MySQL INNER JOIN
What is INNER JOIN in MySQL?
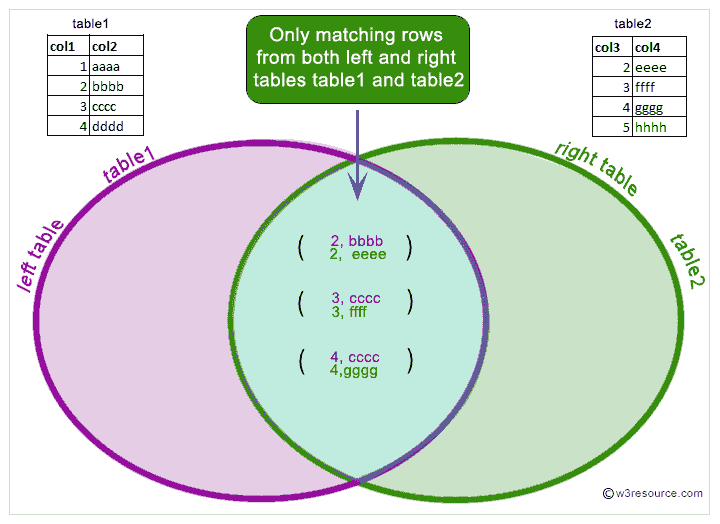
In MySQL the INNER JOIN selects all rows from both participating tables to appear in the result if and only if both tables meet the conditions specified in the ON clause. JOIN, CROSS JOIN, and INNER JOIN are syntactic equivalents. In standard SQL, they are not equivalent. INNER JOIN is used with an ON clause, CROSS JOIN is used otherwise.
Pictorial presentation of MySQL INNER JOIN :
MySQL INNER JOIN Syntax:
MySQL supports the following JOIN syntaxes for the table_references (A table reference is also known as a join expression.) part of SELECT statements and multiple-table UPDATE and DELETE statements:
table_references:
escaped_table_reference [, escaped_table_reference] ...
escaped_table_reference:
table_reference
| { OJ table_reference }
table_reference:
table_factor
| join_table
table_factor:
tbl_name [PARTITION (partition_names)]
[[AS] alias] [index_hint_list]
| table_subquery [AS] alias
| ( table_references )
join_table:
table_reference [INNER | CROSS] JOIN table_factor [join_condition]
| table_reference STRAIGHT_JOIN table_factor
| table_reference STRAIGHT_JOIN table_factor ON conditional_expr
| table_reference {LEFT|RIGHT} [OUTER] JOIN table_reference join_condition
| table_reference NATURAL [{LEFT|RIGHT} [OUTER]] JOIN table_factor
join_condition:
ON conditional_expr
| USING (column_list)
index_hint_list:
index_hint [, index_hint] ...
index_hint:
USE {INDEX|KEY}
[FOR {JOIN|ORDER BY|GROUP BY}] ([index_list])
| IGNORE {INDEX|KEY}
[FOR {JOIN|ORDER BY|GROUP BY}] (index_list)
| FORCE {INDEX|KEY}
[FOR {JOIN|ORDER BY|GROUP BY}] (index_list)
index_list:
index_name [, index_name] ...
Example : MySQL INNER JOIN
When combining records from more than one tables, an user needs to indicate how records in a table can be matched to records in the other. As the both of tables have a cate_id column, we can match using that column. The ON clause is used to match records in two tables, based on the value of cate_id column. Usage of INNER JOIN combines the tables. An INNER JOIN allows rows from either table to appear in the result if and only if both tables meet the conditions specified in the ON clause.
In this example, the ON clause specifies that the cate_id column of both book_mast and category table must match. If a cate_id does not appear in both of the tables, the row will not appear in the result because the condition in the ON clause fails. Only those categories will participate in the JOIN whose books are written in ENGLISH.
