PostgreSQL AVG function
AVG function
The AVG function determines the average of all selected values of a column.
Syntax:
AVG (* | [DISTINCT] ALL | column_name)
Parameters
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| column_name | Name of the column |
| * | The asterisk(*) indicates all the rows. |
| DISTINCT | This clause is optional. It indicates uniqueness. |
| ALL | This clause is optional. It is default clause. |
Contents:
- PostgreSQL AVG function example
- PostgreSQL AVG as a level
- PostgreSQL AVG function two columns
- PostgreSQL AVG with MAX, MIN, COUNT and SUM
- PostgreSQL AVG WHERE clause
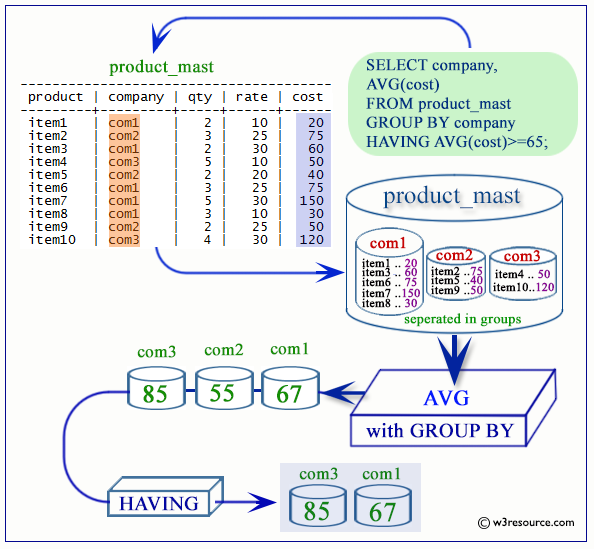
- PostgreSQL AVG with GROUP BY
- PostgreSQL AVG with WHERE CLAUSE and GROUP BY
- PostgreSQL AVG with HAVING and GROUP BY
- PostgreSQL AVG with GROUP BY and ORDER BY
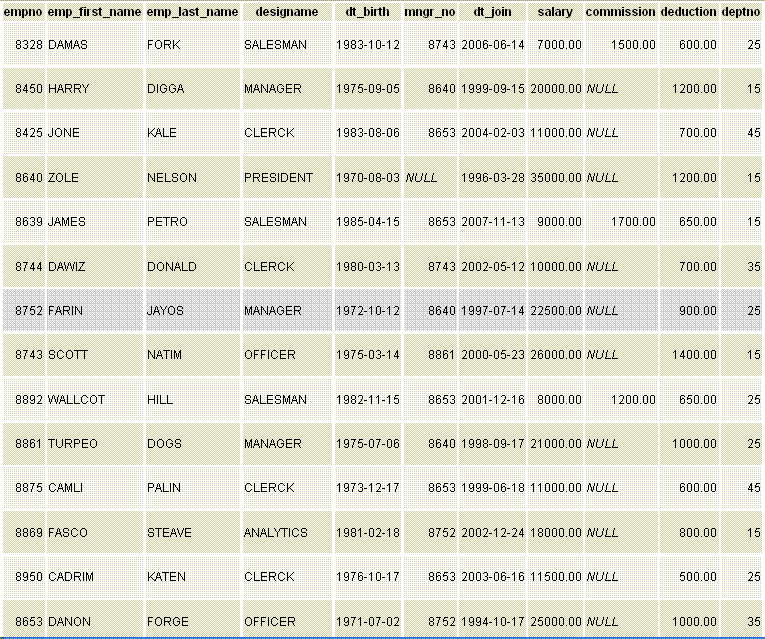
PostgreSQL AVG function example
The sample table
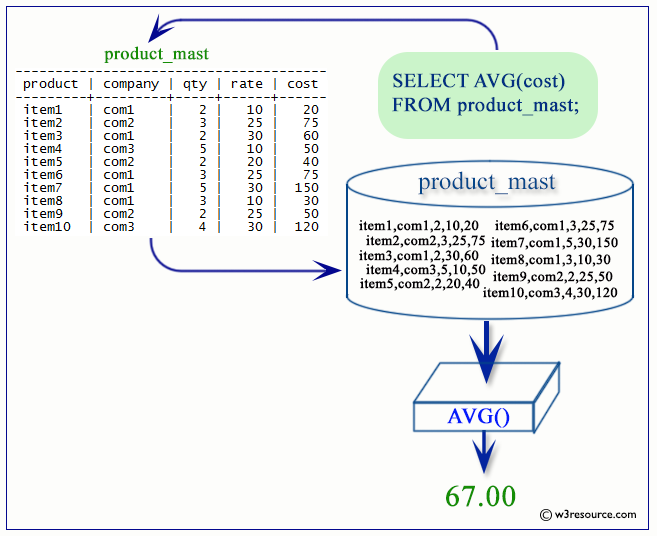
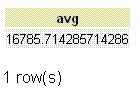
If we want to find the average salary for all employees in the employee table, the following SQL can be used.
