SQL Exercises: Largest and smallest orders on each date
5. From the following tables, write a SQL query to find the salespeople who generated the largest and smallest orders on each date. Sort the result-set on third field. Return salesperson ID, name, order no., highest on/lowest on, order date.
Sample table: Salesman
salesman_id | name | city | commission
-------------+------------+----------+------------
5001 | James Hoog | New York | 0.15
5002 | Nail Knite | Paris | 0.13
5005 | Pit Alex | London | 0.11
5006 | Mc Lyon | Paris | 0.14
5007 | Paul Adam | Rome | 0.13
5003 | Lauson Hen | San Jose | 0.12
Sample table: orders
ord_no purch_amt ord_date customer_id salesman_id ---------- ---------- ---------- ----------- ----------- 70001 150.5 2012-10-05 3005 5002 70009 270.65 2012-09-10 3001 5005 70002 65.26 2012-10-05 3002 5001 70004 110.5 2012-08-17 3009 5003 70007 948.5 2012-09-10 3005 5002 70005 2400.6 2012-07-27 3007 5001 70008 5760 2012-09-10 3002 5001 70010 1983.43 2012-10-10 3004 5006 70003 2480.4 2012-10-10 3009 5003 70012 250.45 2012-06-27 3008 5002 70011 75.29 2012-08-17 3003 5007 70013 3045.6 2012-04-25 3002 5001
Sample Solution:
-- Selecting specific columns (a.salesman_id, name, ord_no, 'highest on', ord_date) from the 'salesman' table (aliased as 'a') and the 'orders' table (aliased as 'b')
SELECT a.salesman_id, name, ord_no, 'highest on', ord_date
-- Joining the 'salesman' table (aliased as 'a') and the 'orders' table (aliased as 'b') based on the condition that 'salesman_id' is equal in both tables and filtering rows based on the condition that 'purch_amt' is equal to the maximum 'purch_amt' for the same 'ord_date'
FROM salesman a, orders b
WHERE a.salesman_id = b.salesman_id
AND b.purch_amt = (
SELECT MAX(purch_amt)
FROM orders c
WHERE c.ord_date = b.ord_date
)
-- Performing a UNION operation with the result set of a subquery that selects specific columns (a.salesman_id, name, ord_no, 'lowest on', ord_date) from the 'salesman' table (aliased as 'a') and the 'orders' table (aliased as 'b')
UNION
-- Selecting specific columns (a.salesman_id, name, ord_no, 'lowest on', ord_date) from the 'salesman' table (aliased as 'a') and the 'orders' table (aliased as 'b')
SELECT a.salesman_id, name, ord_no, 'lowest on', ord_date
-- Joining the 'salesman' table (aliased as 'a') and the 'orders' table (aliased as 'b') based on the condition that 'salesman_id' is equal in both tables and filtering rows based on the condition that 'purch_amt' is equal to the minimum 'purch_amt' for the same 'ord_date'
FROM salesman a, orders b
WHERE a.salesman_id = b.salesman_id
AND b.purch_amt = (
SELECT MIN(purch_amt)
FROM orders c
WHERE c.ord_date = b.ord_date
)
-- Ordering the result set based on the third column (ord_no)
ORDER BY 3
Sample Output:
salesman_id name ord_no ?column? ord_date 5002 Nail Knite 70001 highest on 2012-10-05 5001 James Hoog 70002 lowest on 2012-10-05 5003 Lauson Hen 70003 highest on 2012-10-10 5003 Lauson Hen 70004 highest on 2012-08-17 5001 James Hoog 70005 lowest on 2012-07-27 5001 James Hoog 70005 highest on 2012-07-27 5001 James Hoog 70008 highest on 2012-09-10 5005 Pit Alex 70009 lowest on 2012-09-10 5006 Mc Lyon 70010 lowest on 2012-10-10 5007 Paul Adam 70011 lowest on 2012-08-17 5002 Nail Knite 70012 lowest on 2012-06-27 5002 Nail Knite 70012 highest on 2012-06-27 5001 James Hoog 70013 lowest on 2012-04-25 5001 James Hoog 70013 highest on 2012-04-25
Code Explanation:
The said query in SQL that retrieves information about the highest and lowest orders placed by each salesman, along with the date of the order.
The first query before UNION keyword selects the salesman ID, name, order number, and order date for the highest order placed by each salesman. It does so by joining the 'salesman' and 'orders' tables and selecting rows where the salesman ID matches in both tables, and the purchase amount is equal to the maximum purchase amount for that date, as determined by a subquery.
