PostgreSQL Mathematical Operators
Mathematical Operators
PostgreSQL provided many Mathematical operators for common mathematical conventions. The bitwise operators can be used only with the integer data types.
List of Mathematical Operators
| Operators | Description | Example | Output |
|---|---|---|---|
| + | Addition | 5 + 8 | 13 |
| - | Subtraction | 6 - 9 | -3 |
| * | Multiplication | 5 * 8 | 40 |
| / | Division | 15 / 3 | 5 |
| % | Modulo ( Remainder ) | 15 % 2 | 1 |
| ^ | Exponentiation | 4.0 ^ 2.0 | 16 |
| | / | Square Root | | / 16 | 4 |
| | | / | Cube Root | | | / 27 | 3 |
| ! | Factorial | ! 6 | 720 |
| ! ! | Factorial ( with prefix operator) | ! ! 6 | 720 |
| @ | Absolute Value | @ -15.07 | 15.07 |
| & | Bitwise AND | 53 & 38 | 36 |
| | | Bitwise OR | 53 | 38 | 55 |
| # | Bitwise XOR | 53 # 38 | 19 |
| ~ | Bitwise NOT | ~ 38 | -39 |
| << | Bitwise shift left | 25 << 2 | 100 |
| >> | Bitwise shift right | 120 >> 3 | 15 |
PostgreSQL Plus ( + ) operator example
If we want to add two numbers, the following SQL can be used.
SQL
Code:
SELECT 5+8 AS "Addition";
Output
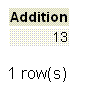
PostgreSQL Minus ( - ) operator example
If we want to subtract two numbers, the following SQL can be used.
SQL
Code:
SELECT 6-9 AS "Subtraction";
Output:

PostgreSQL Multiplication ( * ) operator example
If we want to multiply two numbers, the following SQL can be used.
SQL
Code:
SELECT 5 * 8 AS "Multiplication";
Output:

PostgreSQL Division ( / ) operator example
If we want to division two numbers, the following SQL can be used.
SQL
Code:
SELECT 15 / 3 AS "Division";
Output:

PostgreSQL Modulo ( % ) operator example
If we want to get the remainder of a division by two numbers, the following SQL can be used.
SQL
Code:
SELECT 15 % 2 AS "Remainder";
Output:

PostgreSQL Exponentiation ( ^ ) operator example
If we want to get the exponentiation of a number powered by another number, the following SQL can be used.
SQL
Code:
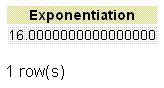
SELECT 4.0 ^ 2.0 AS "Exponentiation";
Output:
PostgreSQL Square Root ( |/ ) operator example
If we want to get the square root of a number, the following SQL can be used.
SQL
Code:
SELECT |/16 AS "Square Root";
Output:

PostgreSQL Cube Root ( | | / ) operator example
If we want to get the cube root of a number, the following SQL can be used.
SQL
Code:
SELECT ||/27 AS "Cube Root";
Output:
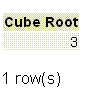
PostgreSQL Factorial (!) operator example
If we want to get the factorial of a number, the following SQL can be used.
SQL
Code:
SELECT 6! AS "Factorial";
Output:

PostgreSQL Factorial(with prefix) (! !) operator example
If we want to get the factorial of a number with factorial prefix operator, the following SQL can be used.
SQL
Code:
SELECT !!6 AS "Factorial ( with prefix )";
Output

PostgreSQL Absolute Value ( @ ) operator example
If we want to get the absolute value of a number, the following SQL can be used.
SQL
Code:
SELECT @ -15.07 AS "Absolute Value";
Output:
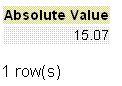
PostgreSQL Bitwise AND ( & ) operator example
The PostgreSQL Bitwise AND ( & ) operator compares corresponding bits for each operand and produces a 1 when both bits are 1 otherwise it returns 0.
SQL
Code:
SELECT 53 & 38 AS "Bitwise AND";
Output:
Pictorial representation of PostgreSQL Bitwise AND ( & ) operator
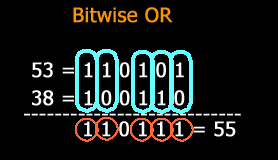
PostgreSQL Bitwise OR ( | ) operator example
The PostgreSQL Bitwise OR ( | ) operator compares corresponding bits for each operand and produces a 1 when either or both bits are 1 otherwise it returns 0.
SQL
Code:
SELECT 53 | 38 AS "Bitwise OR";
Output:

Pictorial representation of PostgreSQL Bitwise OR ( | ) operator
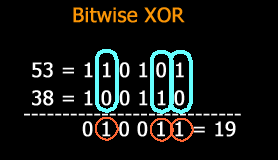
PostgreSQL Bitwise XOR ( # ) operator example
The PostgreSQL Bitwise XOR ( # ) operator is similar to OR operator. It compares corresponding bits for each operand and produces a 1 when either but not both bits is 1 otherwise it returns 0.
SQL
Code:
SELECT 53 # 38 AS "Bitwise XOR";
Output:

Pictorial representation of PostgreSQL Bitwise XOR ( # ) operator
PostgreSQL Bitwise NOT ( ~ ) operator example
The PostgreSQL Bitwise NOT ( ~ ) operator is a unary operator. It produces a toggled result, that is all 0's converted to 1 and all 1's are converted to 0.
SQL
Code:
SELECT ~38 AS "Bitwise NOT";
Output:

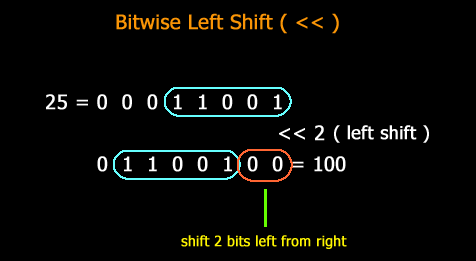
PostgreSQL Bitwise Left Shift ( << ) operator example
The left shift(<<) operator shifts the bits in the first operand to the left by n bits, where n is the second operand. The left shift by n bits is similar to multiply the first operand by 2 to the power n.
SQL
Code:
SELECT 25 << 2 AS "Bitwise Left Shift";
Output:

Pictorial representation of PostgreSQL Bitwise left shift ( << ) operator
PostgreSQL Bitwise Right Shift (>>) operator example
The right shift (>>)operator shifts the bits in the first operand to the right by n bits, where n is the second operand. A right shift by n bits is similar to dividing the first operand by 2 to the power n.
SQL
Code:
SELECT 120 >> 3 AS "Bitwise Right Shift";
Output:

Pictorial representation of PostgreSQL Bitwise right shift ( >> ) operator

Previous: Comparison Operators
Next: Binary String Functions and Operators
