PostgreSQL NOT NULL constraint
NOT NULL constraint
The not-null constraint in PostgreSQL ensures that a column can not contain any null value. This is a column constraint. No name can be defined to create a not-null constraint.
This constraint is placed immediately after the data-type of a column. Any attempt to put NULL values in that column will be rejected. Columns without the NOT NULL constraint allow NULL values.
A NOT NULL constraint is a column constraint and can not be used as a table constraint.
The reverse of NOT NULL constraint is NULL, but it is not necessary to mention NULL to create a table, the default is NULL, which does not mean that the column must contain NULL, it means that the column might contain NULL value.
A column can contain another constraint along with the NOT NULL constraint.
PostgreSQL NOT NULL example
SQL
CREATE TABLE orders(
ord_no integer NOT NULL,
ord_date date NOT NULL,
item_name character(35),
item_grade character(1),
ord_qty numeric NOT NULL,
ord_amount numeric
);
The table structure
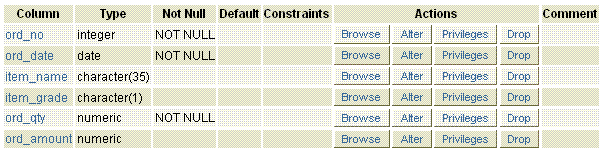
Explanation
The above example shows, the table orders have created in which the ord_no, ord_date and ord_qty column does not allow any NULL value.
PostgreSQL NULL example
SQL
CREATE TABLE orders(
ord_no integer NOT NULL,
ord_date date NULL,
item_name character(35),
item_grade character(1),
ord_qty numeric NULL,
ord_amount numeric
);
The table structure
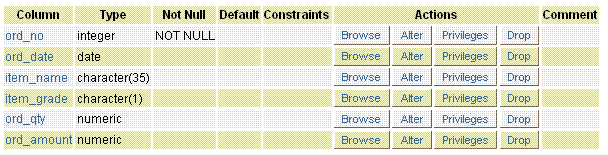
Explanation
The above example shows, the table orders have created in which the ord_no column does not allow any NULL value but the matter is NULL constraint have used as a column constraint with ord_date and ord_qty column but the structure does not show the NULL constraint, because the default value is NULL.
