PostgreSQL COUNT function
COUNT function
The PostgreSQL COUNT function counts a number of rows or non-NULL values against a specific column from a table. When an asterisk(*) is used with count function the total number of rows returns.
Syntax:
COUNT (* | [DISTINCT] ALL | column_name)
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| column_name | Name of the column |
| * | The asterisk(*) indicates all the rows. |
| DISTINCT | This clause is optional. It indicates uniqueness. |
| ALL | This clause is optional. It is default clause. |
Contents:
PostgreSQL COUNT function Example
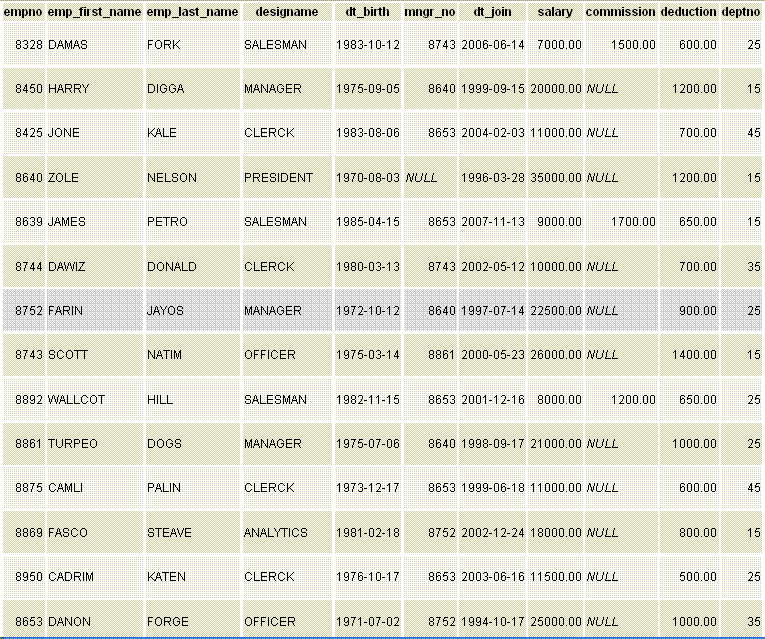
The sample table
If we want to get the number or rows in the employee table, the following SQL can be used.
SQL Code:
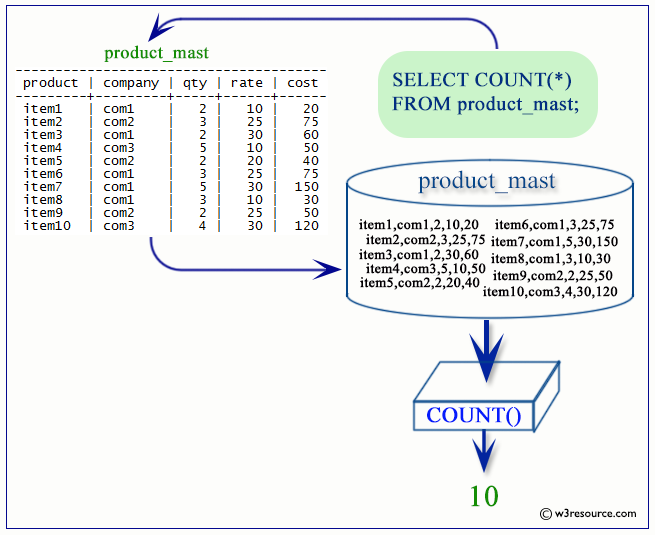
SELECT COUNT(*)
FROM employee;
Output:
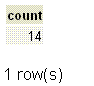
Visual Presentation of PostgreSQL COUNT()
PostgreSQL COUNT on specific column
If we want to get the number of employees who earns commission in the employee table, the following SQL can be used.
SQL Code:
SELECT COUNT(commission)
FROM employee;
Output:
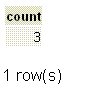
Explanation:
The above example shows that only 3 employees earn commission because the COUNT function ignored the NULL values.
PostgreSQL COUNT DISTINCT
If we want to get the number of designation available in the employee table, the following SQL can be used.
