SQL AVG() function
AVG() function
SQL AVG() function calculates the average value of a column of numeric type. It returns the average of all non NULL values
Syntax:
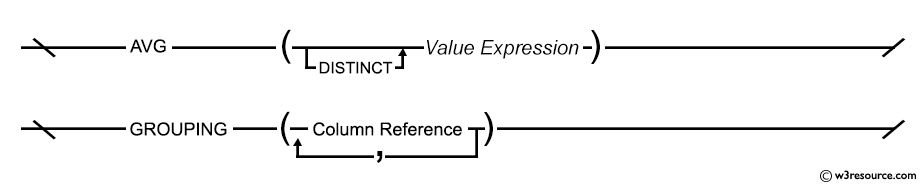
AVG ([ALL | DISTINCT] expression )
DBMS Support: COUNT() function
| DBMS | Command |
| MySQL | Supported |
| PostgreSQL | Supported |
| SQL Server | Supported |
| Oracle | Supported |
DB2 and Oracle Syntax:
AVG ([ALL | DISTINCT] expression ) OVER (window_clause)
Parameters:
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| ALL | Applies to all values. |
| DISTINCT | Return the sum of unique values. |
| expression | Expression made up of a single constant, variable, scalar function, or column name. The expression is an expression of the exact numeric or approximate numeric data type category, except for the bit data type. Aggregate functions and subqueries are not permitted. |
Syntax diagram - AVERAGE() function
Example:
Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200109 3500 800 30-JUL-08 C00011 A010
200101 3000 1000 15-JUL-08 C00001 A008
200111 1000 300 10-JUL-08 C00020 A008
200104 1500 500 13-MAR-08 C00006 A004
200106 2500 700 20-APR-08 C00005 A002
200125 2000 600 10-OCT-08 C00018 A005
200117 800 200 20-OCT-08 C00014 A001
200123 500 100 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002
200120 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200116 500 100 13-JUL-08 C00010 A009
200124 500 100 20-JUN-08 C00017 A007
200126 500 100 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200129 2500 500 20-JUL-08 C00024 A006
200127 2500 400 20-JUL-08 C00015 A003
200128 3500 1500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200135 2000 800 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200131 900 150 26-AUG-08 C00012 A012
200133 1200 400 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002
200100 1000 600 08-JAN-08 C00015 A003
200110 3000 500 15-APR-08 C00019 A010
200107 4500 900 30-AUG-08 C00007 A010
200112 2000 400 30-MAY-08 C00016 A007
200113 4000 600 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
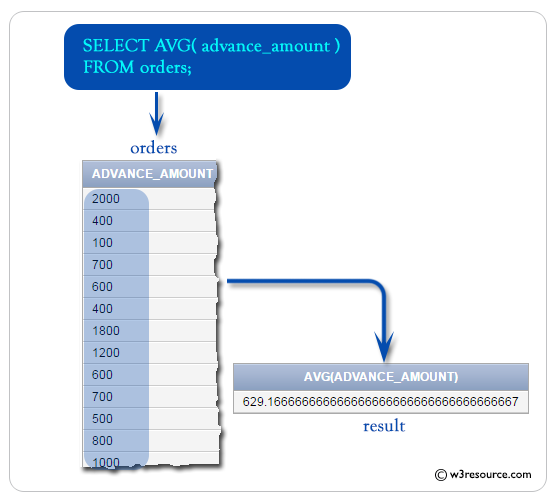
To get the data the average of 'advance_amount' from the 'orders' table, the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT AVG(advance_amount) -- Selects the average value of the 'advance_amount' column
FROM orders; -- Specifies the 'orders' table as the source of data
Explanation:
- SELECT AVG(advance_amount): This is the main part of the SQL query. It uses the AVG() function to calculate the average value of the 'advance_amount' column in the 'orders' table. The result will be a single value representing the average of all values in the 'advance_amount' column.
- FROM orders: This specifies the source of the data for the query, which is the 'orders' table. The FROM keyword is used to indicate the table from which the data will be selected. In this case, it selects data from the 'orders' table.
