SQL SELECT with DISTINCT on multiple columns
DISTINCT on multiple columns
In SQL multiple fields may also be added with DISTINCT clause. DISTINCT will eliminate those rows where all the selected fields are identical.
Contents:
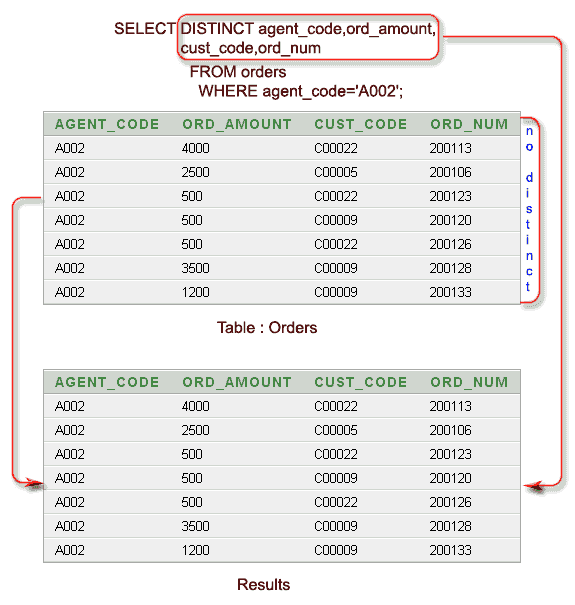
Example: Sample SELECT statement
This query retrieves specific columns from the orders table, filtered by agent_code='A002'
SQL Code:
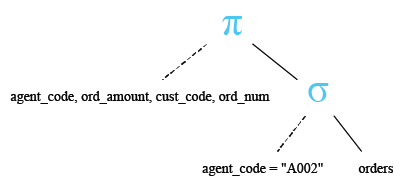
SELECT agent_code, ord_amount, cust_code, ord_num
-- Select specific columns: agent_code, ord_amount, cust_code, ord_num
FROM orders
-- From the table 'orders'
WHERE agent_code='A002';
-- Filter the results to only include rows where the 'agent_code' is 'A002'
Explanation:
- SELECT agent_code, ord_amount, cust_code, ord_num: This line specifies the columns that you want to retrieve data from. It selects the columns 'agent_code', 'ord_amount', 'cust_code', and 'ord_num' from the 'orders' table.
- FROM orders: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'orders' table.
- WHERE agent_code='A002': This line specifies a condition for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where the value in the 'agent_code' column is 'A002'. This condition acts as a filter, allowing only rows with 'A002' as the agent code to be included in the result set.
Relational Algebra Expression:
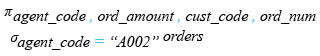
Relational Algebra Tree:
Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200109 3500 800 30-JUL-08 C00011 A010
200101 3000 1000 15-JUL-08 C00001 A008
200111 1000 300 10-JUL-08 C00020 A008
200104 1500 500 13-MAR-08 C00006 A004
200106 2500 700 20-APR-08 C00005 A002
200125 2000 600 10-OCT-08 C00018 A005
200117 800 200 20-OCT-08 C00014 A001
200123 500 100 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002
200120 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200116 500 100 13-JUL-08 C00010 A009
200124 500 100 20-JUN-08 C00017 A007
200126 500 100 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200129 2500 500 20-JUL-08 C00024 A006
200127 2500 400 20-JUL-08 C00015 A003
200128 3500 1500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200135 2000 800 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200131 900 150 26-AUG-08 C00012 A012
200133 1200 400 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002
200100 1000 600 08-JAN-08 C00015 A003
200110 3000 500 15-APR-08 C00019 A010
200107 4500 900 30-AUG-08 C00007 A010
200112 2000 400 30-MAY-08 C00016 A007
200113 4000 600 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
Output:
AGENT_CODE ORD_AMOUNT CUST_CODE ORD_NUM ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- A002 2500 C00005 200106 A002 500 C00022 200123 A002 500 C00009 200120 A002 500 C00022 200126 A002 3500 C00009 200128 A002 1200 C00009 200133 A002 4000 C00022 200113
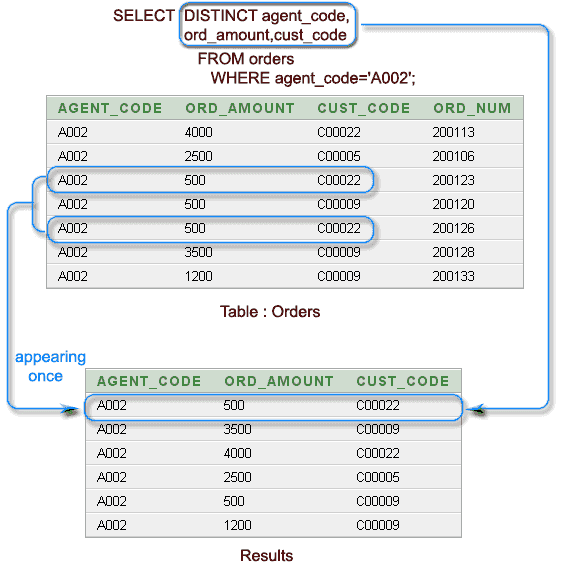
The above result shows the same agent_code, ord_amount and cust_code appears more than once in theorders table.
