after printing some necessary information and waits for a connection. As soon a connection is created, it starts printing log information.
You can use MongoDB Shell to connect to a MongoDB Server. You can use any supported programming language like PHP to connect to also. But for now we will see how to create a connection using shell and discuss how to do that using PHP in an upcoming tutorial.
By default, MongoDB starts at port 27017. But you can access it in a web browser not at that port, rather, at a port number 1000 more than the port at which MongoDB is started. So if you point your browser to http://localhost:28017, you can see MongoDB web interface.
connection to MongoDB Server from shell
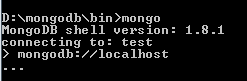
You have to execute the following command (in it's most simple form, without any other options used) to connect to a MongoDB Server. Remember that localhost is the hostname and this option is required.
mongodb://localhost
You see the output as shown below, as soon as you execute the command above.
If you check the command prompt window from where you started MongoDB Server, you can see as follows.
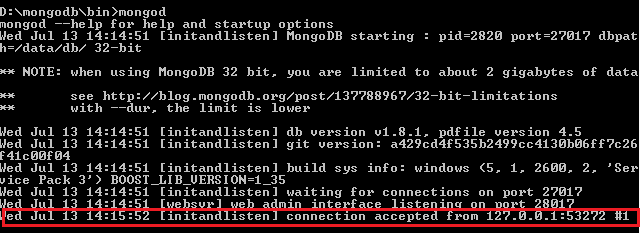
The last line(marked), is printed when you have successfully connected to a MongoDB Server.
Format of MongoDB connect command
Connect and login with username and password to default database
To connect to a MongoDB Server using username and password, you have to use 'username@hostname/dbname'. Where username is the username, password is the password for that user.
mongodb://mongo_admin:AxB6_w3r@localhost/
With the above command, 'mongo_admin' user with a password of 'AxB6_w3r' is connected to default database at localhost. Output of the above command is as follows :
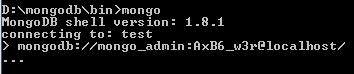
Connect and login with username and password to a particular database
To connect to a MongoDB Server using username and password, you have to use 'username@hostname/dbname'. Where username is the username, password is the password for that user and dbname is the database to which you want to connect to.
mongodb://mongo_admin:AxB6_w3r@localhost/w3r
With the above command, 'mongo_admin' user with a password of 'AxB6_w3r' is connected to 'w3r' database at localhost. Output of the above command is as follows :
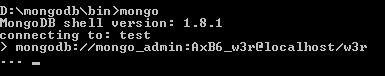
Note : You can use multiple hostname to connect to with a single command.
Connect and login with username and password to a particular database at a specific port
To connect to a MongoDB Server using username and password, you have to use 'username@hostname/dbname'. Where username is the username, password is the password for that user, dbname is the database to which you want to connect to and optionally you can specify a port number at which you want to connect to.
mongodb://mongo_admin:AxB6_w3r@localhost/w3r:29000
With the above command, 'mongo_admin' user with a password of 'AxB6_w3r' is connected to 'w3r' database at localhost at port 29000. If you don't mention the port number, it is connect at port 27107. Output of the above command is as follows :
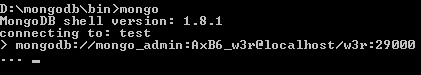
To Connect to multiple MongoDB servers running on different hostnames
To Connect to multiple MongoDB servers running on different hostnames, use the following commands. This kind of situation can arise when 'replica sets' are used. A replica set comprises of two or more nodes that are copies of each other. A Replica set can automatically detect one master node. This mechanism is good to ensure that when a server fails, recovery is possible.
mongodb://example_host1.com:27017,example_host2.com:27017
To Connect to multiple MongoDB servers running on same hostnames but on different ports
To Connect to multiple MongoDB servers running on same hostnames but on different ports, use the following command. This is also used for replica sets.
mongodb://example_host1.com:27110,example_host1.com:27111
Options
There are several options which can be used along with standards format discussed above. The following table describes those :
| Options | Descriptions |
|---|---|
| replicaSet=name | When working with any supported programming language, the driver (piece of code required to connect to work with MongoDB) ensures that the name of the replica set is matching. It attempts to find all the member nodes of the set. |
| slaveOk=true|false | For a replica set with multiple servers, if data is to be written, it is sent to the primary and if it is to be read, sent to all the slaves. |
| safe=true|false | If set to true, the driver sends a getLastError command after every update operation to make sure that the update is successfully accomplished. If set to false, no getLastError command is sent. |
| w=n | { w : n } is added to the getLastError command by driver. It implies safe=true. |
| wtimeoutMS=ms | { wtimeout : ms } is added to the getLastError command by driver. It implies safe=true. |
| fsync=true|false | If set to true, { wtimeout : ms } is added to the getLastError command by driver. It implies safe=true. If set to false, no getLastError command is sent. |
| journal=true|false | If set to true, sync to journal (which writes an entry before it is committed to the database). Implies safe=true |
| connectTimeoutMS=ms | A time limit, exceeding which a time out occurs while a connection is being opened. |
| socketTimeoutMS=ms | A time limit, exceeding which a time out occurs while a send or receive on a socket takes place. |
Previous:
Databases, Documents, Collections
Next:
MongoDB Query and Projection Operators