SQL Code:
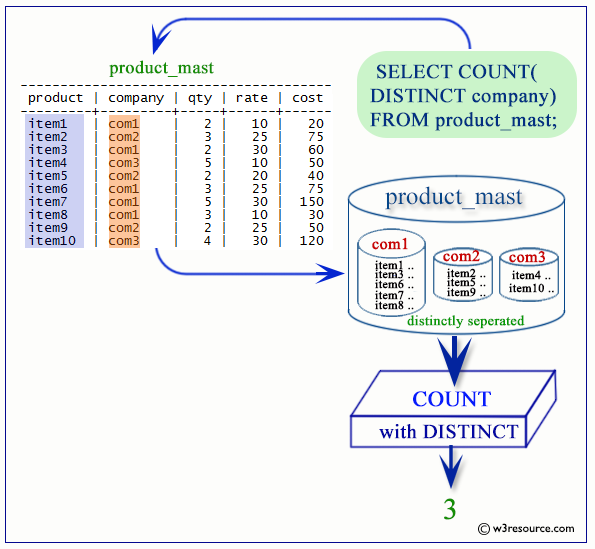
SELECT COUNT ( DISTINCT designame)
FROM employee;
Output:
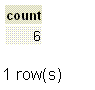
Explanation:
The above example shows that, only 6 rows have returns from the employee table because the DISTINCT clause have used. The DISTINCT clause eliminates the repetition of each designame and returns only once.
Visual Presentation of PostgreSQL COUNT DISTINCT
PostgreSQL COUNT with GROUP BY
Sample table: employees
If we want to get the number of employees working for each designation available in employees table, the following SQL can be used.
SQL Code:
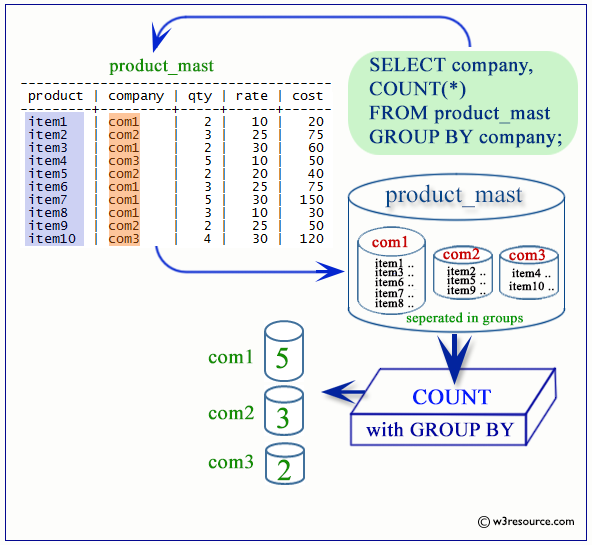
SELECT job_id,COUNT(*) AS "Number of employees"
FROM employees
GROUP BY job_id;
Output:
job_id | Number of employees ------------+--------------------- AC_ACCOUNT | 1 ST_MAN | 5 IT_PROG | 5 SA_MAN | 5 AD_PRES | 1 AC_MGR | 1 FI_MGR | 1 AD_ASST | 1 MK_MAN | 1 PU_CLERK | 5 HR_REP | 1 PR_REP | 1 FI_ACCOUNT | 5 SH_CLERK | 20 AD_VP | 2 SA_REP | 30 ST_CLERK | 20 MK_REP | 1 PU_MAN | 1 (19 rows)
Visual Presentation of PostgreSQL COUNT with GROUP BY
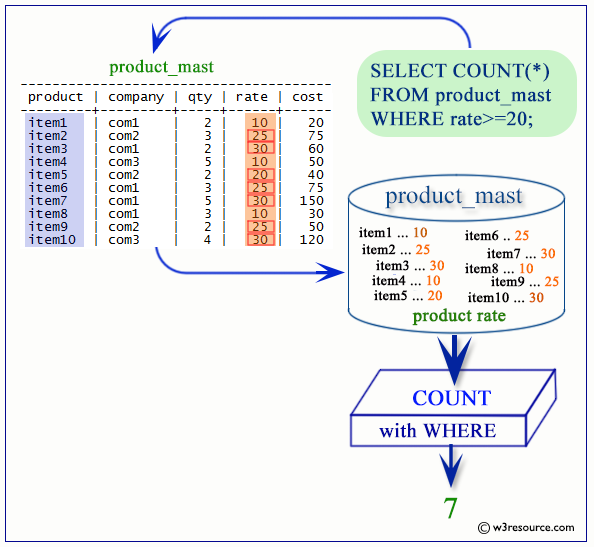
PostgreSQL COUNT with WHERE CLAUSE
Sample table: employees
If we want to get the number of employees working for each designation available in employees table who draws the monthly salary below 12000, the following SQL can be used.
