SQLite LEFT JOIN or LEFT OUTER JOIN
What is left join or left outer join in SQLite?
The Left Join or Left Outer Join operation takes two relations, A and B, and returns the inner join of A and B along with the unmatched rows of A. A is the first relation defined in the FROM clause and is hence the left relation. The left join includes the unmatched rows of the left relation along with the matched columns in the result.
The SQLite LEFT JOIN joins two tables and fetches rows based on a condition, which is matching in both the tables and the unmatched rows will also be available from the table written before the JOIN clause.
So, in case of LEFT JOIN or LEFT OUTER JOIN, SQLite -
1. takes all selected values from the left table
2. combines them with the column names ( specified in the condition ) from the right table
3. retrieve the matching rows from both the associated tables.
4. sets the value of every column from the right table to NULL which is unmatched with the left table.
Syntax:
Here is the basic syntax.
SELECT result FROM table1 LEFT [OUTER] JOIN table2 ON table1.keyfield1 = table2.keyfield2 [WHERE expr]
Pictorial Presentation
Assume that, we have two tables table-A and table-B. The unique columns for two tables are ID. The value in ID column for table-A are 210,211,212 and 213 and the values for table-B are 210,214,215,212 and 212. Here is the pictorial presentation.
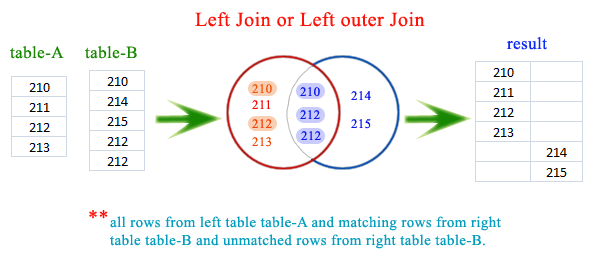
Example: SQLite LEFT JOIN or LEFT OUTER JOIN
A LEFT JOIN will preserve the records of the "left" table. SQLite starts with the left table. For each row from the alias an SQLite scans the table refers if the condition is satisfied and returns the patient_name and vdate. For unmatched rows it returns null. Each item in the left table will be shown in an SQLite result, even if there isn't a match in the other table.
Here are sample tables.
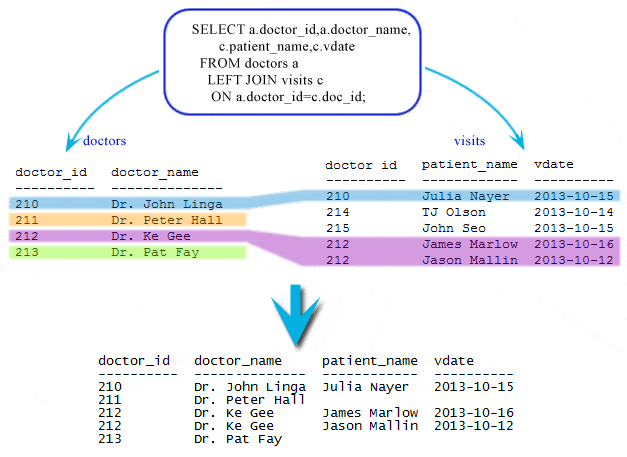
table - doctors doctor_id doctor_name degree ---------- -------------- ---------- 210 Dr. John Linga MD 211 Dr. Peter Hall MBBS 212 Dr. Ke Gee MD 213 Dr. Pat Fay MD table - visits doctor_id patient_name vdate ---------- ------------ ---------- 210 Julia Nayer 2013-10-15 214 TJ Olson 2013-10-14 215 John Seo 2013-10-15 212 James Marlow 2013-10-16 212 Jason Mallin 2013-10-12
Here is the example
If we want to find, which doctor attended which patient and the date for attend, the following SQL can be used.
SELECT a.doctor_id,a.doctor_name,
c.patient_name,c.vdate
FROM doctors a
LEFT JOIN visits c
ON a.doctor_id=c.doctor_id;
Here is the output:
doctor_id doctor_name patient_name vdate ---------- -------------- ------------ ---------- 210 Dr. John Linga Julia Nayer 2013-10-15 211 Dr. Peter Hall 212 Dr. Ke Gee James Marlow 2013-10-16 212 Dr. Ke Gee Jason Mallin 2013-10-12 213 Dr. Pat Fay
From the above result, the rows indicated by color red shows that the specified criteria do not match for the right table, that is visits tables aliased by c. The doctor_id 211 and 213 does not exist in the visits table. So, for these unmatched rows, it returns NULL in the result set for the columns alias of c.
Pictorial Presentation
Example: SQLite LEFT JOIN with USING
The USING keyword can be used to achieve the same result.
Here is the example
SELECT doctor_id,doctor_name,
patient_name,vdate
FROM doctors
LEFT JOIN visits
USING(doctor_id);
Here is the output:
doctor_id doctor_name patient_name vdate ---------- -------------- ------------ ---------- 210 Dr. John Linga Julia Nayer 2013-10-15 211 Dr. Peter Hall 212 Dr. Ke Gee James Marlow 2013-10-16 212 Dr. Ke Gee Jason Mallin 2013-10-12 213 Dr. Pat Fay
The result is same with a sorter SQL statement.
Example: SQLite NATURAL LEFT OUTER JOIN
The NATURAL LEFT OUTER JOIN automatically uses all the matching column names for the join.
Here is the example
SELECT doctor_id,doctor_name,
patient_name,vdate
FROM doctors
NATURAL LEFT OUTER JOIN visits;
Here is the output:
doctor_id doctor_name patient_name vdate ---------- -------------- ------------ ---------- 210 Dr. John Linga Julia Nayer 2013-10-15 211 Dr. Peter Hall 212 Dr. Ke Gee James Marlow 2013-10-16 212 Dr. Ke Gee Jason Mallin 2013-10-12 213 Dr. Pat Fay
LEFT JOIN: SQL and other Relational Databases
Previous:
INNER JOIN
Next:
CROSS JOIN
