MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() function
GROUP_CONCAT() function
Introduction and Overview
MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() function returns a string with concatenated non-NULL value from a group. It is used to concatenate and aggregate values from multiple rows within a specific column into a single string. It's particularly useful for combining and displaying related data in a compact format.
Returns NULL when there are no non-NULL values.
This function is useful in -
- The primary purpose of the GROUP_CONCAT() function is to concatenate values from multiple rows into a single string.
- You can use GROUP_CONCAT() to aggregate data based on a certain column or attribute.
- The GROUP_CONCAT() can use to create a list of tags for each record.
- When working with hierarchical data structures, you can use GROUP_CONCAT() to show parent-child relationships in a readable format.
- In applications, you can use GROUP_CONCAT() to display a user's preferences, settings, or selected options in a user-friendly format.
- GROUP_CONCAT() is useful for displaying data in applications, reports, or user interfaces where a single field needs to show multiple related values.
- The function allows you to define custom separators (other than commas) and order for concatenated values, giving you flexibility in how data is presented.
Syntax:
GROUP_CONCAT(expr
[ORDER BY {unsigned_integer | col_name | expr} ASC | DESC]
[SEPARATOR str_val])
- expr: Expression to concatenate.
- ORDER BY: Optional clause to order concatenated values.
- SEPARATOR: Optional parameter to define the separator (default is comma).
MySQL Version: 8.0
Contents:
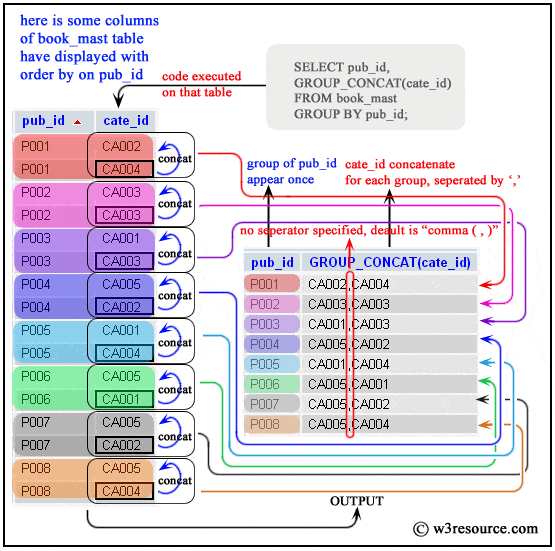
Example : MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() function
The provided MySQL statement will produce a list of comma-separated 'cate_id's for each group of 'pub_id' from the 'book_mast' table.
Sample table: book_mast
Code:
-- This SQL query concatenates category IDs for each publisher.
SELECT pub_id, -- Selects the publisher ID
GROUP_CONCAT(cate_id) -- Concatenates category IDs for books published by each publisher
FROM book_mast -- Specifies the table from which to retrieve data (book_mast table)
GROUP BY pub_id; -- Groups the results by publisher ID, so that the category IDs are concatenated for each publisher separately
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves data from the book_mast table.
- It concatenates category IDs for each publisher.
- The GROUP BY clause ensures that the results are grouped by publisher ID, allowing for category IDs to be concatenated separately for each publisher.
- Here's how the process works:
- The query selects the publisher ID (pub_id).
- It concatenates the category IDs for books published by each publisher using the GROUP_CONCAT(cate_id) function.
- The results are grouped by publisher ID using GROUP BY pub_id, ensuring that the category IDs are concatenated separately for each publisher.
- Finally, the query returns the publisher ID and the concatenated category IDs for books published by each publisher.
Output:
mysql> SELECT pub_id,GROUP_CONCAT(CATE_ID)
-> FROM book_mast
-> GROUP BY pub_id;
+--------+-----------------------+
| pub_id | GROUP_CONCAT(CATE_ID) |
+--------+-----------------------+
| P001 | CA002,CA004 |
| P002 | CA003,CA003 |
| P003 | CA001,CA003 |
| P004 | CA005,CA002 |
| P005 | CA001,CA004 |
| P006 | CA005,CA001 |
| P007 | CA005,CA002 |
| P008 | CA005,CA004 |
+--------+-----------------------+
8 rows in set (0.02 sec)
Pictorial Presentation:
Example: MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() with order by
This MySQL query will provide a list of unique "cate_id"s, presented as strings separated by commas and arranged in ascending order, for each group of 'pub_id' from the 'book_mast' table. To alter the order to descending, replace 'ASC' with 'DESC' at the end of the SELECT statement.
