Oracle CROSS JOIN
What is Cross Join in Oracle?
The CROSS JOIN clause produces the cross-product of two tables. A cross join or Cartesian product is formed when every row from one table is joined to all rows in another. Suppose, the source and target tables have four and three rows, respectively, a cross join between them results in (4 × 3 = 12) rows being returned provided by there is no WHERE clause have been applied with the cross join statement.
Syntax:
SELECT table1.column, table2.column FROM table1 CROSS JOIN table2;
Pictorial presentation of Syntax
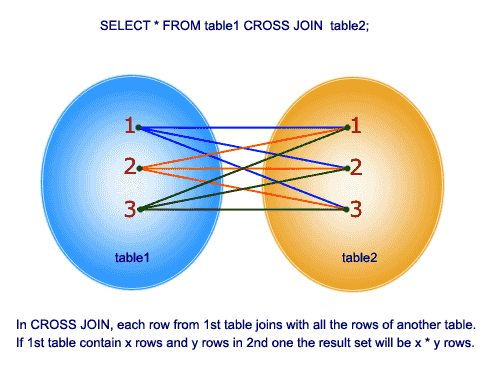
Pictorial presentation of Oracle Cross Join
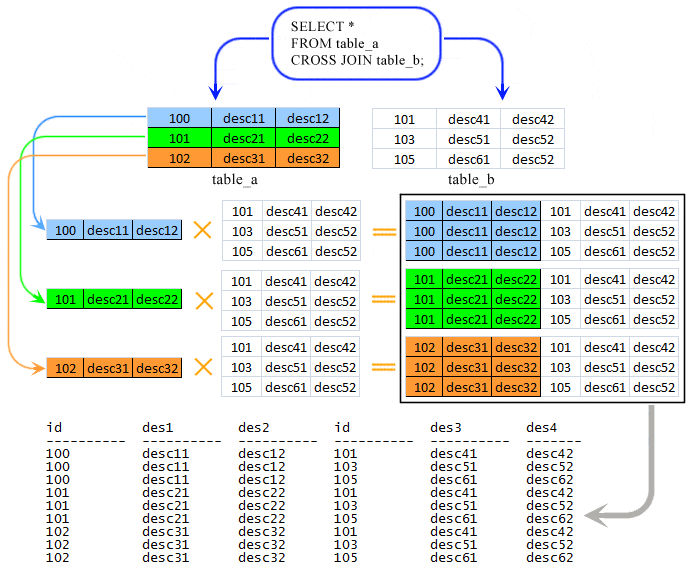
Example: Oracle Cross Join
The following statement will return a cross product or Cartesian product of employees and departments table.
Sample table: employees
Sample table: departments
SELECT first_name, department_name
FROM employees
CROSS JOIN departments ;
Sample Output:
FIRST_NAME DEPARTMENT_NAME -------------------- ------------------------------ Jennifer Retail Sales Eleni Retail Sales Ellen Recruiting Sundar Recruiting Mozhe Recruiting David Recruiting Hermann Recruiting Shelli Recruiting Amit Recruiting Elizabeth Recruiting Sarah Recruiting David Recruiting Laura Recruiting Harrison Recruiting Alexis Recruiting Anthony Recruiting Gerald Recruiting Nanette Recruiting John Recruiting ...
Example: Oracle CROSS JOIN with WHERE clause
The following sql statement produces a Cartesian product of the regions and countries table and filtered the results for the countries which ID is 'AU'.
Sample table: regions
Sample table: countries
SELECT *
FROM regions
CROSS JOIN countries
WHERE country_id='AU';
Sample Output:
REGION_ID REGION_NAME CO COUNTRY_NAME REGION_ID
---------- ------------------------- -- ---------------------------------------- ----------
1 Europe AU Australia 3
2 Americas AU Australia 3
3 Asia AU Australia 3
4 Middle East and Africa AU Australia 3
CROSS JOINS: SQL and other Relational Databases