Example: SELECT with DISTINCT on two columns
The SQL statement below retrieves identical rows based on the 'agent_code' and 'ord_amount' columns from the orders table :
SQL Code:
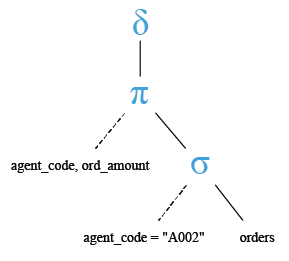
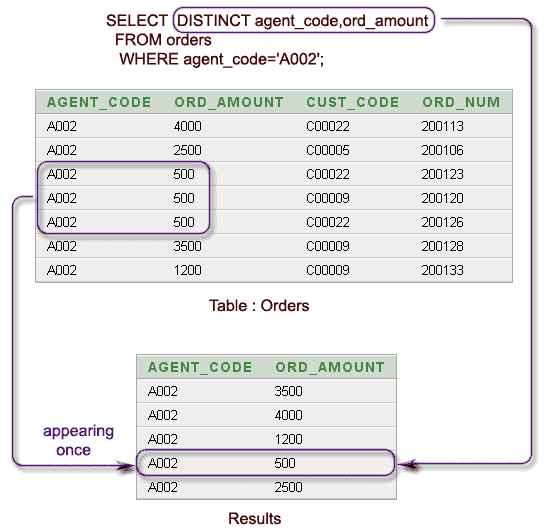
SELECT DISTINCT agent_code, ord_amount
-- Select distinct combinations of 'agent_code' and 'ord_amount'
FROM orders
-- From the table 'orders'
WHERE agent_code='A002';
-- Filter the results to only include rows where the 'agent_code' is 'A002'
Explanation:
- SELECT DISTINCT agent_code, ord_amount: This line specifies that you want to retrieve unique combinations of 'agent_code' and 'ord_amount'. The DISTINCT keyword ensures that only unique combinations are returned; any duplicate combinations will be eliminated.
- FROM orders: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'orders' table.
- WHERE agent_code='A002': This line specifies a condition for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where the value in the 'agent_code' column is 'A002'. This condition acts as a filter, allowing only rows with 'A002' as the agent code to be included in the result set.
Relational Algebra Expression:
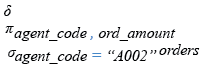
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
AGENT_CODE ORD_AMOUNT ---------- ---------- A002 3500 A002 1200 A002 4000 A002 500 A002 2500
Visual presentation:
Example: SELECT with DISTINCT on three columns
The following SQL statement can be used to retrieve identical rows based on the 'agent_code', 'ord_amount', and 'cust_code' columns once from the orders table:
SQL Code:
SELECT DISTINCT agent_code, ord_amount, cust_code
-- Select distinct combinations of 'agent_code', 'ord_amount', and 'cust_code'
FROM orders
-- From the table 'orders'
WHERE agent_code='A002';
-- Filter the results to only include rows where the 'agent_code' is 'A002'
Explanation:
- SELECT DISTINCT agent_code, ord_amount, cust_code: This line specifies that you want to retrieve unique combinations of 'agent_code', 'ord_amount', and 'cust_code'. The DISTINCT keyword ensures that only unique combinations are returned; any duplicate combinations will be eliminated.