Output:
AVG(ADVANCE_AMOUNT)
-------------------
629.166667
Visual Presentation:
SQL AVG() with null
Sample table: customer+-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+ |CUST_CODE | CUST_NAME | CUST_CITY | WORKING_AREA | CUST_COUNTRY | GRADE | OPENING_AMT | RECEIVE_AMT | PAYMENT_AMT |OUTSTANDING_AMT| PHONE_NO | AGENT_CODE | +-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+ | C00013 | Holmes | London | London | UK | 2 | 6000.00 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 4000.00 | BBBBBBB | A003 | | C00001 | Micheal | New York | New York | USA | 2 | 3000.00 | 5000.00 | 2000.00 | 6000.00 | CCCCCCC | A008 | | C00020 | Albert | New York | New York | USA | 3 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | 6000.00 | BBBBSBB | A008 | | C00025 | Ravindran | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 4000.00 | 8000.00 | AVAVAVA | A011 | | C00024 | Cook | London | London | UK | 2 | 4000.00 | 9000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | FSDDSDF | A006 | | C00015 | Stuart | London | London | UK | 1 | 6000.00 | 8000.00 | 3000.00 | 11000.00 | GFSGERS | A003 | | C00002 | Bolt | New York | New York | USA | 3 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 3000.00 | DDNRDRH | A008 | | C00018 | Fleming | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 2 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 5000.00 | NHBGVFC | A005 | | C00021 | Jacks | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 1 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | WERTGDF | A005 | | C00019 | Yearannaidu | Chennai | Chennai | India | 1 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 8000.00 | ZZZZBFV | A010 | | C00005 | Sasikant | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 1 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 147-25896312 | A002 | | C00007 | Ramanathan | Chennai | Chennai | India | 1 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 9000.00 | 9000.00 | GHRDWSD | A010 | | C00022 | Avinash | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 2 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 9000.00 | 9000.00 | 113-12345678 | A002 | | C00004 | Winston | Brisban | Brisban | Australia | 1 | 5000.00 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | AAAAAAA | A005 | | C00023 | Karl | London | London | UK | 0 | 4000.00 | 6000.00 | 7000.00 | 3000.00 | AAAABAA | A006 | | C00006 | Shilton | Torento | Torento | Canada | 1 | 10000.00 | 7000.00 | 6000.00 | 11000.00 | DDDDDDD | A004 | | C00010 | Charles | Hampshair | Hampshair | UK | 3 | 6000.00 | 4000.00 | 5000.00 | 5000.00 | MMMMMMM | A009 | | C00017 | Srinivas | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 4000.00 | 3000.00 | 9000.00 | AAAAAAB | A007 | | C00012 | Steven | San Jose | San Jose | USA | 1 | 5000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 3000.00 | KRFYGJK | A012 | | C00008 | Karolina | Torento | Torento | Canada | 1 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 9000.00 | 5000.00 | HJKORED | A004 | | C00003 | Martin | Torento | Torento | Canada | 2 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 7000.00 | 8000.00 | MJYURFD | A004 | | C00009 | Ramesh | Mumbai | Mumbai | India | 3 | 8000.00 | 7000.00 | 3000.00 | 12000.00 | Phone No | A002 | | C00014 | Rangarappa | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 12000.00 | AAAATGF | A001 | | C00016 | Venkatpati | Bangalore | Bangalore | India | 2 | 8000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 12000.00 | JRTVFDD | A007 | | C00011 | Sundariya | Chennai | Chennai | India | 3 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | 7000.00 | 11000.00 | PPHGRTS | A010 | +-----------+-------------+-------------+--------------+--------------+-------+-------------+-------------+-------------+---------------+--------------+------------+
To get the data of 'agent_code', sum of 'opening_amt', number of customer for each agent, and 'receive_amt' from the 'customer' table, the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT agent_code, SUM(opening_amt), -- Selects the agent code and calculates the sum of opening amounts for each agent
COUNT(*), -- Calculates the count of rows for each agent
ROUND(SUM(opening_amt) / COUNT(*)) AS MYAVG, -- Calculates the average opening amount per customer for each agent and rounds it
ROUND(AVG(opening_amt)) AS SQLAVG -- Calculates the average opening amount for each agent and rounds it
FROM customer -- Specifies the 'customer' table as the source of data
GROUP BY agent_code; -- Groups the result set by the agent code
;
Explanation:
- SELECT agent_code, SUM(opening_amt), ...: This is the main part of the SQL query. It selects the 'agent_code' column and calculates the sum of 'opening_amt' for each agent. Additionally, it calculates the count of rows (COUNT(*)) for each agent. Then it calculates two types of averages: MYAVG is calculated by dividing the sum of 'opening_amt' by the count of rows for each agent, and SQLAVG is calculated using the AVG() function directly on the 'opening_amt' column. Both averages are rounded using the ROUND() function.