Sample table: book_mast
Code:
-- This SQL query concatenates distinct category IDs for each publisher and orders the results by the concatenated category IDs in ascending order.
SELECT pub_id, -- Selects the publisher ID
GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id) -- Concatenates distinct category IDs for books published by each publisher
FROM book_mast -- Specifies the table from which to retrieve data (book_mast table)
GROUP BY pub_id -- Groups the results by publisher ID, so that the distinct category IDs are concatenated for each publisher separately
ORDER BY GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id) ASC; -- Orders the results by the concatenated category IDs in ascending order
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves data from the book_mast table.
- It concatenates distinct category IDs for each publisher and orders the results by the concatenated category IDs in ascending order.
- The GROUP BY clause ensures that the results are grouped by publisher ID, allowing for distinct category IDs to be concatenated separately for each publisher.
- The ORDER BY clause specifies that the results should be ordered by the concatenated category IDs in ascending order.
- Here's how the process works:
- The query selects the publisher ID (pub_id).
- It concatenates the distinct category IDs for books published by each publisher using the GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id) function.
- The results are grouped by publisher ID using GROUP BY pub_id, ensuring that the distinct category IDs are concatenated separately for each publisher.
- Finally, the query orders the results by the concatenated category IDs in ascending order using ORDER BY GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id) ASC.
- The query returns the publisher ID and the concatenated distinct category IDs for books published by each publisher, ordered by the concatenated category IDs in ascending order.
Output:
mysql> SELECT pub_id,GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id)
-> FROM book_mast
-> GROUP BY pub_id
-> ORDER BY GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id) ASC;
+--------+--------------------------------+
| pub_id | GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id) |
+--------+--------------------------------+
| P003 | CA001,CA003 |
| P005 | CA001,CA004 |
| P001 | CA002,CA004 |
| P002 | CA003 |
| P006 | CA005,CA001 |
| P004 | CA005,CA002 |
| P007 | CA005,CA002 |
| P008 | CA005,CA004 |
+--------+--------------------------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Example : MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() with distinct
The following MySQL statement will return the unique “cate_id”s, as a list of strings separated by the commas, for each group of 'pub_id' from the book_mast table.
Sample table : book_mast
Code:
-- This SQL query concatenates distinct category IDs for each publisher.
SELECT pub_id, -- Selects the publisher ID
GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id) -- Concatenates distinct category IDs for books published by each publisher
FROM book_mast -- Specifies the table from which to retrieve data (book_mast table)
GROUP BY pub_id; -- Groups the results by publisher ID, so that the distinct category IDs are concatenated for each publisher separately
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves data from the book_mast table.
- It concatenates distinct category IDs for each publisher.
- The GROUP BY clause ensures that the results are grouped by publisher ID, allowing for distinct category IDs to be concatenated separately for each publisher.
- Here's how the process works:
- The query selects the publisher ID (pub_id).
- It concatenates the distinct category IDs for books published by each publisher using the GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id) function.
- The results are grouped by publisher ID using GROUP BY pub_id, ensuring that the distinct category IDs are concatenated separately for each publisher.
- Finally, the query returns the publisher ID and the concatenated distinct category IDs for books published by each publisher.
Output:
mysql> SELECT pub_id,GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id)
-> FROM book_mast
-> GROUP BY pub_id;
+--------+--------------------------------+
| pub_id | GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id) |
+--------+--------------------------------+
| P001 | CA002,CA004 |
| P002 | CA003 |
| P003 | CA001,CA003 |
| P004 | CA005,CA002 |
| P005 | CA001,CA004 |
| P006 | CA005,CA001 |
| P007 | CA005,CA002 |
| P008 | CA005,CA004 |
+--------+--------------------------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Example : MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() with separator
The following MySQL query concatenates unique "cate_id"s for each publisher, ordered alphabetically and separated by space from the book_mast table. The sorting order can be reversed to descending by using the 'DESC' option instead of 'ASC' at the end of the SELECT statement.