Code:
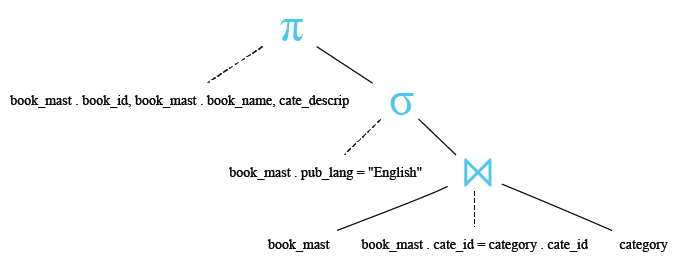
SELECT book_mast.book_id,book_mast.book_name,cate_descrip
FROM book_mast
INNER JOIN category
ON book_mast.cate_id=category.cate_id
WHERE book_mast.pub_lang="English";
Relational Algebra Expression:
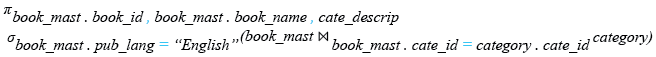
Relational Algebra Tree:
Sample table: book_mast
Sample table: category
Sample Output:
mysql> SELECT book_mast.book_id,book_mast.book_name,cate_descrip
-> FROM book_mast
-> INNER JOIN category
-> ON book_mast.cate_id=category.cate_id
-> WHERE book_mast.pub_lang="English";
+---------+-------------------------------------+--------------+
| book_id | book_name | cate_descrip |
+---------+-------------------------------------+--------------+
| BK001 | Introduction to Electrodynamics | Science |
| BK002 | Understanding of Steel Construction | Technology |
| BK004 | Transfer of Heat and Mass | Technology |
| BK010 | Fundamentals of Thermodynamics | Technology |
| BK012 | The Nature of World | Nature |
| BK009 | Mental Health Nursing | Medical |
+---------+-------------------------------------+--------------+
6 rows in set (0.04 sec)
PHP script:
<!doctype html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>example-inner-join-with-multiple-tables php mysql examples | w3resource</title>
<meta name="description" content="example-inner-join-with-multiple-tables php mysql examples | w3resource">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.5/css/bootstrap.min.css">
</head>
<body>
<div class="container">
<div class="row">
<div class="col-md-12">
<h2>List of the book ids, name of the book and category description:</h2>
<table class='table table-bordered'>
<tr>
<th>Book ID</th><th>Name of the book</th><th>Category description</th>
</tr>
<?php
$hostname="your_hostname";
$username="your_username";
$password="your_password";
$db = "your_dbname";
$dbh = new PDO("mysql:host=$hostname;dbname=$db", $username, $password);
foreach($dbh->query('SELECT book_mast.book_id,book_mast.book_name,cate_descrip
FROM book_mast
INNER JOIN category
ON book_mast.cate_id=category.cate_id
WHERE book_mast.pub_lang="English"') as $row) {
echo "<tr>";
echo "<td>" . $row['book_id'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['book_name'] . "</td>";
echo "<td>" . $row['cate_descrip'] . "</td>";
echo "</tr>";
}
?>
</tbody></table>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
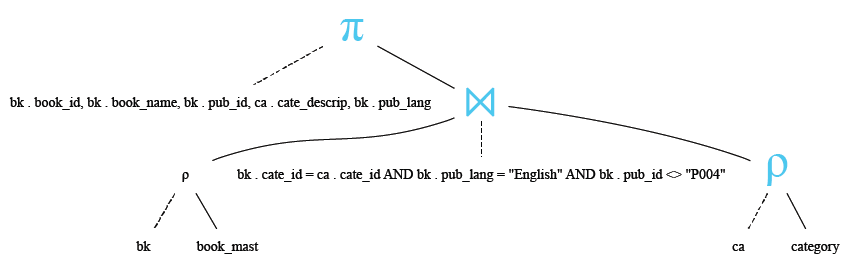
Example : MySQL INNER JOIN with alias
The following MySQL statement returns book ids, the name of the the book, publisher's id, category description and publisher's language, where publisher's language is English and publisher's id is not equal to P004. Notice that aliases have been used to refer the column names. An INNER JOIN is performed based upon the condition that a category id in book_mast table must exist in category table also.
Code:
SELECT bk.book_id,bk.book_name,bk.pub_id,ca.cate_descrip,bk.pub_lang
FROM book_mast AS bk
INNER JOIN category AS ca ON bk.cate_id=ca.cate_id AND
bk.pub_lang="English" AND bk.pub_id<>'P004';
Relational Algebra Expression:
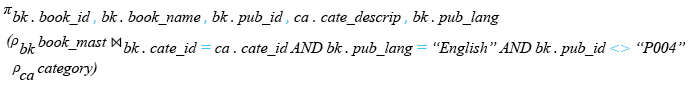
Relational Algebra Tree:
Sample table: book_mast
Sample Output:
mysql> SELECT bk.book_id,bk.book_name,bk.pub_id,ca.cate_descrip,bk.pub_lang
-> FROM book_mast AS bk
-> INNER JOIN category AS ca ON bk.cate_id=ca.cate_id AND
-> bk.pub_lang='English' AND bk.pub_id<>'P004';
+---------+-------------------------------------+--------+--------------+----------+
| book_id | book_name | pub_id | cate_descrip | pub_lang |
+---------+-------------------------------------+--------+--------------+----------+
| BK001 | Introduction to Electrodynamics | P003 | Science | English |
| BK002 | Understanding of Steel Construction | P001 | Technology | English |
| BK010 | Fundamentals of Thermodynamics | P007 | Technology | English |
| BK012 | The Nature of World | P008 | Nature | English |
| BK009 | Mental Health Nursing | P007 | Medical | English |
+---------+-------------------------------------+--------+--------------+----------+
5 rows in set (0.00 sec)
MySQL INNER JOIN using three tables
Sample tables:
table - doctors +-------+---------+ | docid | dname | +-------+---------+ | 1 | A.VARMA | | 2 | D.GOMES | +-------+---------+ table - specialize +------+----------+-------+ | spid | desc | docid | +------+----------+-------+ | 1 | special1 | 1 | | 2 | special2 | 2 | +------+----------+-------+ table - timeschedule +-----+------+----------+-------+ | tid | tday | sit_time | docid | +-----+------+----------+-------+ | 1 | MON | 17:00:00 | 1 | | 2 | WED | 08:00:00 | 1 | | 3 | TUE | 16:00:00 | 2 | | 4 | FRI | 09:00:00 | 2 | +-----+------+----------+-------+
The above tables are related to each other. In doctors, specialize and timeschedule tables the docid, spid and tid are primary key consecutively. The docid in specialize table and timeschedule tables are a foreign key, which is the reference to primary key docid of doctors table.