- FROM orders: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'orders' table.
- WHERE agent_code='A002': This line specifies a condition for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where the value in the 'agent_code' column is 'A002'. This condition acts as a filter, allowing only rows with 'A002' as the agent code to be included in the result set.
Relational Algebra Expression:
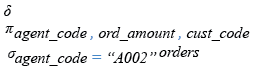
Relational Algebra Tree:
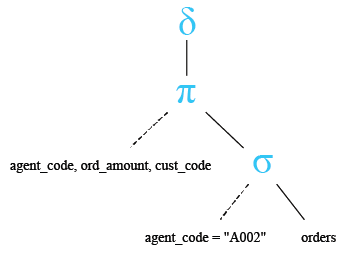
Output:
AGENT_CODE ORD_AMOUNT CUST_CODE ---------- ---------- ---------- A002 500 C00022 A002 3500 C00009 A002 2500 C00005 A002 500 C00009 A002 4000 C00022 A002 1200 C00009
Visual presentation:
Example : SELECT with DISTINCT on all columns of the first query
To get the identical rows (on four columns agent_code, ord_amount, cust_code, and ord_num) once from the orders table , the following SQL statement can be used :
SQL Code:
SELECT DISTINCT agent_code, ord_amount, cust_code, ord_num
-- Select distinct combinations of 'agent_code', 'ord_amount', 'cust_code', and 'ord_num'
FROM orders
-- From the table 'orders'
WHERE agent_code='A002';
-- Filter the results to only include rows where the 'agent_code' is 'A002'
Explanation:
- SELECT DISTINCT agent_code, ord_amount, cust_code, ord_num: This line specifies that you want to retrieve unique combinations of 'agent_code', 'ord_amount', 'cust_code', and 'ord_num'. The DISTINCT keyword ensures that only unique combinations are returned; any duplicate combinations will be eliminated.
- FROM orders: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'orders' table.
- WHERE agent_code='A002': This line specifies a condition for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where the value in the 'agent_code' column is 'A002'. This condition acts as a filter, allowing only rows with 'A002' as the agent code to be included in the result set.
Relational Algebra Expression:
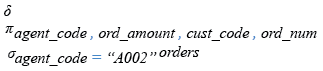
Relational Algebra Tree:
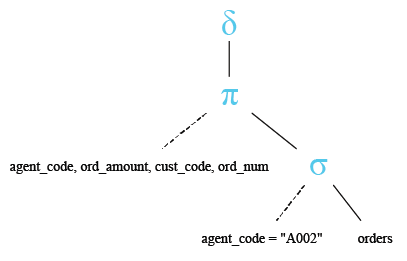
Output:
AGENT_CODE ORD_AMOUNT CUST_CODE ORD_NUM ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- A002 500 C00022 200126 A002 2500 C00005 200106 A002 500 C00009 200120 A002 1200 C00009 200133 A002 4000 C00022 200113 A002 3500 C00009 200128 A002 500 C00022 200123
In the above output, all rows whose agent_code is 'A002' have returned because there is no identical rows on agent_code, ord_amount, cust_code and ord_num. See the following presentation :
