Python: reversed() function
reversed() function
The reversed() function is used to get a reverse iterator.
Version:
(Python 3.2.5)
Syntax:
reversed(seq)
Parameter:
| Name | Description | Required / Optional |
|---|---|---|
| seq | Any iterable object | Required |
Return value:
An iterator in reverse order.
Example: Python reversed() function
# for string
seqStr = 'Exercise'
print(list(reversed(seqStr)))
# for tuple
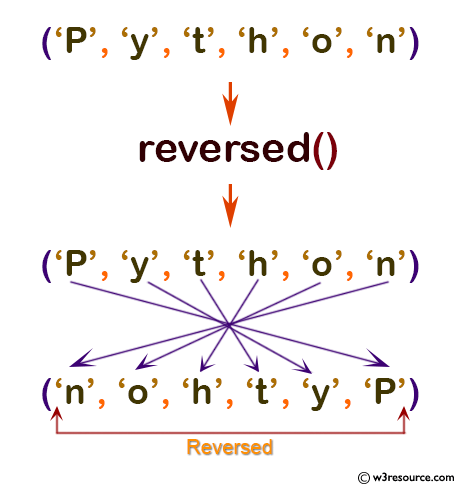
seqTup = ('P', 'y', 't', 'h', 'o', 'n')
print(list(reversed(seqTup)))
# for range
seqRan = range(2, 12)
print(list(reversed(seqRan)))
# for list
seqList = [1, 2, 4, 3, 5, 6]
print(list(reversed(seqList)))
Output:
['e', 's', 'i', 'c', 'r', 'e', 'x', 'E'] ['n', 'o', 'h', 't', 'y', 'P'] [11, 10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2] [6, 5, 3, 4, 2, 1]
Pictorial Presentation:
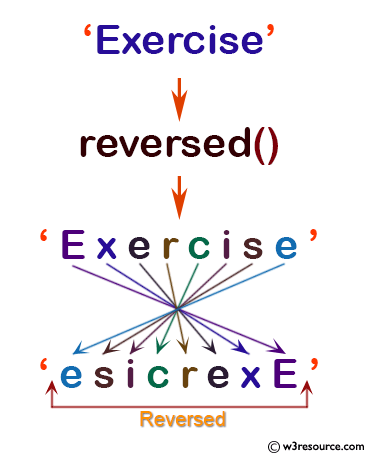
Pictorial Presentation:
Python Code Editor:
Previous: repr()
Next: round()
Test your Python skills with w3resource's quiz
