Java: Remove duplicate letters and arrange in lexicographical order
Remove Duplicate Letters
Write a Java program to remove duplicate letters and arrange them in lexicographical order from a given string containing only lowercase letters.
Note: In mathematics, the lexicographic or lexicographical order (also known as lexical order, dictionary order, alphabetical order or lexicographic(al) product) is a generalization of the way words are alphabetically ordered based on the alphabetical order of their component letters.
Visual Presentation:
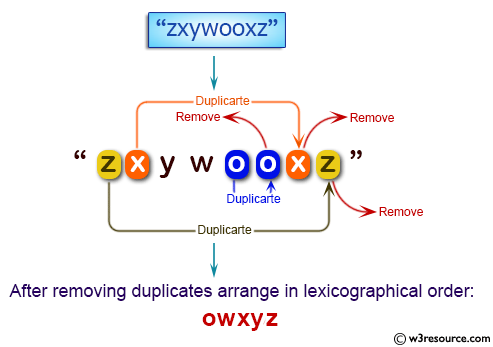
Sample Solution:
Java Code:
// Import Scanner class from java.util package for user input
import java.util.*;
// Main class for the solution
public class Main {
// Main method to execute the solution
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Sample input string for testing duplicate letter removal
String str = "zxywooxz";
// Display the original string
System.out.print("Original string: " + str);
// Display the result after removing duplicate characters and arranging in lexicographical order
System.out.print("\nAfter removing duplicate characters and arranging in lexicographical order: " + removeDuplicateLetters(str));
}
// Function to remove duplicate letters from the given string and arrange in lexicographical order
public static String removeDuplicateLetters(String s) {
// Array to track whether a letter is already in the result
boolean[] inResult = new boolean[26];
// Array to count the occurrences of each lowercase letter
int[] count = new int[26];
// Stack to store the characters
Stack<Character> stack = new Stack<>();
// Count the occurrences of each letter in the input string
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
count[c - 'a']++;
}
// Iterate through the characters in the input string
for (char c : s.toCharArray()) {
// Decrement the count of the current character in the occurrences array
count[c - 'a']--;
// If the character is already in the result, skip
if (inResult[c - 'a']) continue;
// Pop characters from the stack while conditions are met
while (!stack.isEmpty() && c < stack.peek() && count[stack.peek() - 'a'] > 0) {
inResult[stack.pop() - 'a'] = false;
}
// Push the current character onto the stack
stack.push(c);
inResult[c - 'a'] = true;
}
// Sort the characters in the stack
Collections.sort(stack);
// Build the result string from the characters in the stack
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
for (char c : stack) {
result.append(c);
}
return result.toString();
}
}
Sample Output:
Original string: zxywooxz After removing duplicate characters and arranging in lexicographical order: owxyz
For more Practice: Solve these Related Problems:
- Write a Java program to remove duplicate words from a sentence and sort the remaining words in alphabetical order.
- Write a Java program to count the frequency of each character in a string and then output the string with duplicates removed.
- Write a Java program to remove duplicate letters from a string while preserving the order of their first appearance.
- Write a Java program to remove duplicate letters from a string in a case-insensitive manner and then sort them lexicographically.
Go to:
PREV : String Follows Pattern.
NEXT :
Divide Array into Equal Sum Subsets.
Java Code Editor:
Company: Google
Contribute your code and comments through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.