SQL Code:
SELECT job_id,COUNT(*) AS "Number of employees"
FROM employees
WHERE salary<12000
GROUP BY job_id;
Output:
job_id | Number of employees ------------+--------------------- AC_ACCOUNT | 1 ST_MAN | 5 IT_PROG | 5 SA_MAN | 2 AD_ASST | 1 PU_CLERK | 5 HR_REP | 1 PR_REP | 1 FI_ACCOUNT | 5 SH_CLERK | 20 SA_REP | 30 ST_CLERK | 20 MK_REP | 1 PU_MAN | 1 (14 rows)
Visual Presentation of PostgreSQL COUNT with WHERE
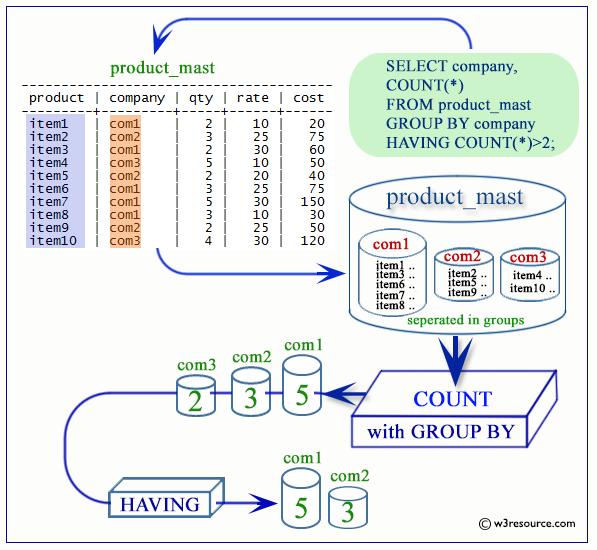
PostgreSQL COUNT with HAVING clause
Sample table: employees
If we want to get those designations, where at least 5 employees working and draw a monthly salary below 12000, the following SQL can be used.
SQL Code:
SELECT job_id,COUNT(*) AS "Number of employees"
FROM employees
WHERE salary<12000
GROUP BY job_id
HAVING COUNT(*)>=5;
Output:
job_id | Number of employees ------------+--------------------- ST_MAN | 5 IT_PROG | 5 PU_CLERK | 5 FI_ACCOUNT | 5 SH_CLERK | 20 SA_REP | 30 ST_CLERK | 20 (7 rows)
Visual Presentation of PostgreSQL COUNT with HAVING
PostgreSQL COUNT with GROUP BY and ORDER BY
Sample table: employees
The following query will return the designation where at least 5 employees are working with a maximum salary below 12000 and the number of employees for each designation in descending order.
SQL Code:
SELECT job_id,COUNT(*) AS "Number of employees"
FROM employees
WHERE salary<12000
GROUP BY job_id
HAVING COUNT(*)>=5
ORDER BY COUNT(*) DESC;
Output:
job_id | Number of employees ------------+--------------------- SA_REP | 30 SH_CLERK | 20 ST_CLERK | 20 ST_MAN | 5 FI_ACCOUNT | 5 IT_PROG | 5 PU_CLERK | 5 (7 rows)
Previous: AGGREGATE FUNCTIONS
Next: SUM