- FROM customer: This specifies the source of the data for the query, which is the 'customer' table. The FROM keyword is used to indicate the table from which the data will be selected. In this case, it selects data from the 'customer' table.
- GROUP BY agent_code: This clause groups the result set by the 'agent_code' column. The GROUP BY clause is used to aggregate the rows based on the values in the 'agent_code' column. This means that calculations performed in the SELECT statement will be applied separately for each unique value in the 'agent_code' column.
Output:
AGENT_CODE SUM(OPENING_AMT) COUNT(*) MYAVG SQLAVG ---------- ---------------- ---------- ---------- ---------- A002 22000 3 7333 7333 A004 25000 3 8333 8333 A007 16000 2 8000 8000 A009 6000 1 6000 6000 A011 5000 1 5000 5000 A012 5000 1 5000 5000 A010 22000 3 7333 7333 A001 8000 1 8000 8000 A008 13000 3 4333 4333 A006 8000 2 4000 4000 A005 19000 3 6333 6333 A003 12000 2 6000 6000
SQL AVG() with where
Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200109 3500 800 30-JUL-08 C00011 A010
200101 3000 1000 15-JUL-08 C00001 A008
200111 1000 300 10-JUL-08 C00020 A008
200104 1500 500 13-MAR-08 C00006 A004
200106 2500 700 20-APR-08 C00005 A002
200125 2000 600 10-OCT-08 C00018 A005
200117 800 200 20-OCT-08 C00014 A001
200123 500 100 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002
200120 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200116 500 100 13-JUL-08 C00010 A009
200124 500 100 20-JUN-08 C00017 A007
200126 500 100 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200129 2500 500 20-JUL-08 C00024 A006
200127 2500 400 20-JUL-08 C00015 A003
200128 3500 1500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200135 2000 800 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200131 900 150 26-AUG-08 C00012 A012
200133 1200 400 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002
200100 1000 600 08-JAN-08 C00015 A003
200110 3000 500 15-APR-08 C00019 A010
200107 4500 900 30-AUG-08 C00007 A010
200112 2000 400 30-MAY-08 C00016 A007
200113 4000 600 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
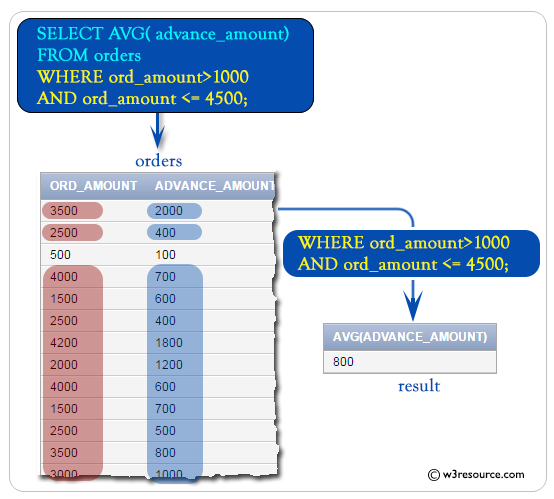
To get the average of 'advance_amount' from the 'orders' table with the following conditions -
1. 'ord_amount' must be more than 1000,
2. and 'ord_amount' must be up to 4500,
the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT AVG(advance_amount) -- Selects the average value of the 'advance_amount' column
FROM orders -- Specifies the 'orders' table as the source of data
WHERE ord_amount > 1000 AND ord_amount <= 4500; -- Filters the rows to include only those with 'ord_amount' greater than 1000 and less than or equal to 4500
Explanation:
- SELECT AVG(advance_amount): This is the main part of the SQL query. It uses the AVG() function to calculate the average value of the 'advance_amount' column in the 'orders' table. The result will be a single value representing the average of all 'advance_amount' values that meet the specified conditions.
- FROM orders: This specifies the source of the data for the query, which is the 'orders' table. The FROM keyword is used to indicate the table from which the data will be selected. In this case, it selects data from the 'orders' table.
- WHERE ord_amount > 1000 AND ord_amount <= 4500;: This clause filters the rows from the 'orders' table. It restricts the calculation of the average to only include rows where the 'ord_amount' column has values greater than 1000 and less than or equal to 4500. This condition ensures that only orders with amounts within the specified range are considered in the calculation of the average advance amount.