Sample table : book_mast
Code:
-- This SQL query concatenates distinct category IDs for each publisher, ordered alphabetically, with space as separator.
SELECT pub_id, -- Selects the publisher ID
GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id -- Concatenates distinct category IDs for books published by each publisher
ORDER BY cate_id ASC -- Orders the category IDs alphabetically in ascending order
SEPARATOR ' ') -- Specifies space as the separator for concatenated category IDs
FROM book_mast -- Specifies the table from which to retrieve data (book_mast table)
GROUP BY pub_id; -- Groups the results by publisher ID, so that the distinct category IDs are concatenated for each publisher separately
Explanation:
- This SQL query retrieves data from the book_mast table.
- It concatenates distinct category IDs for each publisher, ordered alphabetically, with space as separator.
- The GROUP BY clause ensures that the results are grouped by publisher ID, allowing for distinct category IDs to be concatenated separately for each publisher.
- The ORDER BY clause orders the category IDs alphabetically in ascending order before concatenating.
- The SEPARATOR clause specifies space as the separator for concatenated category IDs.
- Here's how the process works:
- The query selects the publisher ID (pub_id).
- It concatenates the distinct category IDs for books published by each publisher using the GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id ...) function.
- The category IDs are ordered alphabetically in ascending order using ORDER BY cate_id ASC before concatenating.
- Space is specified as the separator for concatenated category IDs using SEPARATOR ' '.
- The results are grouped by publisher ID using GROUP BY pub_id, ensuring that the distinct category IDs are concatenated separately for each publisher.
- Finally, the query returns the publisher ID and the concatenated distinct category IDs for books published by each publisher, with category IDs ordered alphabetically and separated by spaces.
Output:
mysql> SELECT pub_id,GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id
-> ORDER BY cate_id ASC SEPARATOR ' ')
-> FROM book_mast
-> GROUP BY pub_id ;
+--------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+
| pub_id | GROUP_CONCAT(DISTINCT cate_id
ORDER BY cate_id ASC SEPARATOR ' ') |
+--------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+
| P001 | CA002 CA004 |
| P002 | CA003 |
| P003 | CA001 CA003 |
| P004 | CA002 CA005 |
| P005 | CA001 CA004 |
| P006 | CA001 CA005 |
| P007 | CA002 CA005 |
| P008 | CA004 CA005 |
+--------+--------------------------------------------------------------------+
8 rows in set (0.00 sec)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) - MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() Function
1. What is the MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() function used for?
The GROUP_CONCAT() function in MySQL is used to concatenate non-NULL values from a group into a single string. It aggregates values from multiple rows within a specific column, making it useful for combining and displaying related data in a compact format.
2. When does MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() return NULL?
If all values being concatenated are NULL, the GROUP_CONCAT() function returns NULL.
3. In what scenarios is MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() particularly useful?
GROUP_CONCAT() is beneficial in several scenarios:
- Aggregating data based on a specific column or attribute.
- Creating lists of tags associated with each record.
- Displaying hierarchical relationships, such as parent-child structures, in a readable format.
- Presenting user preferences, settings, or selected options in a user-friendly manner.
- Showing multiple related values in a single field for applications, reports, or user interfaces.
4. Can the output of MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() be customized?
Yes, the function allows customization:
- Custom Separators: Besides the default comma, you can define any separator character or string.
- Ordering: Values can be ordered in ascending or descending order before concatenation.
5. Which MySQL versions support the MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() function?
The GROUP_CONCAT() function is documented for MySQL Version 8.0 and later versions.
6. How does MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() handle duplicate values?
By default, GROUP_CONCAT() includes all values, including duplicates. To retrieve unique values, the DISTINCT keyword can be used within the function.
7. What should we consider when using MySQL GROUP_CONCAT() in MySQL?
Ensure that the GROUP BY clause correctly aligns with the aggregation logic to group values appropriately before applying GROUP_CONCAT(). Also, verify the ordering and separator requirements based on specific output needs.
Previous:
COUNT(DISTINCT)
Next:
MySQL Aggregate Functions and Grouping - Max()