SQL Code:
SELECT AVG(salary)
FROM employee;
Output:
Visual Presentation of PostgreSQL AVG() function
PostgreSQL AVG as a level
If we want to get the average salary for all employees and show the result against 'Average Salary' head in the employee table, the following SQL can be used.
SQL Code:
SELECT AVG(salary) "Average Salary"
FROM employee;
OR
SQL Code:
SELECT AVG(DISTINCT salary) "Average Salary"
FROM employee;
OR
SQL Code:
SELECT AVG(ALL salary) "Average Salary"
FROM employee;
Output:
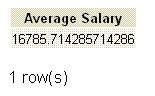
PostgreSQL AVG two columns
If we want to get the average salary and deduction from employee table, the following SQL can be used.
SQL Code:
SELECT AVG(salary) "Average Salary" ,
AVG(deduction) "Average Deduction"
FROM employee;
Output:
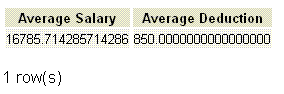
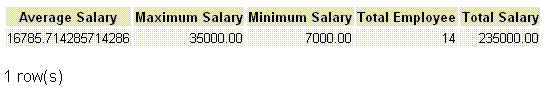
PostgreSQL AVG with MAX, MIN, COUNT and SUM
If we want to get the average salary, maximum salary, minimum salary, total employee and total salary from employee table, the following SQL can be used.
SQL Code:
SELECT AVG(salary) "Average Salary" ,
MAX(salary) "Maximum Salary",
MIN(salary) "Minimum Salary",
COUNT(*) "Total Employee",
SUM(salary) "Total Salary"
FROM employee;
Output:
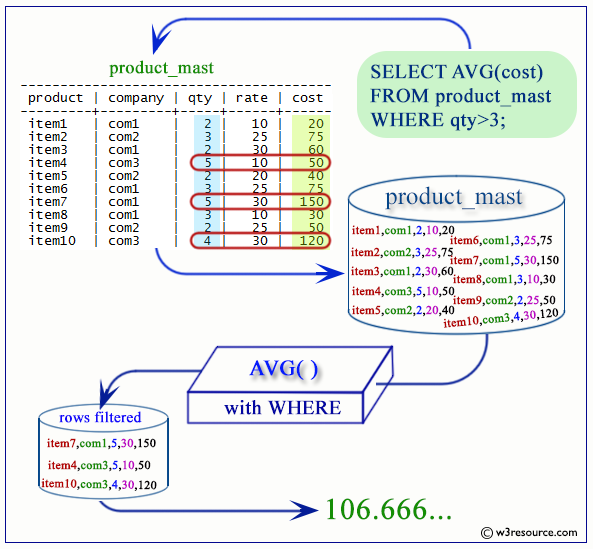
PostgreSQL AVG WHERE clause
If we want to get the average salary and deduction from employee table who belongs to the designation 'SALESMAN', the following SQL can be used.
SQL Code:
SELECT AVG(salary) "Average Salary" ,
AVG(deduction) "Average Deduction"
FROM employee
WHERE designame='SALESMAN';
Output:
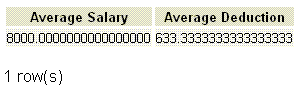
Pictorial Presentation of PostgreSQL AVG with WHERE clause
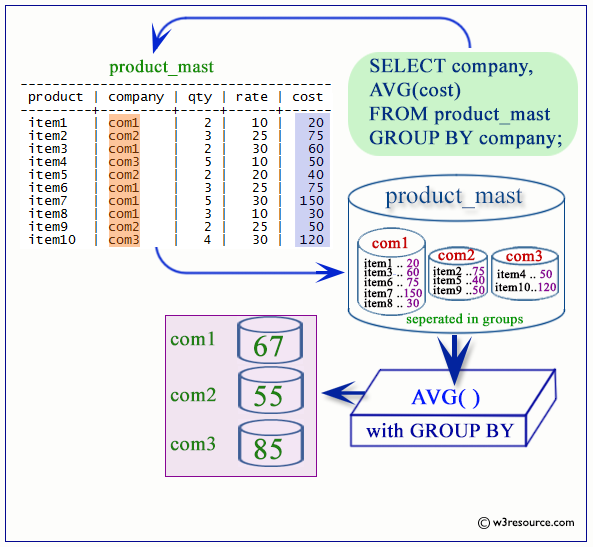
PostgreSQL AVG with GROUP BY
Sample table: employees
The following statement will return the designation and average salary against each designation from the employees table.