Visual presentation:
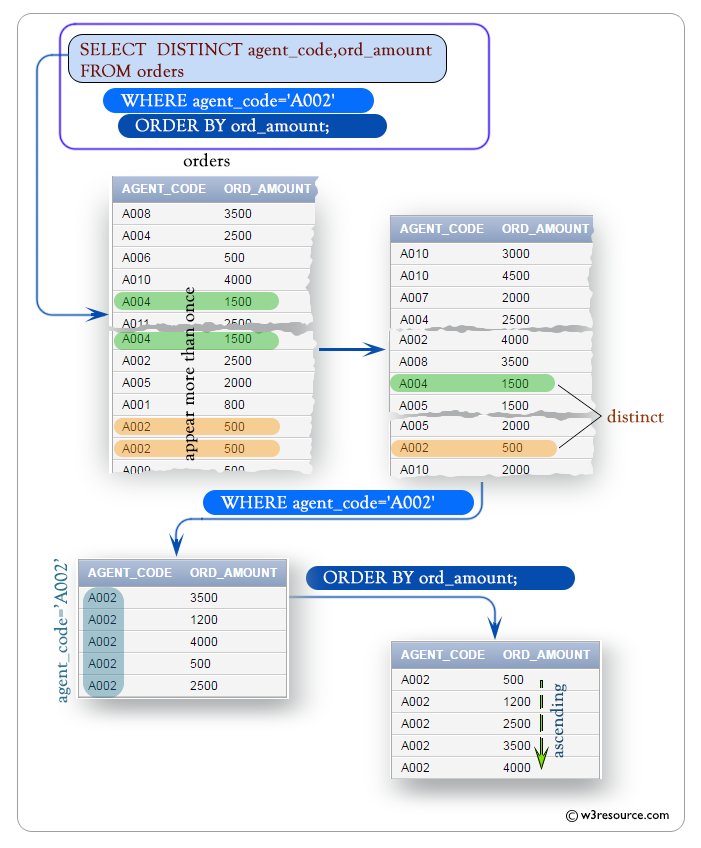
SELECT with DISTINCT on multiple columns and ORDER BY clause
You can use an order by clause in the select statement with distinct on multiple columns. Here is an example:
SQL Code:
SELECT DISTINCT agent_code, ord_amount
-- Select distinct combinations of 'agent_code' and 'ord_amount'
FROM orders
-- From the table 'orders'
WHERE agent_code='A002'
-- Filter the results to only include rows where the 'agent_code' is 'A002'
ORDER BY ord_amount;
-- Sort the results in ascending order based on the 'ord_amount' column
Explanation:
- SELECT DISTINCT agent_code, ord_amount: This line specifies that you want to retrieve unique combinations of 'agent_code' and 'ord_amount'. The DISTINCT keyword ensures that only unique combinations are returned; any duplicate combinations will be eliminated.
- FROM orders: This line specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'orders' table.
- WHERE agent_code='A002': This line specifies a condition for filtering the results. It filters the results to only include rows where the value in the 'agent_code' column is 'A002'. This condition acts as a filter, allowing only rows with 'A002' as the agent code to be included in the result set.
- ORDER BY ord_amount: This line specifies how the results should be sorted. It sorts the results in ascending order based on the 'ord_amount' column. This means that the rows will be arranged from the smallest to the largest 'ord_amount'.
Relational Algebra Expression:
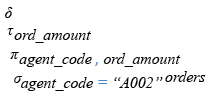
Relational Algebra Tree:
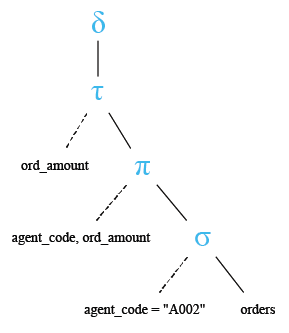
Output:
AGENT_CODE ORD_AMOUNT ---------- ---------- A002 500 A002 1200 A002 2500 A002 3500 A002 4000
Visual presentation:
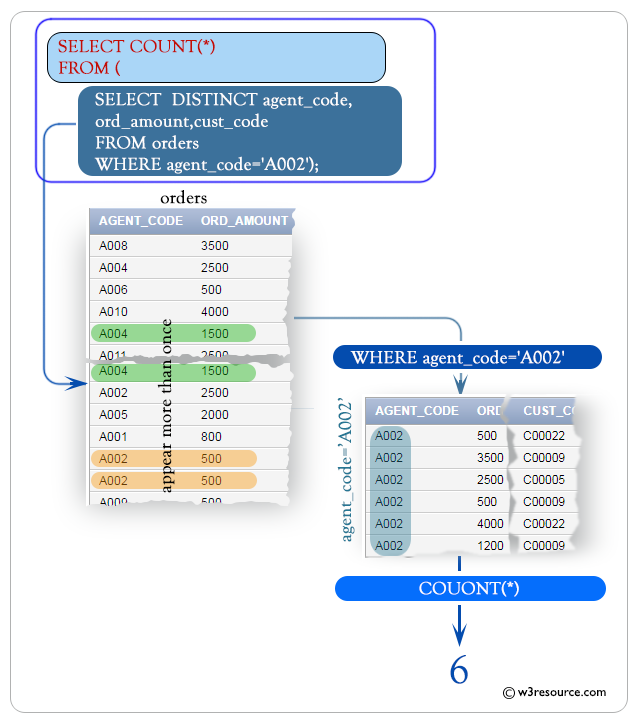
COUNT() function and SELECT with DISTINCT on multiple columns
You can use the count() function in a select statement with distinct on multiple columns to count the distinct rows. Here is an example:
SELECT COUNT(*)
-- Count the number of rows in the result set
FROM (
SELECT DISTINCT agent_code, ord_amount, cust_code
-- Select distinct combinations of 'agent_code', 'ord_amount', and 'cust_code'
FROM orders
-- From the table 'orders'
WHERE agent_code='A002'
-- Filter the results to only include rows where the 'agent_code' is 'A002'
);
Explanation:
- SELECT COUNT(*): This line specifies that you want to count the number of rows in the result set.