The second query after UNION keyword selects the lowest order for each salesman.
The "UNION" keyword combines the results of the two queries into a single table.
The ORDER BY clause orders the results by the third column, which is the order number.
Go to:
PREV : Largest and smallest orders on each date.
NEXT : Salesmen who do not have customers in their cities.
Practice Online
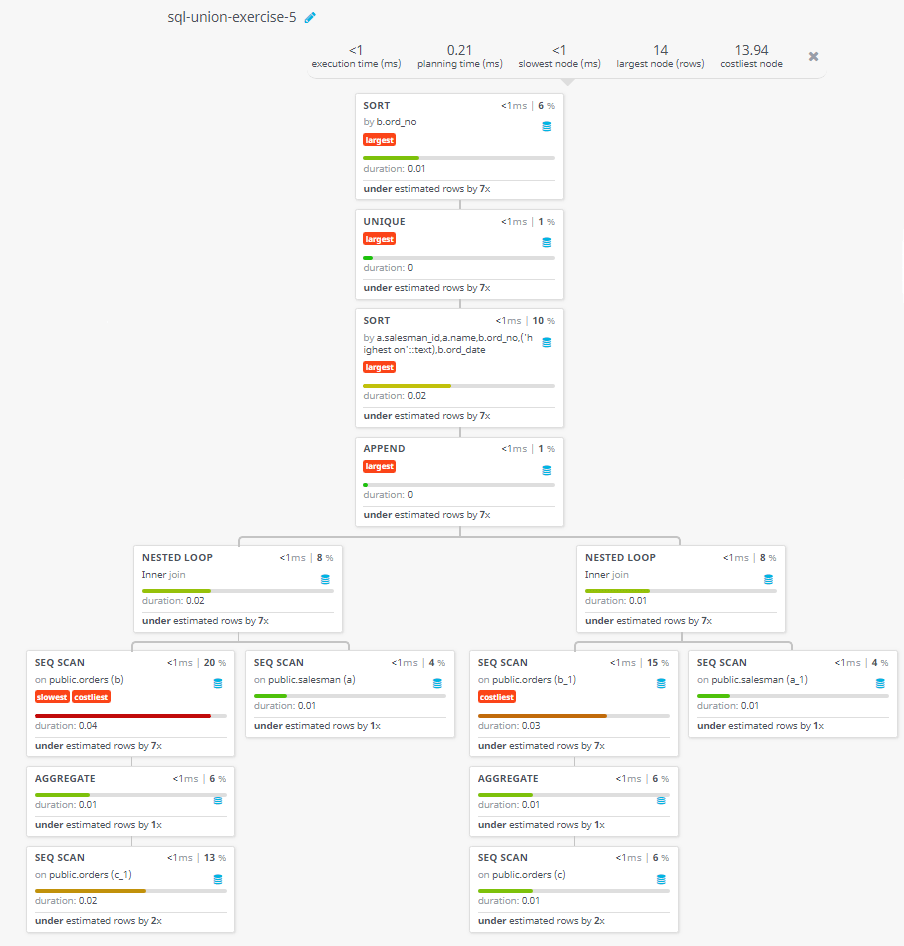
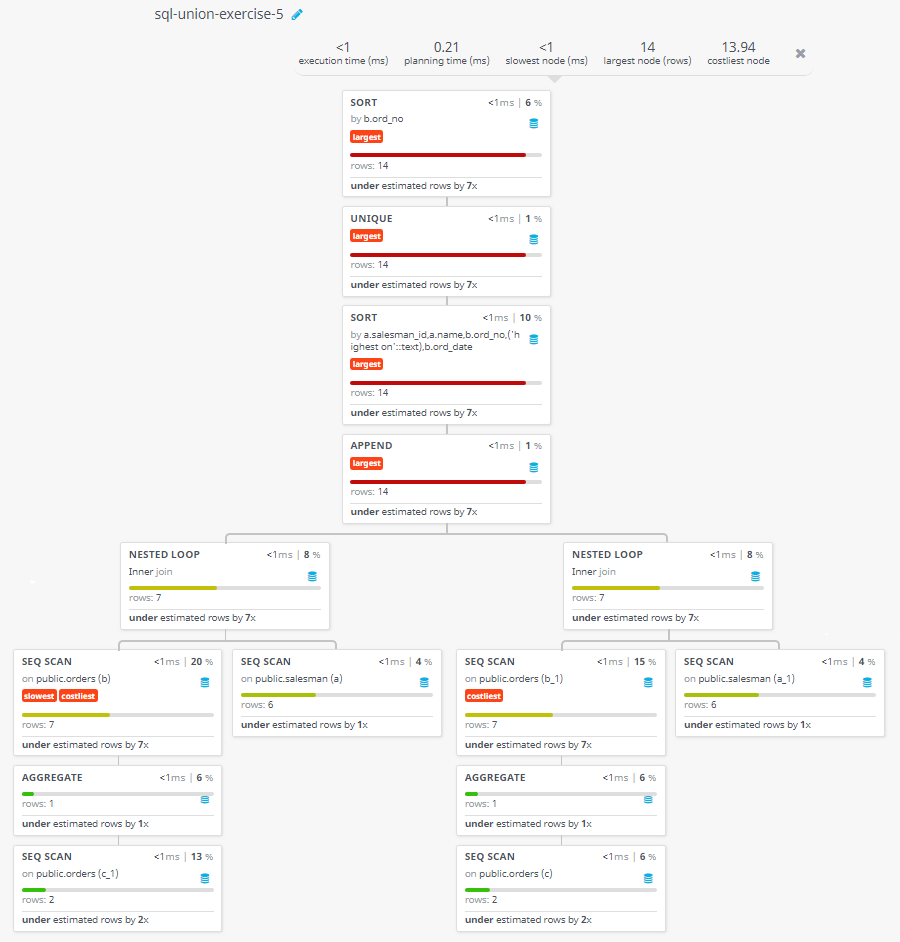
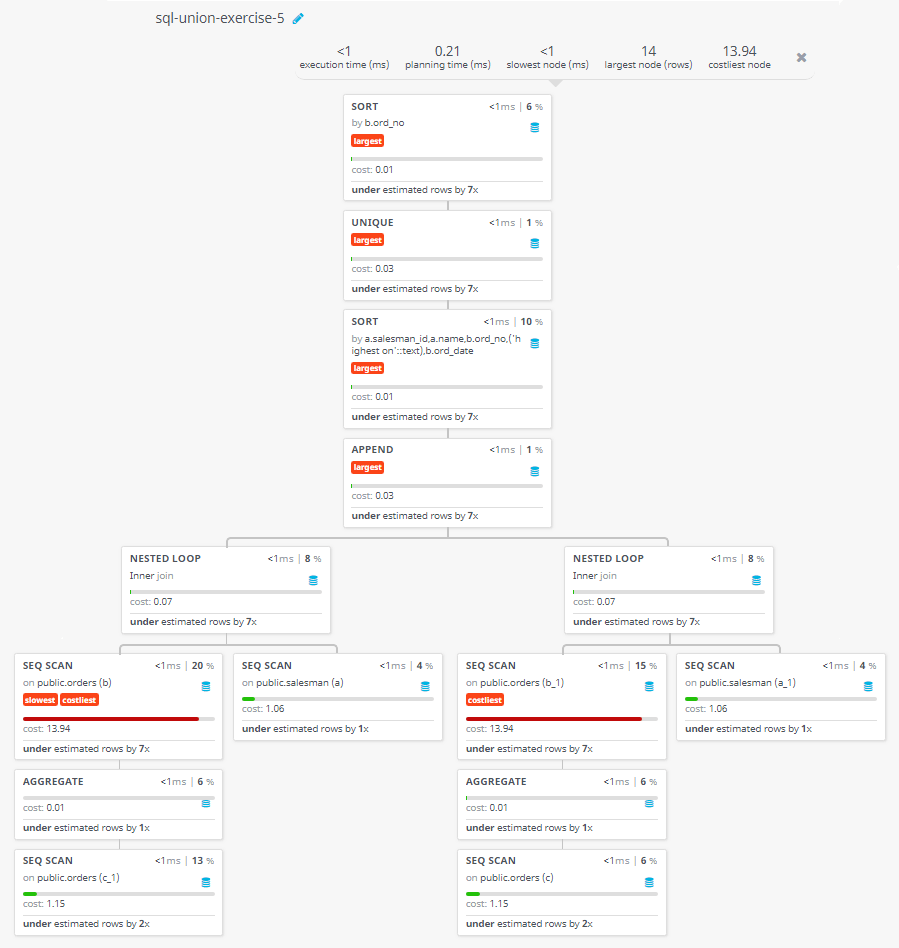
Query Visualization:
Duration:
Rows:
Cost:
Have another way to solve this solution? Contribute your code (and comments) through Disqus.
What is the difficulty level of this exercise?
Test your Programming skills with w3resource's quiz.