SQLite Comparison operator
Introduction
A comparison (or relational) operator is a mathematical symbol which is used to compare two values.
Comparison operators are used in conditions that compares one expression with another. The result of any binary operator is either a numeric value ( 1 (true), 0(false) ) or NULL, except for the || concatenation operator which always evaluates to either NULL or a text value.
The following table describes different types of comparison operators -
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| = | Test for equality. |
| == | Test for equality. |
| > | Greater than. |
| < | Less than. |
| >= | Greater than equal to. |
| <= | Less than equal to. |
| <> | Test for inequality. |
| != | Test for inequality. |
The IS and IS NOT operators work like = and != except when one or both of the operands are NULL. In this case, if both operands are NULL, then the IS operator evaluates to 1 (true) and the IS NOT operator evaluates to 0 (false). If one operand is NULL and the other is not, then the IS operator evaluates to 0 (false) and the IS NOT operator is 1 (true). It is not possible for an IS or IS NOT expression to evaluate to NULL. Operators IS and IS NOT have the same precedence as =.
Syntax:
SELECT [column_name | * | expression] <comparison operator> [column_name | * | expression ] FROM <table_name> WHERE <expression> [ comparison operator] <expression>;
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| column_name | Name of the column of a table. |
| * | Indicates all the columns of a table. |
| expression | Expression made up of a single constant, variable, scalar function, or column name and can also be the pieces of an SQLite query that compare values against other values or perform arithmetic calculations. |
| table_name | Name of the table. |
| comparison operator | Equal to (=), not equal to(<>), greater than(>), less than(<), greater than or equal to (>=), less than or equal to (<=). |
Table of Contents:
- Equal to Operator
- Greater than Operator
- Less than Operator
- Greater than or equal to Operator
- Less than or equal to Operator
- Not equal to Operator
Example:
To get a comparison between two numbers the following SQLite statement can be used :
SELECT 115>112;
Here is the result.
Sample Output:
1
SQLite Equal to ( = ) operator
The equal to operator is used for equality test within two numbers or expressions.
Example:
Sample table: agents
To get data of all columns from the 'agents' table with the following condition -
1. 'commission' is equal to .15, the following SQLite statement can be used:
SELECT agent_code, agent_name, commission
FROM agents
WHERE commission = 0.15;
Relational Algebra Expression:
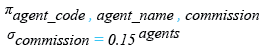
Relational Algebra Tree:
Here is the result.
Sample Output:
AGENT_CODE AGENT_NAME COMMISSION ---------- ---------- ---------- A007 Ramasundar 0.15 A011 Ravi Kumar 0.15 A006 McDen 0.15 A004 Ivan 0.15
SQLite Greater than ( > ) operator
The greater than operator is used to test whether an expression (or number) is greater than another one.
Example:
To get data of all columns from the 'agents' table with the following condition -
1. 'commission' is greater than .14, the following SQLite statement can be used:
SELECT agent_code, agent_name, commission
FROM agents
WHERE commission > 0.14;
Relational Algebra Expression:
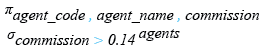
Relational Algebra Tree:
Here is the result.
Sample Output:
AGENT_CODE AGENT_NAME COMMISSION ---------- ---------- ---------- A007 Ramasundar 0.15 A011 Ravi Kumar 0.15 A006 McDen 0.15 A004 Ivan 0.15
SQLite Less than ( < ) operator
The less than operator is used to test whether an expression (or number) is less than another one.
Example
To get data of all columns from the 'agents' table with the following condition -
1. 'commission' is less than .15, the following SQLite statement can be used:
SELECT agent_code,agent_name,commission
FROM agents
WHERE commission < 0.15;
Relational Algebra Expression:
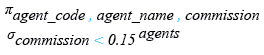
Relational Algebra Tree:
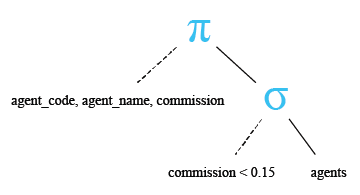
Here is the result.
Sample Output:
AGENT_CODE AGENT_NAME COMMISSION ---------- ---------------------------------------- ---------- A003 Alex 0.13 A008 Alford 0.12 A010 Santakumar 0.14 A012 Lucida 0.12 A005 Anderson 0.13 A001 Subbarao 0.14 A002 Mukesh 0.11 A009 Benjamin 0.11
SQLite Greater than or equal to ( >= ) operator
The greater than equal to operator is used to test whether an expression (or number) is either greater than or equal to another one.
Example:
To get data of all columns from the 'agents' table with the following condition -
1. 'commission' is greater than or equal to .14, the following SQLite statement can be used:
SELECT agent_code, agent_name, commission
FROM agents
WHERE commission >= 0.14;
Relational Algebra Expression:
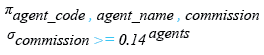
Relational Algebra Tree:
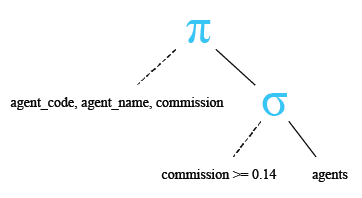
Here is the result.
Sample Output:
AGENT_CODE AGENT_NAME COMMISSION ---------- ---------- ---------- A007 Ramasundar 0.15 A011 Ravi Kumar 0.15 A010 Santakumar 0.14 A001 Subbarao 0.14 A006 McDen 0.15 A004 Ivan 0.15
SQLite Less than or equal to ( <= ) operator
The less than equal to operator is used to test whether an expression (or number) is either less than or equal to another one.
Example:
To get data of all columns from the 'agents' table with the following condition -
1. commission is less than or equal to .13,the following SQLite statement can be used:
SELECT agent_code, agent_name, commission
FROM agents
WHERE commission <= 0.13;
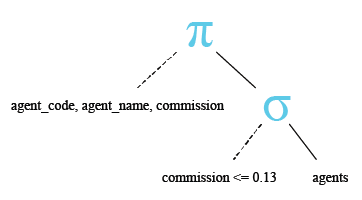
Relational Algebra Expression:
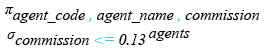
Relational Algebra Tree:
Here is the result.
Sample Output:
AGENT_CODE AGENT_NAME COMMISSION ---------- ---------------------------------------- ---------- A003 Alex 0.13 A008 Alford 0.12 A012 Lucida 0.12 A005 Anderson 0.13 A002 Mukesh 0.11 A009 Benjamin 0.11
SQLite Not equal to ( <> ) operator
The not equal to operator is used for inequality test between two numbers or expression.
Example:
To get data of all columns from the 'agents' table with the following condition -
1. commission is not equal to .15,
the following SQLite statement can be used:
SELECT agent_code, agent_name, commission
FROM agents
WHERE commission <> 0.15;
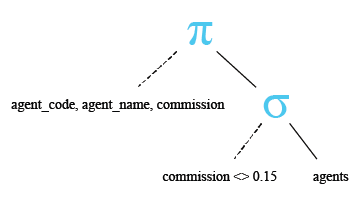
Relational Algebra Expression:
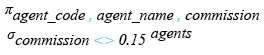
Relational Algebra Tree:
Here is the result.
Sample Output:
AGENT_CODE AGENT_NAME COMMISSION ---------- ---------------------------------------- ---------- A003 Alex 0.13 A008 Alford 0.12 A010 Santakumar 0.14 A012 Lucida 0.12 A005 Anderson 0.13 A001 Subbarao 0.14 A002 Mukesh 0.11 A009 Benjamin 0.11
Previous:
Arithmetic Operators
Next:
Boolean Operators