Relational Algebra Expression:
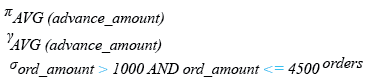
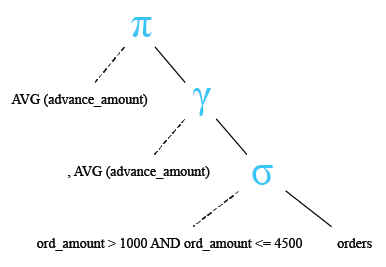
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
AVG(ADVANCE_AMOUNT)
-------------------
800
Visual Presentation:
SQL AVG() with SUM()
Sample table: orders
ORD_NUM ORD_AMOUNT ADVANCE_AMOUNT ORD_DATE CUST_CODE AGENT_CODE ORD_DESCRIPTION
---------- ---------- -------------- --------- --------------- --------------- -----------------
200114 3500 2000 15-AUG-08 C00002 A008
200122 2500 400 16-SEP-08 C00003 A004
200118 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00023 A006
200119 4000 700 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200121 1500 600 23-SEP-08 C00008 A004
200130 2500 400 30-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200134 4200 1800 25-SEP-08 C00004 A005
200108 4000 600 15-FEB-08 C00008 A004
200103 1500 700 15-MAY-08 C00021 A005
200105 2500 500 18-JUL-08 C00025 A011
200109 3500 800 30-JUL-08 C00011 A010
200101 3000 1000 15-JUL-08 C00001 A008
200111 1000 300 10-JUL-08 C00020 A008
200104 1500 500 13-MAR-08 C00006 A004
200106 2500 700 20-APR-08 C00005 A002
200125 2000 600 10-OCT-08 C00018 A005
200117 800 200 20-OCT-08 C00014 A001
200123 500 100 16-SEP-08 C00022 A002
200120 500 100 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200116 500 100 13-JUL-08 C00010 A009
200124 500 100 20-JUN-08 C00017 A007
200126 500 100 24-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200129 2500 500 20-JUL-08 C00024 A006
200127 2500 400 20-JUL-08 C00015 A003
200128 3500 1500 20-JUL-08 C00009 A002
200135 2000 800 16-SEP-08 C00007 A010
200131 900 150 26-AUG-08 C00012 A012
200133 1200 400 29-JUN-08 C00009 A002
200100 1000 600 08-JAN-08 C00015 A003
200110 3000 500 15-APR-08 C00019 A010
200107 4500 900 30-AUG-08 C00007 A010
200112 2000 400 30-MAY-08 C00016 A007
200113 4000 600 10-JUN-08 C00022 A002
200102 2000 300 25-MAY-08 C00012 A012
To get the sum of 'advance_amount' and average of 'advance_amount' from the 'orders' table, the following SQL statement can be used :
SELECT SUM(advance_amount), AVG(advance_amount) -- Selects the sum and average of the 'advance_amount' column
FROM orders; -- Specifies the 'orders' table as the source of data
Explanation:
- SELECT SUM(advance_amount), AVG(advance_amount): This is the main part of the SQL query. It selects two aggregate functions applied to the 'advance_amount' column of the 'orders' table. The SUM() function calculates the sum of all values in the 'advance_amount' column, while the AVG() function calculates the average value of the 'advance_amount' column. The result will be a single row with two columns: the sum and average of the 'advance_amount' column.
- FROM orders: This specifies the source of the data for the query, which is the 'orders' table. The FROM keyword is used to indicate the table from which the data will be selected. In this case, it selects data from the 'orders' table.
Relational Algebra Expression:
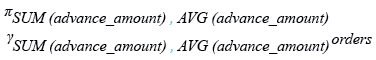
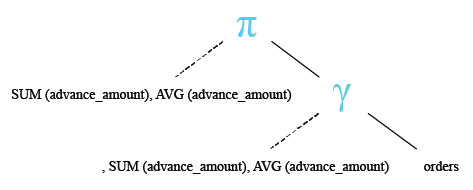
Relational Algebra Tree:
Output:
SUM(ADVANCE_AMOUNT) AVG(ADVANCE_AMOUNT)
------------------- -------------------
22650 629.166667
Note: Outputs of the said SQL statement shown here is taken by using Oracle Database 10g Express Edition
Here is a slide presentation of all aggregate functions.
Check out our 1000+ SQL Exercises with solution and explanation to improve your skills.
Previous: SUM and COUNT Using Variable and inner join
Next: Avg Decimal Places Using Cast within and outside avg
