SQL LOWER() function
LOWER() function
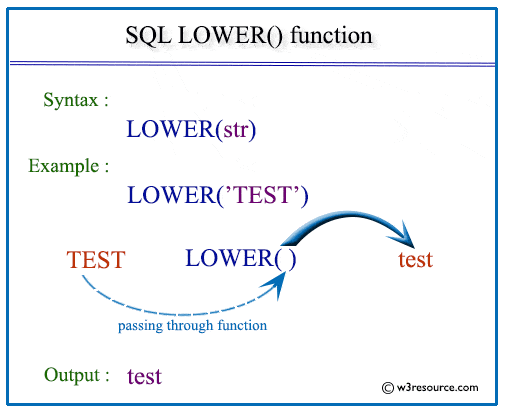
The SQL LOWER() function is used to convert all characters of a string to lower case.
Syntax:
LOWER(string)
PostgreSQL, MySQL, SQL Server and Oracle
All of above platforms support the SQL syntax of LOWER().
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| string | A string. |
Visual Presentation:
Application of LOWER()
In the subsequent pages, we have discussed how to apply LOWER() with various SQL clauses. we have used Oracle 10g Express Edition.
Example:
If we want to get the string 'TESTING FOR LOWER FUNCTION' in lower case from the DUAL table, the following SQL statement can be used :
-- This SQL query converts a given string to lowercase using the LOWER function and returns the result with an alias.
-- SELECT statement begins
SELECT
LOWER('TESTING FOR LOWER FUNCTION') -- Convert the given string 'TESTING FOR LOWER FUNCTION' to lowercase
AS Testing_Lower -- Alias the result of the lowercase conversion as 'Testing_Lower'
FROM
dual; -- Dual is a dummy table in Oracle, used here as a placeholder since we're not actually querying any table
Explanation:
- This SQL code is a SELECT statement that demonstrates the use of the LOWER function to convert a string to lowercase.
- The string 'TESTING FOR LOWER FUNCTION' is passed as an argument to the LOWER function.
- The result of the conversion is then given an alias 'Testing_Lower'.
- The query is executed against the dummy table 'dual', which is commonly used in Oracle databases when you want to perform a calculation or evaluate an expression without actually querying a specific table.
Output:
TESTING_LOWER -------------------------- testing for lower function
Here is a new document which is a collection of questions with short and simple answers, useful for learning SQL as well as for interviews.
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.
PREV : Character Function
NEXT : UPPER