SQL JOINS
What is SQL Joins?
An SQL JOIN clause combines rows from two or more tables. It creates a set of rows in a temporary table.
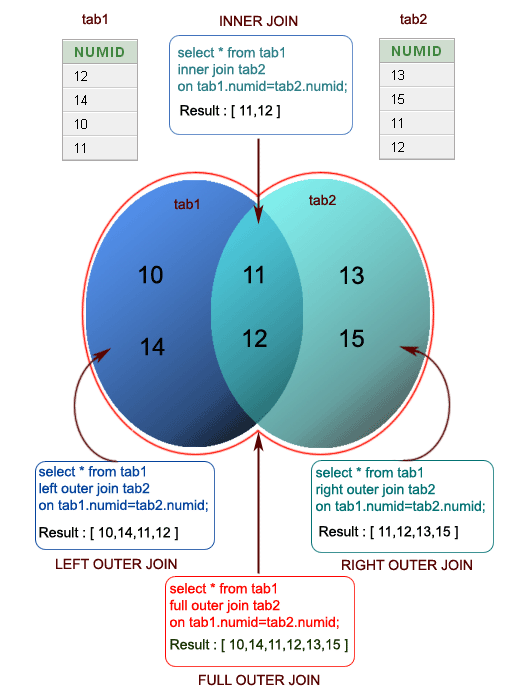
Visual Presentation of SQL Joins:
How to Join two tables in SQL?
A JOIN works on two or more tables if they have at least one common field and have a relationship between them.
JOIN keeps the base tables (structure and data) unchanged.
Join vs. Subquery
- JOINs are faster than a subquery and it is very rare that the opposite.
- In JOINs the RDBMS calculates an execution plan, that can predict, what data should be loaded and how much it will take to processed and as a result this process save some times, unlike the subquery there is no pre-process calculation and run all the queries and load all their data to do the processing.
- A JOIN is checked conditions first and then put it into table and displays; where as a subquery take separate temp table internally and checking condition.
- When joins are using, there should be connection between two or more than two tables and each table has a relation with other while subquery means query inside another query, has no need to relation, it works on columns and conditions.
SQL JOINS: EQUI JOIN and NON EQUI JOIN
The are two types of SQL JOINS - EQUI JOIN and NON EQUI JOIN
1) SQL EQUI JOIN :
The SQL EQUI JOIN is a simple SQL join uses the equal sign(=) as the comparison operator for the condition. It has two types - SQL Outer join and SQL Inner join.
2) SQL NON EQUI JOIN :
The SQL NON EQUI JOIN is a join uses comparison operator other than the equal sign like >, <, >=, <= with the condition.
SQL EQUI JOIN : INNER JOIN and OUTER JOIN
The SQL EQUI JOIN can be classified into two types - INNER JOIN and OUTER JOIN
1. SQL INNER JOIN
This type of EQUI JOIN returns all rows from tables where the key record of one table is equal to the key records of another table.
2. SQL OUTER JOIN
This type of EQUI JOIN returns all rows from one table and only those rows from the secondary table where the joined condition is satisfying i.e. the columns are equal in both tables.
In order to perform a JOIN query, the required information we need are:
a) The name of the tables
b) Name of the columns of two or more tables, based on which a condition will perform.
Syntax:
FROM table1 join_type table2 [ON (join_condition)]
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| table1, table2 | Tables participating in joining. |
| join_type | Type of the join. |
| join_condition | Some condition. This is optional. |
Example:
Sample table: company+------------+---------------+--------------+ | COMPANY_ID | COMPANY_NAME | COMPANY_CITY | +------------+---------------+--------------+ | 18 | Order All | Boston | | 15 | Jack Hill Ltd | London | | 16 | Akas Foods | Delhi | | 17 | Foodies. | London | | 19 | sip-n-Bite. | New York | +------------+---------------+--------------+Sample table: foods
+---------+--------------+-----------+------------+ | ITEM_ID | ITEM_NAME | ITEM_UNIT | COMPANY_ID | +---------+--------------+-----------+------------+ | 1 | Chex Mix | Pcs | 16 | | 6 | Cheez-It | Pcs | 15 | | 2 | BN Biscuit | Pcs | 15 | | 3 | Mighty Munch | Pcs | 17 | | 4 | Pot Rice | Pcs | 15 | | 5 | Jaffa Cakes | Pcs | 18 | | 7 | Salt n Shake | Pcs | | +---------+--------------+-----------+------------+
To join two tables 'company' and 'foods', the following SQL statement can be used :
SQL Code:
SELECT company.company_id,company.company_name, -- This line specifies the columns to be selected from the 'company' table, namely 'company_id' and 'company_name'.
foods.item_id,foods.item_name -- This line specifies the columns to be selected from the 'foods' table, namely 'item_id' and 'item_name'.
FROM company,foods; -- This line specifies the tables involved in the query, 'company' and 'foods', and indicates that a Cartesian product (or cross join) will be performed.
Explanation:
- This SQL code performs a Cartesian product (or cross join) between the 'company' and 'foods' tables, meaning it combines every row from the 'company' table with every row from the 'foods' table.
- The SELECT statement then retrieves specific columns from the resulting Cartesian product.
- The 'company.company_id' and 'company.company_name' columns are selected from the 'company' table.
- The 'foods.item_id' and 'foods.item_name' columns are selected from the 'foods' table.
- However, it's important to note that Cartesian products can lead to large result sets and are usually not desired. Typically, JOIN clauses with appropriate join conditions should be used instead to retrieve related data from multiple tables.
Output:
COMPAN COMPANY_NAME ITEM_ID ITEM_NAME ------ ------------------------- -------- --------------- 18 Order All 1 Chex Mix 18 Order All 6 Cheez-It 18 Order All 2 BN Biscuit 18 Order All 3 Mighty Munch 18 Order All 4 Pot Rice 18 Order All 5 Jaffa Cakes 18 Order All 7 Salt n Shake 15 Jack Hill Ltd 1 Chex Mix 15 Jack Hill Ltd 6 Cheez-It 15 Jack Hill Ltd 2 BN Biscuit 15 Jack Hill Ltd 3 Mighty Munch 15 Jack Hill Ltd 4 Pot Rice 15 Jack Hill Ltd 5 Jaffa Cakes 15 Jack Hill Ltd 7 Salt n Shake 16 Akas Foods 1 Chex Mix 16 Akas Foods 6 Cheez-It 16 Akas Foods 2 BN Biscuit 16 Akas Foods 3 Mighty Munch 16 Akas Foods 4 Pot Rice 16 Akas Foods 5 Jaffa Cakes 16 Akas Foods 7 Salt n Shake ......... ......... .........
JOINS: Relational Databases
Key points to remember:
Click on the following to get the slides presentation -
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.
Previous: SQL Delete with subqueries
Next: SQL EQUI JOIN