- FROM (...): This line wraps the inner query in parentheses and treats it as a subquery. The subquery selects distinct combinations of 'agent_code', 'ord_amount', and 'cust_code' from the 'orders' table where the 'agent_code' is 'A002'.
- The inner query:
- SELECT DISTINCT agent_code, ord_amount, cust_code: Selects distinct combinations of 'agent_code', 'ord_amount', and 'cust_code' from the 'orders' table.
- FROM orders: Specifies the table from which you want to retrieve data. In this case, it's the 'orders' table.
- WHERE agent_code='A002': Filters the results to only include rows where the value in the 'agent_code' column is 'A002'.
Output:
COUNT(*)
----------
6
Visual presentation:
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) - SQL SELECT with DISTINCT on multiple columns
1. What is the purpose of using DISTINCT on multiple columns in SQL?
- DISTINCT on multiple columns eliminates rows where all selected fields are identical, ensuring unique combinations of the specified columns in the result set.
2. How does DISTINCT work with multiple columns?
- When used with multiple columns, DISTINCT considers the combination of values across these columns. Only rows with unique combinations of the specified columns will be included in the result set.
3. Can we use DISTINCT with an ORDER BY clause?
- Yes, we can use DISTINCT with an ORDER BY clause to sort the distinct results based on one or more columns.
4. How does the COUNT() function interact with DISTINCT on multiple columns?
- The COUNT() function can be used with a subquery containing DISTINCT to count the number of unique rows based on the specified columns.
5. What happens if we use DISTINCT on all columns of a table?
- Using DISTINCT on all columns of a table ensures that only completely unique rows, without any duplicates, are included in the result set.
6. Can we filter the results when using DISTINCT on multiple columns?
- Yes, we can filter the results using a WHERE clause in conjunction with DISTINCT to only include rows that meet specific criteria.
7. Is it possible to apply DISTINCT on a single column while selecting multiple columns?
- No, when using DISTINCT, it applies to the combination of all columns listed in the SELECT statement.
8. What is the performance impact of using DISTINCT on multiple columns?
- Using DISTINCT can impact performance, especially on large tables, because the database needs to sort and compare rows to eliminate duplicates.
9. How can we use DISTINCT to retrieve unique rows based on a subset of columns?
- Specify the subset of columns in the SELECT statement with the DISTINCT keyword to retrieve rows with unique combinations of these columns.
10. Can we use DISTINCT with aggregate functions?
- DISTINCT can be used within aggregate functions like COUNT(), but the distinct clause itself does not work directly with aggregate functions like SUM() or AVG() without subqueries.
11. What is the relational algebra equivalent of DISTINCT on multiple columns?
- In relational algebra, DISTINCT corresponds to the projection operator with duplicate elimination on the specified attributes.
12. How does the database engine handle DISTINCT on multiple columns internally?
- The database engine typically sorts the result set based on the specified columns and then eliminates duplicate rows to produce the final distinct result set.
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.