SQLite avg() function
Description
SQLite avg() function retrieves the average value of a given expression. If the function does not find a matching row, it returns NULL. String and BLOB values that do not look like numbers are interpreted as 0. The result of avg() is always a floating point value as long as at there is at least one non-NULL input even if all inputs are integers. The result of avg() is NULL if and only if there are no non-NULL inputs.
Syntax
avg([DISTINCT] expr)
Where expr is a given expression. The DISTINCT option can be used to return the average of the distinct values of expr.
Table of Contents
Example: SQLite avg() function
SQLite avg() function with group by and example
SQLite avg() function with distinct and example
SQLite avg() function decimal places and example
SQLite avg() function with count() function and example
SQLite avg() function with having and example
Example: SQLite avg() function
The following SQLite statement will return an average number of pages (of books) from the book_mast table.
Sample table: book_mast
Sample Output:
sqlite> SELECT avg(no_page) FROM book_mast; 286.625
Example: SQLite avg() function with group by
SQLite avg() function retrieves the average value of a given expression for each group, if it is used with group by option. The following statement will return the average number of pages for each group of 'pub_id' from book_mast table.
Sample table: book_mast
Sample Output:
sqlite> SELECT pub_id,avg(no_page) FROM book_mast GROUP BY pub_id; pub_id avg(no_page) ---------- ------------ P001 232.5 P002 337.5 P003 148.0 P004 460.0 P005 236.0 P006 216.5 P007 375.0 P008 287.5
Pictorial Presentation
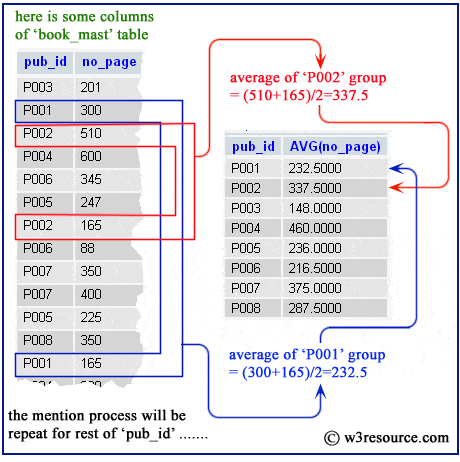
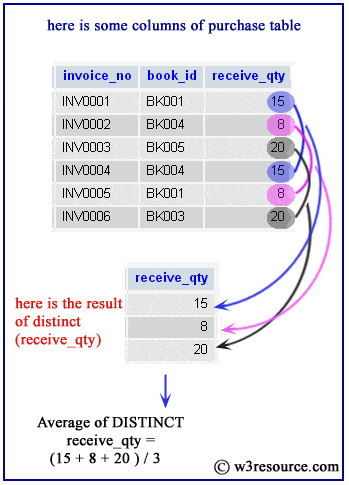
Example: SQLite avg() function with distinct
SQLite avg() function retrieves the unique average value of a given expression when used with DISTINCT keyword. The following statement will return the average of unique 'receive_qty' from the purchase table.
Sample table: purchase
Sample Output:
sqlite> SELECT avg(DISTINCT(receive_qty)) ...> FROM purchase; avg(DISTINCT(receive_qty)) -------------------------- 14.3333333333333
Pictorial Presentation
Example: SQLite avg() function decimal places
Here we have discussed how to use ROUND() along with avg() to retrieve a value calculated upto a specific number of decimal places of a given value. The following statement will return the average number of pages up to 2 decimal places for each group of 'pub_id' from book_mast table.
Sample table: book_mast
Sample Output:
sqlite> SELECT pub_id,ROUND(avg(no_page),2) ...> FROM book_mast ...> GROUP BY pub_id; pub_id ROUND(avg(no_page),2) ---------- --------------------- P001 232.5 P002 337.5 P003 148.0 P004 460.0 P005 236.0 P006 216.5 P007 375.0 P008 287.5
Example: SQLite avg() function with count() function
Here we have discussed how to use SQLite avg() function with count() function to fetch suitable data. The following statement will return the average 'no_page' and number of the publisher for each group of the publisher from book_mast table.
Sample table: book_mast
Sample Output:
sqlite> SELECT pub_id, avg(no_page) ...> FROM book_mast ...> GROUP BY pub_id; pub_id avg(no_page) ---------- --------------------- P001 232.50 P002 337.50 P003 148.00 P004 460.00 P005 236.00 P006 216.50 P007 375.00 P008 287.50
SQLite avg() function with having
SQLite avg() function retrieves the average value of a given expression against a condition specified after HAVING clause for each group specified after the GROUP BY clause. This way you can use HAVING and GROUP BY with SQLite avg() function. The following statement will return the average no_page for those group whose 'pub_id' is 'P008' from the book_mast table.
Sample table: book_mast
Sample Output:
sqlite> SELECT pub_id, avg(no_page) ...> FROM book_mast ...> GROUP BY pub_id ...> HAVING pub_id='P008'; pub_id avg(no_page) ---------- ------------ P008 287.5
Previous:
Collating Sequences
Next:
Count()