SQL Code:
SELECT job_id, ROUND(AVG(salary),2) AS "Average Salary rounded"
FROM employees
GROUP BY job_id;
Output:
job_id | Average Salary ------------+---------------- AC_ACCOUNT | 8300.00 ST_MAN | 7280.00 IT_PROG | 5760.00 SA_MAN | 12200.00 AD_PRES | 24000.00 AC_MGR | 12000.00 FI_MGR | 12000.00 AD_ASST | 4400.00 MK_MAN | 13000.00 PU_CLERK | 2780.00 HR_REP | 6500.00 PR_REP | 10000.00 FI_ACCOUNT | 7920.00 SH_CLERK | 3215.00 AD_VP | 17000.00 SA_REP | 8350.00 ST_CLERK | 2785.00 MK_REP | 6000.00 PU_MAN | 11000.00 (19 rows)
Visual Presentation of PostgreSQL AVG with GROUP BY
PostgreSQL AVG with WHERE CLAUSE and GROUP BY
Sample table: employees
The following statement will return the designation wise average salary for that designation which salary does not exceed 12000 and above, from employees table.
SQL Code:
SELECT job_id,ROUND(AVG(salary),2) AS "Avereage Salary"
FROM employees
WHERE salary<12000
GROUP BY job_id;
Output:
job_id | Avereage Salary ------------+----------------- AC_ACCOUNT | 8300.00 ST_MAN | 7280.00 IT_PROG | 5760.00 SA_MAN | 10750.00 AD_ASST | 4400.00 PU_CLERK | 2780.00 HR_REP | 6500.00 PR_REP | 10000.00 FI_ACCOUNT | 7920.00 SH_CLERK | 3215.00 SA_REP | 8350.00 ST_CLERK | 2785.00 MK_REP | 6000.00 PU_MAN | 11000.00 (14 rows)
PostgreSQL AVG with HAVING and GROUP BY
Sample table : employees
The following sql statement will return, designation wise total employees and the average salary for that designation which salary does not exceed 12000 and above and a minimum of five employees have this designation.
SQL Code:
SELECT job_id,COUNT(*) AS "Number of Employees",
ROUND(AVG(salary),2) AS "Average Salary"
FROM employees
WHERE salary<12000
GROUP BY job_id
HAVING COUNT(*)>=5;
Output:
job_id | Number of Employees | Average Salary ------------+---------------------+---------------- ST_MAN | 5 | 7280.00 IT_PROG | 5 | 5760.00 PU_CLERK | 5 | 2780.00 FI_ACCOUNT | 5 | 7920.00 SH_CLERK | 20 | 3215.00 SA_REP | 30 | 8350.00 ST_CLERK | 20 | 2785.00 (7 rows)
Visual Presentation of PostgreSQL AVG with HAVING
PostgreSQL AVG with GROUP BY and ORDER BY
Sample table: employees
The following statement will return, the designation wise total employees and average salary, arranged in descending order according to the total number of employees, for that designation which salary does not exceed 12000 and above and a minimum of five employees has this designation.
SQL Code:
SELECT job_id,COUNT(*) AS "Number of employees" ,
ROUND(AVG(salary),2) AS "Average Salary"
FROM employees
WHERE salary<12000
GROUP BY job_id
HAVING COUNT(*)>=5
ORDER BY COUNT(*) DESC;
Output:
job_id | Number of employees | Average Salary ------------+---------------------+---------------- SA_REP | 30 | 8350.00 SH_CLERK | 20 | 3215.00 ST_CLERK | 20 | 2785.00 ST_MAN | 5 | 7280.00 FI_ACCOUNT | 5 | 7920.00 IT_PROG | 5 | 5760.00 PU_CLERK | 5 | 2780.00 (7 rows)
Previous: MIN
Next: Logical Operators