SQLite Boolean operator
Introduction
The Boolean operators are those that are true or false. They return a true or false values to combine one or more true or false values.
In SQLite Boolean operators are:
| Operator | Description |
|---|---|
| AND | Logical AND compares between two Booleans as expression and return true when both expressions are true |
| OR | Logical OR compares between two Booleans as expression and returns true when one of the expression is true |
Syntax:
SELECT [column_name | * | expression] [boolean operator] [column_name | * | expression .....] FROM <table_name> WHERE <expressions> [ boolean operator | arithmetic operator | ...] <expressions>;
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| column_name | Name of the column of a table. |
| * | All the columns of a table. |
| expression | Expression made up of a single constant, variable, scalar function, or column name and can also be the pieces of a SQLite query that compare values against other values or perform arithmetic calculations. |
| table_name | Name of the table. |
| boolean operator | AND, OR , NOT. |
| arithmetic operator | Plus(+), minus(-), multiply(*) and divide(/). |
SQLite Boolean AND operator
Logical AND compares two Booleans as expression and returns TRUE when both of the conditions are TRUE and returns FALSE when either is FALSE; otherwise, returns UNKNOWN (an operator that has one or two NULL expressions returns UNKNOWN).
Example:
Sample table: customer
To get data of 'cust_code', 'cust_name', 'cust_city' and 'grade' from the 'customer' table with following conditions -
1. 'cust_country' must be ’UK’,
2. and 'grade' of the 'customer' must be 2,
the following SQLite statement can be used:
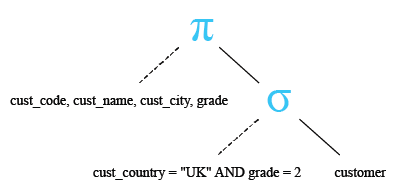
SELECT cust_code, cust_name, cust_city,grade
FROM customer
WHERE cust_country = 'UK' AND grade = 2;
Relational Algebra Expression:
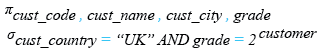
Relational Algebra Tree:
Here is the result.
Sample Output:
CUST_CODE CUST_NAME CUST_CITY GRADE ---------- ---------- ----------------------------------- ---------- C00013 Holmes London 2 C00024 Cook London 2
SQLite Boolean OR operator
Logical OR compares two Booleans as expression and returns TRUE when either of the conditions is TRUE and returns FALSE when both are FALSE. otherwise, returns UNKNOWN (an operator that has one or two NULL expressions returns UNKNOWN).
Example:
To get data of 'cust_code', 'cust_name', 'cust_city'' and 'grade' from the 'customer' with following conditions -
1. either 'cust_country' is ’UK’,
2. or 'grade' of the 'customer' is 3,
the following SQLite statement can be used:
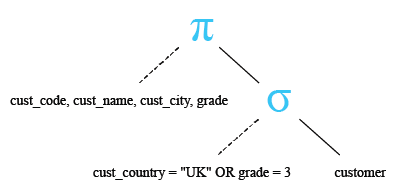
SELECT cust_code, cust_name, cust_city,grade
FROM customer
WHERE cust_country = 'UK' OR grade = 3;
Relational Algebra Expression:
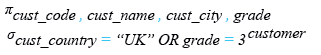
Relational Algebra Tree:
Here is the result.
Sample Output:
CUST_CODE CUST_NAME CUST_CITY GRADE ---------- ---------- ----------------------------------- ---------- C00013 Holmes London 2 C00020 Albert New York 3 C00024 Cook London 2 C00015 Stuart London 1 C00002 Bolt New York 3 C00023 Karl London 1 C00010 Charles Hampshair 3 C00009 Ramesh Mumbai 3 C00011 Sundariya Chennai 3
SQLite boolean AND, OR comparison operator
In the following topic, we are discussing the usage of 'AND' and 'OR' operator.
Using AND OR comparison operator with the select statement an example have shown.
Example:
To get data of 'cust_code', 'cust_name', 'cust_city' and 'grade' from the 'customer' table with following conditions -
1. 'cust_country' is ’UK’ or cust_city is 'London' ,
2. and 'grade' of the 'customer' must be other than 3,
the following SQLite statement can be used:
SELECT cust_code, cust_name, cust_city, cust_country, grade
FROM customer
WHERE (cust_country = 'UK' OR cust_city = 'London')
AND grade <> 3;
Relational Algebra Expression:
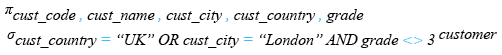
Relational Algebra Tree:
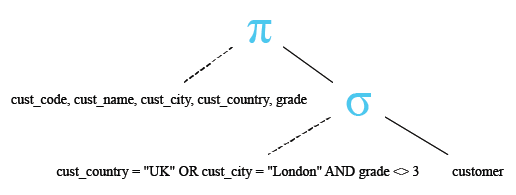
Here is the result.
Sample Output:
CUST_CODE CUST_NAME CUST_CITY CUST_COUNTRY GRADE ---------- ---------- ----------------------------------- ------------ ---------- C00013 Holmes London UK 2 C00024 Cook London UK 2 C00015 Stuart London UK 1 C00023 Karl London UK 1
Previous:
Comparison Operators
Next:
LIKE and GLOB Operators