If we want all records for a doctor who are specialized in special1 and seat in his chamber on Wednesday (WED) in his schedule time, the following SQL can be used-
Code:
SELECT a.docid,a.dname,
b.desc,c.tday,c.sit_time
FROM doctors a
INNER JOIN specialize b
ON a.docid=b.docid
INNER JOIN timeschedule c
ON a.docid=c.docid
WHERE a.docid=1 AND c.tday='WED';
Sample Output:
+-------+---------+----------+------+----------+ | docid | dname | desc | tday | sit_time | +-------+---------+----------+------+----------+ | 1 | A.VARMA | special1 | WED | 08:00:00 | +-------+---------+----------+------+----------+
Explanation :
Step-1
SELECT a.docid,a.dname,b.desc FROM doctors a INNER JOIN specialize b ON a.docid=b.docid;
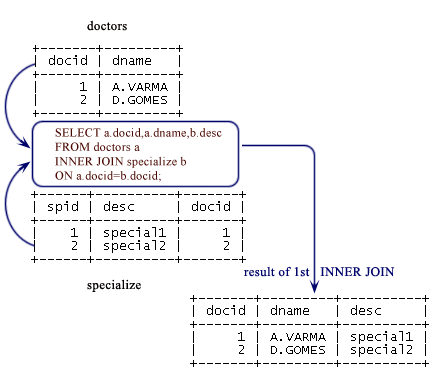
Step-2
SELECT a.docid,a.dname, b.desc,c.tday,c.sit_time FROM doctors a INNER JOIN specialize b ON a.docid=b.docid INNER JOIN timeschedule c ON a.docid=c.docid;
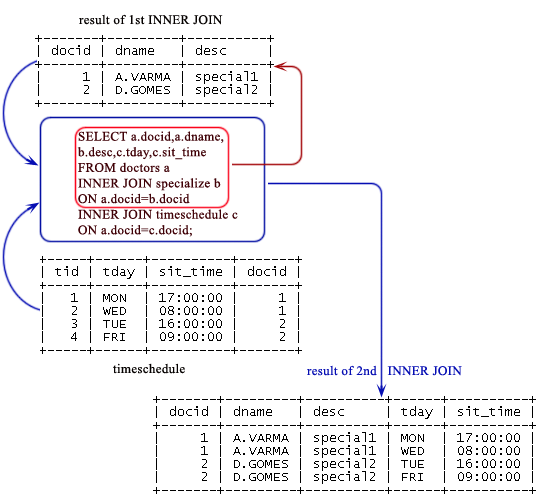
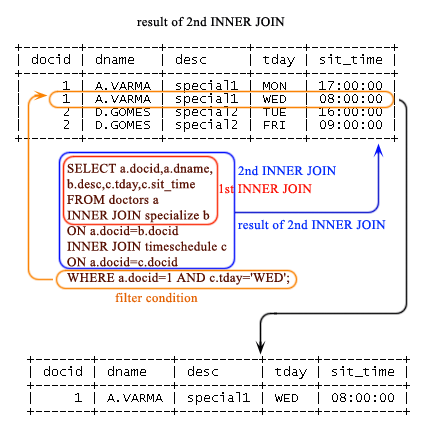
Step-3
SELECT a.docid,a.dname, b.desc,c.tday,c.sit_time FROM doctors a INNER JOIN specialize b ON a.docid=b.docid INNER JOIN timeschedule c ON a.docid=c.docid WHERE a.docid=1 AND c.tday='WED';
Key points to remember
Click on the following to get the slides presentation -

INNER JOINS: SQL and other Relational Databases
Previous: Select with date_add()
Next: Left join
