SQL DISTINCT
Select with distinct
Redundancy is the repetition of certain data in a table. With the use of DISTINCT clause data redundancy may be avoided. This clause will eliminate the repetitive appearance of same data. DISTINCT can come only once in a given select statement.
Syntax:
SELECT DISTINCT <column_name> FROM <table_name> WHERE <conditions>;
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| column_name | Name of the column. |
| table_name | Name of the table. |
| conditions | It may be a condition, a select query or an expression. |
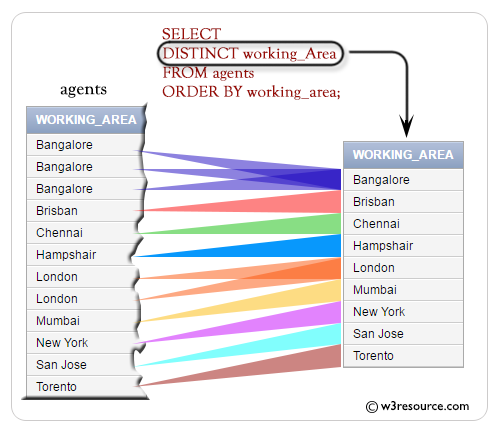
Visual presentation :
Some important questions related to the SQL DISTINCT keyword
What is the purpose of the DISTINCT keyword in SQL?
Does using the DISTINCT keyword affect the order of the result set?
Can you use the DISTINCT keyword with multiple columns?
Can you use the DISTINCT keyword with aggregate functions?
How does the DISTINCT keyword differ from the GROUP BY clause?
Can you use the DISTINCT keyword with subqueries?
What happens if you use the DISTINCT keyword with a column that contains NULL values?
What is the performance impact of using the DISTINCT keyword?
When should you use the DISTINCT keyword?
Are there any alternatives to using the DISTINCT keyword?
Example-1: SQL DISTINCT
Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
..........
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
You can use the following SQL statement to retrieve all 'agent_code' values from the 'orders' table.
SQL Code:
SELECT agent_code FROM orders;
-- Select the 'agent_code' column from the 'orders' table
Explanation:
- SELECT agent_code: This line specifies the column that you want to retrieve data from. It selects the 'agent_code' column from the 'orders' table.
- FROM orders: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'orders' table.
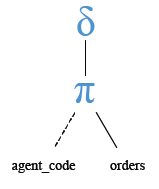
Relational Algebra Expression:
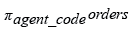
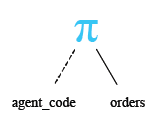
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
AGENT_CODE ---------- A008 A004 A006 A010 A004 A011 A005 A013 A004 A005 A011 ... ...
The above picture shows the same 'agent_code' appears more than once.
Example-2: SQL DISTINCT
To retrieve each unique 'agent_code' from the 'orders' table, you can use the following SQL statement.:
SQL Code:
SELECT DISTINCT agent_code
-- Select distinct values of the 'agent_code' column
FROM orders;
-- From the table 'orders'
Explanation:
- SELECT DISTINCT agent_code: This line specifies that you want to retrieve unique/distinct values from the 'agent_code' column. The DISTINCT keyword ensures that only unique values are returned; any duplicate values will be eliminated.
- FROM orders: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'orders' table.
Relational Algebra Expression:
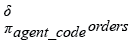
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
AGENT_CODE ---------- A004 A002 A007 A009 A011 A012 A010 A013 A001 A008 A006 A005 A003
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.
PREV : SQL SELECT statement
NEXT : SQL SELECT with DISTINCT on multiple columns